Current issue
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse Articles > Current issue
Review
- [Korean]
- Research trends in dietary behaviors and nutrition education among individuals with developmental disabilities in Korea: a scoping review (2015–2025)
- Nakyung Kwak, Wonyeong Park, Yu-Ri Kim, Jieun Oh
- Korean J Community Nutr 2026;31(1):1-20. Published online February 28, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00374
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
We mapped trends in studies on dietary behaviors, nutritional status, and nutrition-related education among individuals with developmental disabilities in Korea over the past decade to identify research gaps and inform future research and policy development.
Methods
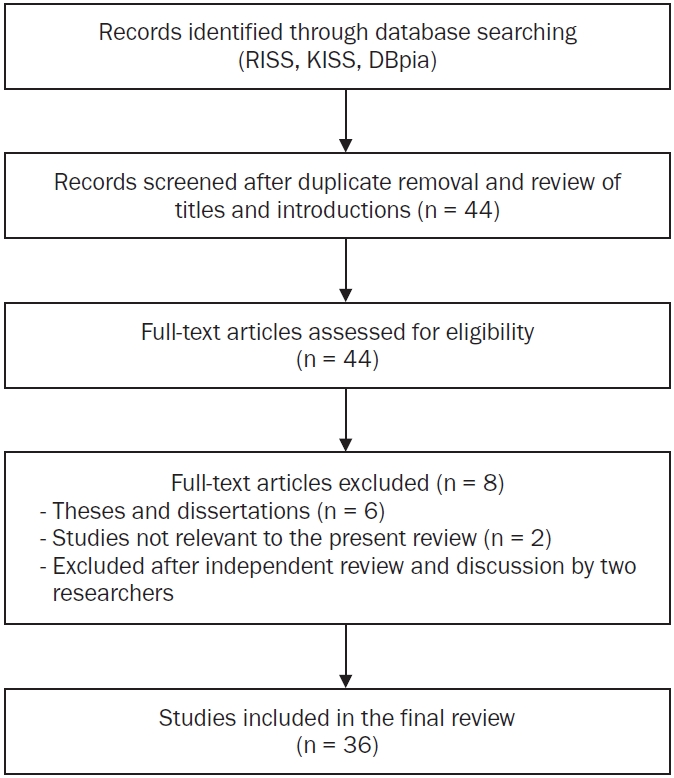
A scoping review was conducted using three major Korean academic databases (RISS, KISS, and DBpia). Studies published between 2015 and September 2025 were identified using combinations of keywords related to developmental disabilities, dietary behavior, nutrition, and health-related interventions. Eligible studies included empirical studies and secondary research (e.g., systematic or scoping reviews) conducted in Korea that focused on dietary behaviors, nutrition, health promotion, or nutrition-related education for individuals with developmental disabilities. Thirty-six studies met our inclusion criteria and were analyzed based on study design, study population, disability type, research topic, and publication period.
Results
Observational quantitative, qualitative, intervention-based experimental, and evidence synthesis accounted for 27.8%, 13.9%, 22.2%, and 36.1% of all included studies, respectively. Children and adolescents (27.8%) and adults (25.0%) were the most frequently studied populations, with limited studies focusing on professionals or teachers. Most studies targeted individuals with developmental disabilities as a combined group (61.1%), followed by those specifically targeting autism spectrum disorder. Research topics included dietary behaviors and nutritional status, nutrition-related education and interventions, health promotion, and medical or clinical issues, with many small-scale and shortterm intervention studies.
Conclusion
Although research on dietary and nutrition-related issues among individuals with developmental disabilities in Korea has expanded in scope and methodology, significant limitations remain. Future research should adopt longitudinal and community-based approaches, incorporate diverse populations, and strengthen policy-oriented nutrition support systems to promote sustainable health and quality of life for individuals with developmental disabilities.
- 108 View
- 7 Download

Research Articles
- [English]
- Psychosocial factors related to the stages of change in reducing sugar intake among adults in Seoul, Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Ju Young Lee, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2026;31(1):21-35. Published online February 28, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2026.00024
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the factors associated with stages of change (SOC) in reducing sugar intake among adults, applying the theory of planned behavior.
Methods
An online survey was conducted among adults aged 19–49 years residing in Seoul, Korea. Based on their SOC in reducing sugar intake, participants (n = 380) were categorized into a pre-action group (45.3%) and an action group (54.7%). Statistical analysis was performed using χ2-test, analysis of covariance, and one-way analysis of variance with linear contrast.
Results
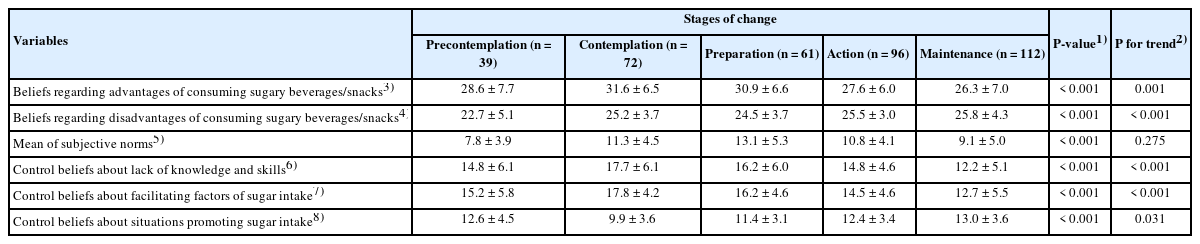
The consumption frequency of sugary foods was significantly higher in the pre-action group than in the action group (P < 0.001). Compared with the action group, participants in the pre-action group perceived the advantages of sugar intake more favorably (P < 0.001), perceived the disadvantages less strongly (P = 0.002), and reported greater influence from significant others (P = 0.004). In contrast, participants in the action group agreed less with insufficient knowledge/skills (P < 0.001), had greater control over the facilitating factors of sugar intake (P < 0.001), and had stronger control beliefs in situations promoting sugar intake (P < 0.001). Behavioral beliefs (P < 0.001) and control beliefs (P < 0.001) showed a significant linear trend across the five SOC, whereas subjective norms did not (P = 0.275).
Conclusion
Psychosocial factors related to sugar intake reduction clearly differed between the SOC groups. In the pre-action group, nutrition education should emphasize lowering the perceived benefits of sugar intake while increasing awareness of its adverse consequences. Strengthening the perception of control over sugar intake is important, despite the factors or situations promoting sugar intake. This can be achieved by providing practical tips and developing skills to reduce sugar intake. For the action group, it is necessary to maintain the reduced sugar intake through continual support and encouragement.
- 89 View
- 8 Download

- [English]
- Impact of a foodservice establishment manager’s willingness to perform duties on hygiene management levels and the mediating effects of extrinsic motivations: a cross-sectional study
- Tae Yang Kim, Mi Young Lee, Young Eun Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2026;31(1):36-49. Published online February 28, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00332
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Consumer demand is growing for more rigorous hygiene management within foodservice establishments. The aim of this study was to provide customized data specific to each foodservice establishment, thereby informing policy formulation to improve hygiene management levels.
Methods
We surveyed 310 managers of directly managed foodservice establishments (excluding franchises) that were subject to hygiene inspections by the Chungbuk Provincial Office in Korea between September 1 and 27, 2023. Additionally, 30 investigators trained in methods for evaluating the hygiene management levels of foodservice establishments objectively assessed 310 establishments using evaluation sheets. All 310 managers provided consent and personally completed the questionnaires. Data from 277 managers were included in the analysis. General characteristics were analyzed with descriptive statistics in IBM SPSS Statistics 28 (IBM Corp.). Univariate normality verification, measurement model verification, structural model verification, and mediation effect significance analysis were conducted using R’s lavaan package (version 4.3.2.).
Results
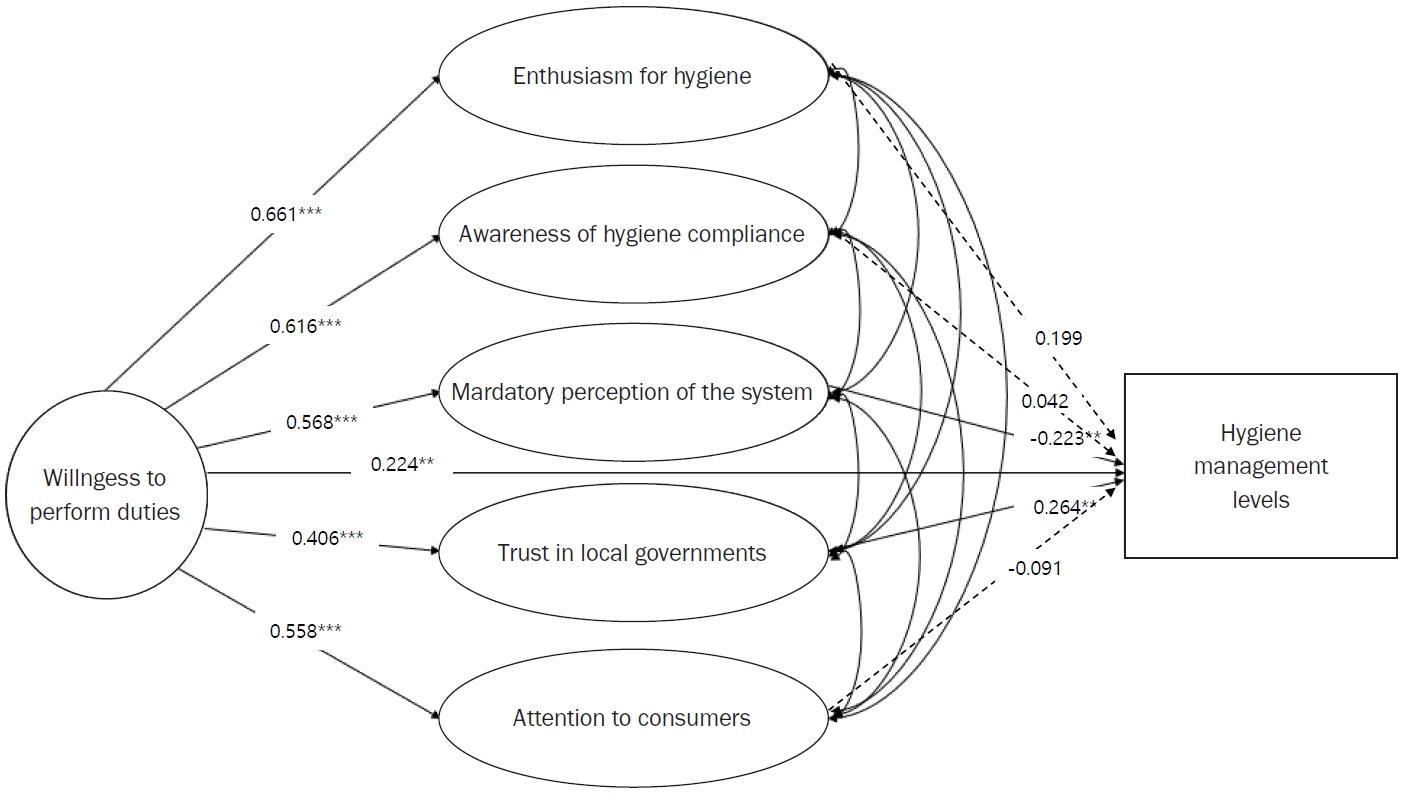
Managers’ willingness to perform duties had a positive influence on hygiene management level (0.224), enthusiasm for hygiene (0.661), awareness of hygiene compliance (0.616), mandatory perception of the system (0.568), trust in local governments (0.406), and attention to consumers (0.558). In the relationship between managers’ willingness to perform duties and hygiene management level, mandatory perception of the system had a negative mediating effect (–0.223), while trust in local governments had a positive mediating effect (0.264).
Conclusion
Structural equation modeling was used to identify the complex pathways by which foodservice establishment managers’ willingness to perform duties, mediated by their human factors, influences their hygiene management level. Accordingly, policy implications were presented, suggesting that the hygiene management level of foodservice establishments could be enhanced by increasing managers’ willingness to perform their duties, and that a shift from mandatory regulations by local governments to support-oriented systems that foster trust in local governments is necessary.
- 72 View
- 5 Download

- [English]
- Understanding the drivers of continuance intention in online grocery shopping using technology continuance theory: a cross-national comparison
- Binglin Liu, Min A Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2026;31(1):50-63. Published online February 28, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2026.00017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the determinants of consumers’ continuance intention (CI) toward online grocery shopping (OGS) across different country markets. Drawing on technology continuance theory (TCT), this study compared key drivers of CI in a different countries market.
Methods
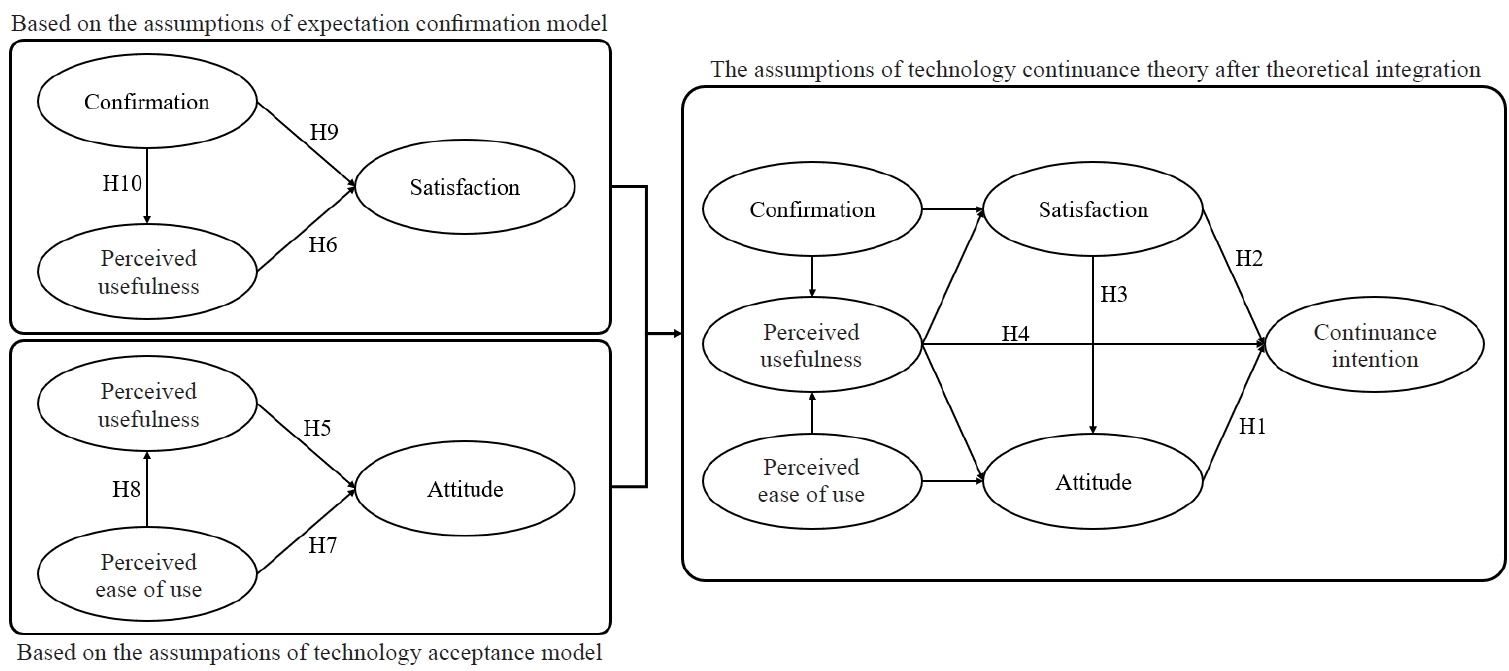
Data were collected via online surveys from 638 OGS users in China (n = 338) and South Korea (n = 300) between November and December 2023. A TCT-based model incorporating satisfaction, attitude, perceived usefulness (PU), perceived ease of use, confirmation, and CI was tested using partial least squares structural equation modeling. Partial measurement invariance testing was conducted to ensure valid cross-national comparison.
Results
In South Korea, both satisfaction and attitude significantly predicted CI, with satisfaction exerting a particularly strong effect. In China, attitude was the primary determinant of CI, whereas satisfaction had minimal impact. Across both countries, PU consistently and positively influenced satisfaction and attitude, thereby indirectly enhancing CI. Partial measurement invariance was confirmed, validating comparisons of the model across contexts.
Conclusion
The findings suggest that the drivers of online grocery continuance differ by cross-national market. In Korean markets, strategies must enhance customer satisfaction (and its influence on attitude) to sustain OGS usage. In Chinese markets, fostering favorable consumer attitudes toward OGS is essential for promoting continued use. This cross-national analysis advances the theoretical understanding of continuance behavior while providing practical guidance for designing market-specific strategies to sustain online grocery engagement.
- 82 View
- 6 Download

- [English]
- Association between number of teeth and oxidative balance score in Korean adults: a population-based study
- Jung-Eun Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2026;31(1):64-74. Published online February 28, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00325
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the relationship between oxidative balance score (OBS), a metric indicating an individual’s oxidative balance status, and the number of teeth in a sample of Korean adults.
Methods
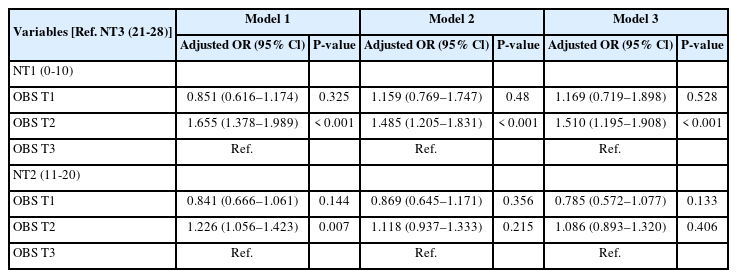
This cross-sectional study included 13,199 adults aged 19 and older who participated in a health survey and oral examination. Subsequent to the adjustment for confounding factors, a logistic regression analysis was employed to evaluate the probability of a subject belonging to a number of teeth category based on OBS level.
Results
In the group with OBS level T2, the likelihood of having NT1 (0–10 teeth) was found to be significant adjusted for all variables (odds ratios: 1.51, 95% confidence intervals: 1.195–1.908). In the multinomial model, a significant association was observed for the NT1 category, whereas no significant association was found for the NT2 (11–20 teeth) category after adjustment.
Conclusion
In the group with OBS level T2, the likelihood of having NT1 (0–10 teeth) was found to be significant. As this study examines cross-sectional associations, the necessity of conducting longitudinal research as subsequent studies is evident to ascertain the existence of causality.
- 61 View
- 2 Download

- [Korean]
- Evaluation of young children’s dietary behaviors by parental growth concern levels in Gyeonggi area: a descriptive study
- Youn-Rok Kang, Hyung-Sook Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2026;31(1):75-86. Published online February 28, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00269
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
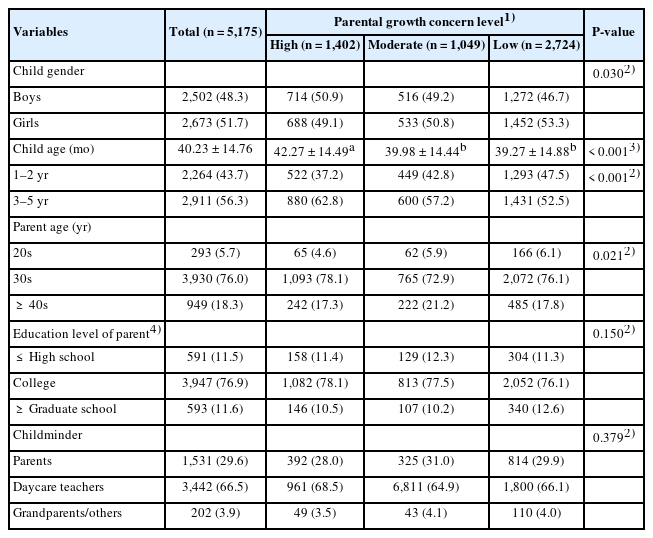
This study investigated differences in dietary habits, lifestyle patterns, and feeding- related developmental issues among Korean preschool children based on their parents’ levels of growth concern, and examined the associations between parental growth concern and children’s eating behaviors.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was conducted with parents of children aged 1–5 years residing in Gyeonggi Province, Korea. Participants were classified into high, moderate, and low growth concern groups using the children’s dietary screening test. Data were collected on the children’s anthropometric status, lifestyle routines, dietary intake patterns, eating behaviors, and mealtime media exposure.
Results
Children in the high growth concern group showed a higher prevalence of underweight; irregular sleep and mealtime routines; and more frequent eating difficulties, including picky eating, slow eating, and oral processing problems. Mealtime media exposure was associated with lower fruit and vegetable intake and higher consumption of processed and sugar-rich foods. Higher parental growth concern did not correlate with healthier dietary or lifestyle outcomes.
Conclusion
Preschool children’s dietary behaviors and routines differed according to the parents’ levels of growth concern. Higher levels of parental concern were associated with increased feeding difficulties and greater mealtime media exposure. These findings suggest that excessive concern may contribute to maladaptive eating patterns in children. Evidence- based parental guidance and structured nutrition education are essential to promote healthy growth and eating behaviors during early childhood.
- 69 View
- 3 Download

- [Korean]
- Comparison of dietary behaviors and nutrient intake by gender and household type among older Koreans: a cross-sectional study using data from the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Dana Park, Soo-Kyung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2026;31(1):87-100. Published online February 28, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00367
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to identify gender- and household type-specific nutritional vulnerability among older Koreans by comparing dietary behaviors, nutrient intake, and diet quality.
Methods
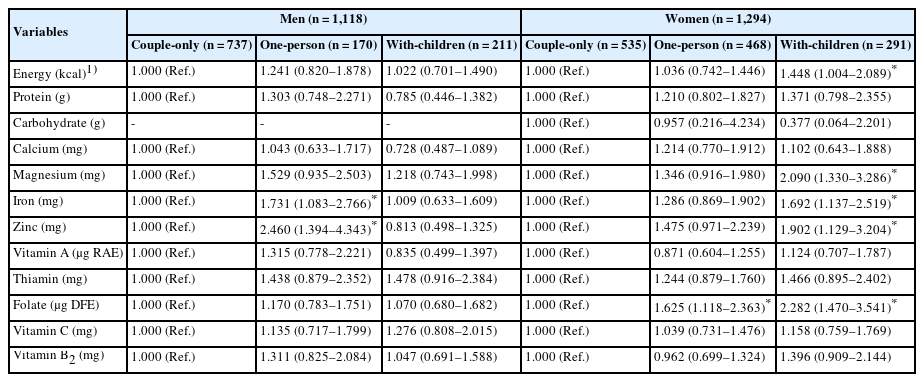
We analyzed data from 2,412 adults aged ≥ 65 years (1,118 men; 1,294 women) from the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019–2021). Household type was classified as one-person, couple-only, or with-children. Outcome variables included dietary behavior, daily energy and nutrient intake, and diet quality, assessed using the Korean Healthy Eating Index (KHEI). Analyses were carried out accounting for the complex sampling design, adjusting for age, residential area, education level, household income level, economic activity status, self-rated health status, and survey year.
Results
Elderly men in one-person households, compared with those in couple-only households, were more likely to skip breakfast and lunch and to consume less energy. The odds of intake below the estimated average requirement (EAR) were higher for iron (odds ratio [OR] = 1.731, P = 0.022) and zinc (OR = 2.460, P = 0.002) among men in one-person households. The KHEI score was the lowest among men in one-person households. Elderly women in with-children households, compared with those in couple-only households, were more likely to skip breakfast and to consume less energy. The risks of intake below the estimated energy requirement (EER) and EAR were higher among women in with-children households than those in couple-only households (EER: OR = 1.448; magnesium: OR = 2.090; iron: OR = 1.692; zinc: OR = 1.902; folate: OR = 2.282; all P < 0.05). The KHEI score was lower among women in with-children households.
Conclusion
Elderly men living alone and elderly women living with children showed significantly greater nutritional vulnerability. More attention should be given to understanding how gender-specific household types can affect nutritional vulnerability in later life.
- 62 View
- 2 Download

- [Korean]
- Effects of senior-friendly foods on health, nutritional status, and dietary intake among rural elderly women in Korea: a quasi-experimental study
- Sang-ju Lee, Ji-hyeon Kim, Jin-suk Han
- Korean J Community Nutr 2026;31(1):101-113. Published online February 28, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00353
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
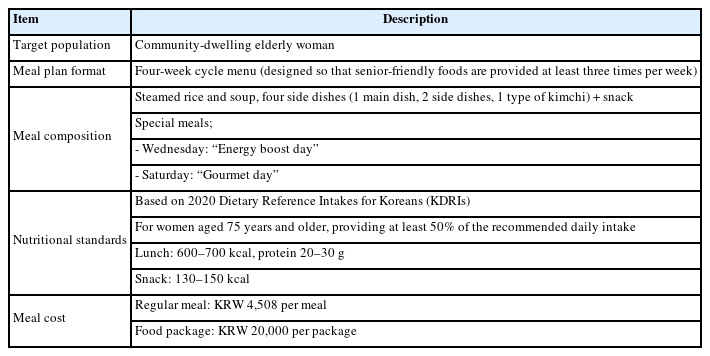
We evaluated the impacts on health, nutritional status, and dietary intake of providing senior-friendly foods to community-dwelling elderly women in a rural area in Korea.
Methods
A pretest–posttest nonequivalent control group design with repeated measures was conducted among 71 rural-dwelling elderly women. Changes in health indicators, nutritional status, and dietary intake were assessed at three time points: baseline, post-intervention, and two months after intervention.
Results
Immediately after a three month intervention, significant differences were observed between the intervention and control groups in frailty score, Dysphagia Handicap Index, Mini Nutritional Assessment, social isolation, resilience, quality of life, and depression (P < 0.05). Significant group-by-time interaction effects were found for muscle mass, hemoglobin A1c, and energy, protein, and micronutrient intake, all of which showed significant improvements in the intervention group (P < 0.05).
Conclusion
Providing senior-friendly foods effectively improved physical and physiological health and emotional well-being among rural older adults. This intervention also contributed broadly to improved dietary intake. These findings provide empirical evidence to support the development of community-based integrated care models and tailored nutrition intervention programs for rural elderly populations in Korea. Trial Registration: Clinical Research Information Service Identifier: KCT0011666.
- 54 View
- 1 Download


 KSCN
KSCN


 First
First Prev
Prev



