Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [English]
- Psychosocial factors related to the stages of change in reducing sugar intake among adults in Seoul, Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Ju Young Lee, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2026;31(1):21-35. Published online February 28, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2026.00024
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the factors associated with stages of change (SOC) in reducing sugar intake among adults, applying the theory of planned behavior.
Methods
An online survey was conducted among adults aged 19–49 years residing in Seoul, Korea. Based on their SOC in reducing sugar intake, participants (n = 380) were categorized into a pre-action group (45.3%) and an action group (54.7%). Statistical analysis was performed using χ2-test, analysis of covariance, and one-way analysis of variance with linear contrast.
Results
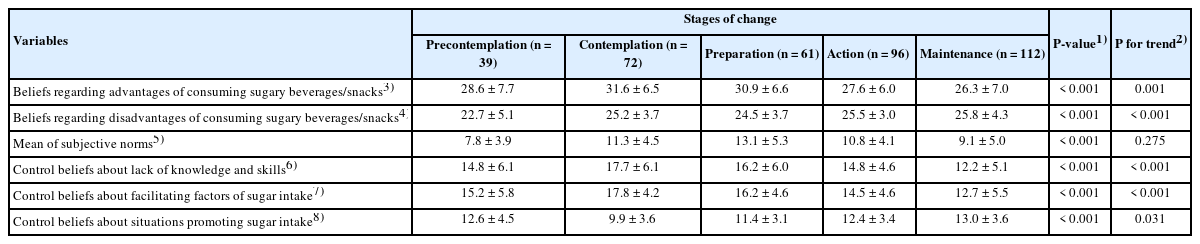
The consumption frequency of sugary foods was significantly higher in the pre-action group than in the action group (P < 0.001). Compared with the action group, participants in the pre-action group perceived the advantages of sugar intake more favorably (P < 0.001), perceived the disadvantages less strongly (P = 0.002), and reported greater influence from significant others (P = 0.004). In contrast, participants in the action group agreed less with insufficient knowledge/skills (P < 0.001), had greater control over the facilitating factors of sugar intake (P < 0.001), and had stronger control beliefs in situations promoting sugar intake (P < 0.001). Behavioral beliefs (P < 0.001) and control beliefs (P < 0.001) showed a significant linear trend across the five SOC, whereas subjective norms did not (P = 0.275).
Conclusion
Psychosocial factors related to sugar intake reduction clearly differed between the SOC groups. In the pre-action group, nutrition education should emphasize lowering the perceived benefits of sugar intake while increasing awareness of its adverse consequences. Strengthening the perception of control over sugar intake is important, despite the factors or situations promoting sugar intake. This can be achieved by providing practical tips and developing skills to reduce sugar intake. For the action group, it is necessary to maintain the reduced sugar intake through continual support and encouragement.
- 67 View
- 7 Download

- [Korean]
- Factors associated with nutritional risk among disabled persons in the Republic of Korea: a cross-sectional study using 2020 Disability and Life Dynamics Panel
- Seong-Ah Kim, Seul Ki Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(5):364-375. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00262

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Persons with disabilities face heightened nutritional risks due to barriers in dietary management, yet research remains limited. This study examined the nutritional health status and associated risk factors among disabled adults in Korea.
Methods
Data were drawn from the 2020 Disability and Life Dynamics Panel, a nationally representative survey of registered disabled Koreans aged ≥ 20 years. Nutritional health was assessed using the Nutrition Screening Initiative checklist and categorized as low, moderate, or high risk. Multivariate multinomial logistic regression was applied to identify predictors of nutritional risk.
Results
Among adults with disabilities aged 20–64 years, the prevalence of low, moderate, and high nutritional risk was 62.6%, 19.8%, and 17.5%, respectively. In the ≥ 65 years group, the distribution was 56.8% (low), 22.0% (moderate), and 21.2% (high). Moderate to high nutritional risk was most prevalent among individuals with facial deformity or internal organ disability (51.2%) in the 20–64 years group, and those with mental disabilities (61.7%) in the ≥ 65 years group. Significant predictors of high nutritional risk included living alone, lowest income quartile, chronic disease, depressive symptoms, and perceived underweight for both age groups. Compared with visual or speech impairments, facial deformity or internal organ disability (in the 20–64 years group) and physical disability (in the ≥ 65 years group) were significantly associated with moderate or high nutritional risk.
Conclusion
Nearly 40% of disabled Koreans are at nutritional risk. Tailored dietary interventions that address disability type, socioeconomic status, and health conditions are required to reduce disparities in nutritional health.
- 597 View
- 32 Download

- [Korean]
- Effects of primary caregivers’ food literacy, social support, food environment, and household income on the nutritional status of school-aged children: a cross-sectional study
- Seyeon Park, Ji-Yun Hwang, Sohyun Park, Hyun Joo Ryou, Jieun Oh
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(5):352-363. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00248

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The dietary habits of school-aged children play a critical role in their growth and development, and are strongly influenced by the home environment. Household income is closely associated with caregivers’ food literacy, social support, and food environment. This directly affects the nutritional status of children. This study aimed to provide evidence to inform policies and educational programs for improving dietary habits in children, and to establish a foundation for tailored support strategies for low-income families.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 846 primary caregivers of school-aged children from 17 regions across Korea, recruited through an online survey. Household income, caregivers’ food literacy, social support, and food environment were assessed. Nutritional status in children was measured using the Nutrition Quotient for Children (NQ-C). Statistical analyses included descriptive statistics, chi-square tests, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), analysis of covariance (ANCOVA), correlation analyses, and multiple linear regression.
Results
Caregivers from higher income households demonstrated significantly greater food literacy and social support (P < 0.001). Children from these households showed high balance scores and a large proportion of these children were in the “high” NQ-C grade. The NQ-C score in children was positively correlated with food literacy (r = 0.425), social support (r = 0.471), and the food environment (r = 0.235) (P < 0.001). Multiple regression analysis showed that food literacy (β = 0.256) and social support (β = 0.348) were significant predictors of nutritional status in children.
Conclusion
This study confirmed that the nutritional status in children is not only determined solely by household income but is also mediated by caregivers’ food literacy, social support, and food environment. These findings highlighted the limitations of providing only economic support. The findings underscore the need for multifaceted interventions such as strengthening parental nutrition education, expanding social support networks, and improving access to healthy foods.
- 846 View
- 43 Download

- [English]
- Sex differences in the association between Korean Healthy Eating Index and type 2 diabetes mellitus in Korean adults: a prospective cohort study
- Yeeun Park, Minji Kim, Kyong Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(5):331-340. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00227

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
Dietary quality is a modifiable determinant of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). However, evidence on the Korean Healthy Eating Index (KHEI) and sex-specific differences in its association with T2DM risk remains limited. This study is to examine the longitudinal association between KHEI and incident T2DM in Korean adults, with a focus on potential sex differences.
Methods
We analyzed 56,000 adults (37,684 women and 18,316 men) from the Health Examinee cohort of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study. Dietary intake was assessed using a validated semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire, and KHEI scores were constructed based on national guidelines. Incident T2DM was defined using physician diagnosis, treatment history, or biochemical criteria. Cox proportional hazards models and restricted cubic spline analyses were applied to evaluate associations, with adjustments for demographic, lifestyle, and clinical covariates.
Results
Over a median follow-up of 4.2 years, 2,252 women and 1,776 men developed T2DM. Women in the highest quartile of KHEI had a 18% lower risk of T2DM compared with those in the lowest quartile (hazard ratio [HR]: 0.82, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.71–0.93; P for trend = 0.007). In men, no significant association was observed (HR: 1.11, 95% CI: 0.95–1.29). The interaction by sex was statistically significant (P for interaction < 0.05). Spline analyses indicated a linear inverse association between KHEI and T2DM risk in women, whereas no trend was evident in men.
Conclusion
Higher diet quality, as measured by the KHEI, was associated with a reduced risk of T2DM in women but not in men, suggesting sex-specific effects of dietary patterns on diabetes prevention. These findings highlight the need for tailored nutritional strategies that consider biological and behavioral differences between women and men in Korea.
- 873 View
- 32 Download

- [English]
- Eating habits and dietary supplement utilization according to food-related lifestyle among Korean adults: a cross-sectional study
- EunJung Lee, Jin A Jang, Ji-Myung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):253-264. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
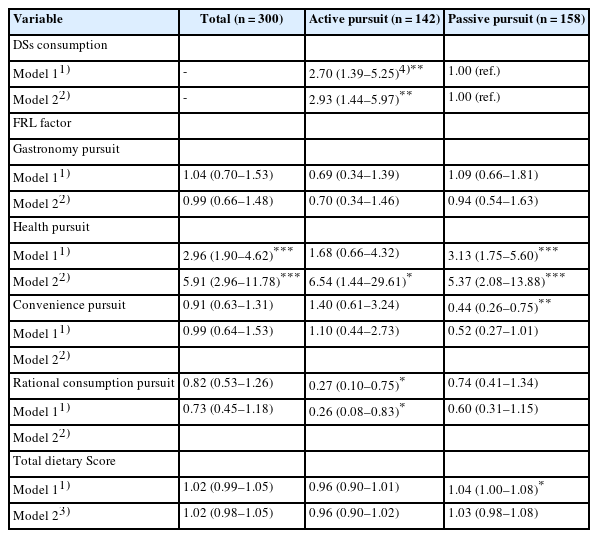
This study investigated the association between eating habits and the utilization of dietary supplements (DSs) according to food-related lifestyle (FRL) among Korean adults. Methods: This study included a total of 300 participants (150 men and 150 women) in their 20s to 60s living in Seoul and Gyeonggi Province. We identified two groups by factor and cluster analysis: an ‘active pursuit’ group and a ‘passive pursuit’ group. Differences in eating habits and DS utilization between the two groups were analyzed by chi-square test and t-test. Logistic regression analysis was used to analyze the effect of variables on DS consumption according to FRL. Results: There were significant differences between the two groups in terms of age, alcohol drinking frequency, total dietary score, change in DS consumption after coronavirus disease 2019, and current DS consumption (P < 0.05). The proportion who perceived many health benefits of DSs was higher in the ‘active pursuit’ group than in the ‘passive pursuit’ group (P = 0.003). The most commonly consumed type of DSs was multivitamins & minerals for the ‘active pursuit’ group, and omega-3 fatty acids for the ‘passive pursuit’ group. The ‘an active pursuit’ group consumed DSs 2.93 times more (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.44–5.97) compared to the ‘passive pursuit’ group, after adjusting for confounders. In the ‘active pursuit’ group, the health pursuit (odds ratio [OR] = 6.54, 95% CI: 1.44– 29.61) and rational consumption pursuit factors (OR = 0.26, 95% CI: 0.08–0.83) were associated with DS consumption, whereas only the health pursuit factor had a significant association (OR = 5.37, 95% CI: 2.08–13.88) within the ‘passive pursuit’ group. However, total dietary score and DSs consumption did not show a relationship. Conclusions: By understanding the consumption characteristics of DSs according to FRL, this can serve as basic data necessary for promoting health through the utilization of DSs and healthy behaviors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Discovering Vitamin-D-Deficiency-Associated Factors in Korean Adults Using KNHANES Data Based on an Integrated Analysis of Machine Learning and Statistical Techniques
Hongryul Ahn, Seungwon Kim, Jinmyung Jung, Chan Park
Nutrients.2025; 17(4): 618. CrossRef - Demographic and behavioral correlation of red ginseng consumption in Korea
DeYu Tian, KeunOh Choi, Yong-ung Kim, YoungJoo Lee
Integrative Medicine Research.2025; : 101287. CrossRef
- Discovering Vitamin-D-Deficiency-Associated Factors in Korean Adults Using KNHANES Data Based on an Integrated Analysis of Machine Learning and Statistical Techniques
- 5,267 View
- 95 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [Korean]
- The Relationship Between the Korean Adults Diet Evaluated Using Dietary Quality Indices and Metabolic Risk Factors: Based on the 2016 ~ 2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Chong-Yu Ding, Pil-Sook Park, Mi-Yeon Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(3):223-244. Published online June 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.3.223
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was designed to investigate the relationship between metabolic risk factors, Index of Nutrition Quality, and the dietary quality index score of Korean adults.
Methods
The subjects were 18,652 Korean adults aged 19 years or older (7,899 males, 10,753 females) who participated in the 2016-2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Subjects were divided into normal, pre-metabolic syndrome, and metabolic syndrome (MetS) groups according to the number of their metabolic risk factors. Data were analyzed using the SPSS program.
Results
About 44.7% of men in the MetS group were at least college graduates (P < 0.001), whereas 52.0% of women in the MetS group were middle school graduates or lower (P < 0.001). The frequency of fruit and dairy products intake tended to decrease as the number of metabolic risk factors increased in both men and women (P for trend < 0.001). As the number of metabolic risk factors decreased, the frequency of grain intake tended to decrease in men (P for trend < 0.001) while the frequency of intake of red meat (P for trend = 0.001), poultry (P for trend < 0.001), and eggs (P for trend < 0.001) decreased in women. The total scores of Diet Quality Index-International (DQI-I) (men P < 0.001, women P < 0.01) and Korean Healthy Eating Index (KHEI) (men and women P < 0.001) were significantly lower in the MetS group compared to the other groups, and the total score of DQI-I and KHEI tended to decrease as the number of metabolic risk factors increased.
Conclusions
Dietary quality evaluation using various indices can provide more information on the dietary problems related to metabolic risk factors. Nutrients and foods that have been confirmed to be related to metabolic risk factors can be used to develop dietary guidelines for the nutritional management of metabolic diseases. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between the Korean Healthy Eating Index sub-domains and the risk of metabolic syndrome in Korean adults: data from the 2022–2023 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Ha-Jeong An, Sang-Jin Chung
Nutrition Research and Practice.2026; 20(1): 114. CrossRef - Relationship between diet quality and risk factors for diabetes complications in Korean adults with type 2 diabetes: based on the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019–2021)
Ye-In Son, Soo-Kyung Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2025; 58(2): 179. CrossRef - Associations between Home Meal Replacement Consumption Frequency and Public Health Outcomes Among Adults in Their 20s and 30s in Daegu
Hye-Sun Jung, Kyung-Suck Park, Pil-Sook Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2025; 50(2): 200. CrossRef - Associations between diet quality and regional factors in Korea vary according to individuals’ characteristics: a cross-sectional study
Hyunmi Han, Clara Yongjoo Park, Jeonghwa Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(4): 274. CrossRef - Cardiocerebrovascular Disease or Fatty Liver Incidence Associated with Pattern of Metabolic Risk Factors and Nutritional Status of Korean Adults: A Prospective Cohort Study
Pil Sook Park, Mei Sheng Li, Chong Yu Ding, Mi Yeon Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(2): 165. CrossRef - Assessment of Nutrient Intake and Dietary Quality of Korean Adults in Metabolic Syndrome Patients According to Taking Medical Care: Based on the 2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Juhee Lee, Kyungsuk Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(4): 321. CrossRef
- Association between the Korean Healthy Eating Index sub-domains and the risk of metabolic syndrome in Korean adults: data from the 2022–2023 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,925 View
- 24 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Dietary Factors Associated with Metabolic Syndrome Status in Korean Menopausal Women: Based on the 2016 ~ 2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Pil-Sook Park, Mei-Sheng Li, Mi-Yeon Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(6):482-494. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.6.482
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study evaluated dietary behavior and nutritional status according to the metabolic syndrome status in Korean menopausal women.
Methods
The subjects were 1,392 menopausal women aged 50 to 64 who took part in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey of 2016 and 2017. Subjects were classified into normal (NOR) group, pre-metabolic syndrome (Pre-MetS) group, and metabolic syndrome (MetS) groups according to the number of metabolic syndrome risk factors present.
Results
The overall prevalence of metabolic syndrome was 33.7%. Using the NOR group as a reference, the odds of belonging to the MetS group in Model 1 adjusted for age were higher at 53% (OR = 1.53, 95% CI:1.011-2.307) for ‘not used’ subjects compared to ‘used’ subjects of the nutrition labeling system. Using the NOR group as a reference, every 1g increase in the intake of monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA) and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) decreased the odds of belonging to the MetS group in Model 1 adjusted for age by 3% (MUFA, OR = 0.97, 95% CI:0.946-0.991; PUFA, OR = 0.97, 95% CI:0.942-0.993).
Conclusions
These results suggest that to reduce the number of risk factors of metabolic syndrome in menopausal women, nutritional education should emphasize the adequate intake of riboflavin, unsaturated fatty acids, protein, and calcium, and also encourage the recognition and use of nutritional labeling. Results of this study are expected to be utilized as basic data for the health management of menopausal women. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cardiocerebrovascular Disease or Fatty Liver Incidence Associated with Pattern of Metabolic Risk Factors and Nutritional Status of Korean Adults: A Prospective Cohort Study
Pil Sook Park, Mei Sheng Li, Chong Yu Ding, Mi Yeon Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(2): 165. CrossRef - The Relationship Between the Korean Adults Diet Evaluated Using Dietary Quality Indices and Metabolic Risk Factors: Based on the 2016 ~ 2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Chong-Yu Ding, Pil-Sook Park, Mi-Yeon Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(3): 223. CrossRef
- Cardiocerebrovascular Disease or Fatty Liver Incidence Associated with Pattern of Metabolic Risk Factors and Nutritional Status of Korean Adults: A Prospective Cohort Study
- 1,565 View
- 20 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Interpersonal and Community Factors Related to Food Sufficiency and Variety: Analysis of Data from the 2017 Community Health Survey
- Jiyoun Hong, Taisun Hyun
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(5):416-429. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.5.416
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the personal, interpersonal and community factors related to food sufficiency and variety among Korean adults using data from the 2017 Community Health Survey. Methods A total of 228,310 adults aged ≥ 19 years were classified into three groups: food sufficiency with variety, food sufficiency without variety and food insufficiency. Personal factors included sociodemographic characteristics, health behavior and health status. Interpersonal factors included social networking and social activities, and community factors included safety, natural environment, living environment, availability of public transportation and health care services. The association of food sufficiency and variety with interpersonal and community factors was assessed using multivariable logistic regression analyses. Results Of the total sample, the food-sufficiency-without-variety group and food insufficiency group accounted for 31.5% and 3.2%, respectively. The sociodemographic factors associated with food insufficiency and non-variety were women, ≥ 65 years of age, with low education level, low household income, unemployed, single, and living in areas of small population sizes. There were significant differences in health behavior and health status, interpersonal and community factors among the three groups. Multivariable logistic regression analyses conducted after adjusting for confounding factors showed that lack of social networking and social activities and lower satisfaction derived from community environments were associated with the risk of food insufficiency and non-variety. Conclusions Our results showed that interpersonal and community factors as well as personal factors were related to food sufficiency and variety. Therefore, public policies to help build social networks and participation in social activities, and improve community environment are needed together with food assistance to overcome the problems of food insufficiency and non-variety. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Health Status and Life Satisfaction According to Food Security in Single-Person Households of Elderly Population
Dong Hoon Jung, Jae Won Han, Wonha Kim, Hee-Sook Lim
Clinical Nutrition Research.2024; 13(1): 42. CrossRef - 광주광역시 서구지역 경로식당 이용 노인의 식품안정성에 따른 식생활 실태연구
지수 백, 영란 허
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(5): 402. CrossRef - Trends in Dietary Behavior Changes by Region using 2008 ~ 2019 Community Health Survey Data
Yun-Hui Jeong, Hye-Young Kim, Hae-Young Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(2): 132. CrossRef
- Comparison of Health Status and Life Satisfaction According to Food Security in Single-Person Households of Elderly Population
- 1,131 View
- 5 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- A study on the Utilization and Satisfaction of Commercially available Lunchbox by Dietary Lifestyle
- Hyosuk Kim, In-Joon Huh, Sim-Yeol Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(4):267-279. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.4.267
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF
Objective
This study investigated the utilization and satisfaction of lunchbox by considering the dietary lifestyle of the consumer, in order to refine the purchasing behavior of adults with experience in using lunchboxes, and to provide basic data for efficient menu configuration and direction towards improvement.
Methods
A total of 600 adults in Seoul and Gyeonggi-do answered a self-administered questionnaire designed to investigate general characteristics, utilization, menu preference, satisfaction, prospection, and improvement of lunchbox, according to the dietary lifestyle.
Results
The study subjects were classified into 5 groups: ‘taste seeking group’, ‘safety seeking group’, ‘health seeking group’, ‘economic seeking group’ and ‘convenience seeking group. Considering purchase value of the lunchbox, the ‘taste seeking group’ had a high utilization rate (35.1%) for prices less than 4,000 won (p < 0.05). Lunchboxes were mainly purchased at the lunchbox store (43.3%) and convenience store (37.7%). The important factor that contributed to purchasing a lunchbox was taste (61.3%), which was highest in the ‘taste seeking group’ (p < 0.01). The ‘health seeking group’ showed the highest preference for the low-salt diet lunchbox menu (26.0%) (p < 0.05). The satisfaction of ‘health seeking groups’ was lowest when considering addition of condiments (2.34%), origin of ingredient (2.59%), and provided calorie (2.81%) (p < 0.05). The overall response indicated future use of the lunchbox (69.6%) (p < 0.01); 35.8% respondents recommended the purchase of lunchbox, where convenience of purchase was the highest factor contributing to recommendation (50.2%) (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Taken together, our results indicate that taste was emphasized in every group purchasing the lunch box. Convenience of purchase was the highest factor contributing to satisfaction, which was relatively low when considering addition of condiments, nutrition and origin of ingredients. We propose that it is necessary to improve the development of various menus for increasing satisfaction by selecting the right ingredients contributing to good health of the consumer.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Survey on the Consumption Patterns and HACCP Awareness of Dosirak Customers
Ji-Won Ma, Hye-Yeon Lee, Hyun-Joo Bae
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2025; 35(3): 192. CrossRef - A Study on the Selection Attributes of Frozen Mandu (Korean Dumpling) for Adults in the Jeonbuk Area Using Conjoint Analysis
Da Eun Gong, Sun A Choi, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2024; 53(3): 297. CrossRef - Study on the Eating Out Behavior and the Status of Meal Delivery and Take-Out Consumption according to the Food-related Lifestyles of Adolescents : Using the Consumption Behavior Survey for Food in 2020
Eun Jung Lee, Hyeon Min Yang, Yeong Ju Lee, Sun A Choi, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(4): 284. CrossRef - Comparison of Eating Habits and Behaviors of Young Single-Person Households based on Food-Related Lifestyle
Dokyung Kim, Sim-Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2023; 23(3): 117. CrossRef - Beef Consumption Behavior amongst Korean Women: A Study Based on the Demographic Characteristics and Food-Related Lifestyle
Kyung-Ran Lee, EunJung Lee, Jung-Tak Lee, Jin A Jang
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(3): 323. CrossRef - How Does Adolescents’ Usage of Social Media Affect Their Dietary Satisfaction?
Harry Jeong, Kwangsoo Shin
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(6): 3621. CrossRef - A Franchise Hamburger Menu for University Students Determined by Identifying Selection Attributes Using Conjoint Analysis
Yu-Ni Choi, Sung-Suk Chung, Jeong-Ok Rho
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2022; 32(4): 250. CrossRef - Studies of Selection Attributes for Lunch Boxes (Dosirak) Using Conjoint Analysis among Single Men
A Reum Han, Sung Suk Chung, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2021; 50(8): 884. CrossRef - E-commerce Food Purchases by Adult Women according to their Household Types
Yu-Jin Park, Yu-Mi Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(6): 464. CrossRef
- A Survey on the Consumption Patterns and HACCP Awareness of Dosirak Customers
- 1,567 View
- 13 Download
- 9 Crossref

Original Articles
- [English]
- Dietary and Lifestyle Factors Associated with Weight Status among Korean Adolescents from Multicultural Families: Using Data from the 2017–2018 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Surveys
- SuJin Song, Hyojune Song
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(6):465-475. Published online December 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.6.465
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study investigated dietary and lifestyle factors associated with the weight status among Korean adolescents in multicultural families.
METHODS
This cross-sectional study analyzed 1,751 multicultural families' adolescents who participated in the 2017–2018 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Surveys. Information on dietary and lifestyle factors was self-reported using a web-based questionnaire and this information included breakfast and foods consumption, perceived health status, alcohol drinking, smoking, physical activity, and weight control efforts. Body mass index (BMI) was calculated based on the self-reported height and body weight (kg/m²). Weight status was assessed according to the 2017 Korean National Growth Chart: underweight (weight-for-age <5(th) percentiles), overweight (85(th)≤ BMI-for-age <95(th) percentiles), and obese (BMI-for-age ≥95(th) percentiles). Multiple logistic regression analysis was performed to examine the dietary and lifestyle factors associated with weight status after adjustment for covariates.
RESULTS
Among Korean adolescents from multicultural families, the prevalence of overweight/obesity was 20.9%, whereas about 7% of adolescents were underweight. The weight status did not show differences according to gender, school level, area of residence, and household income. Compared to adolescents who did not have breakfast during the previous week, those who had breakfast 3–4 days/week and ≥5 days/week had a 42% (p=0.021) and a 37% (p=0.009) lower prevalence of overweight/obesity, respectively. The adolescents who frequently consumed carbonated soft drinks (≥5 times/week) showed an odds ratio (OR) of 1.69 (95% CI=1.01–2.83) for overweight/obesity relative to those adolescents who did not consume carbonated soft drinks. The OR of being underweight for adolescents who ate fast food ≥3 times/week was 1.97 (95% CI=1.04–3.71) compared to those adolescents who had not eaten fast food during the previous week.
CONCLUSIONS
Dietary and lifestyle factors were associated with overweight/obesity as well as underweight among Korean adolescents in multicultural families. Our findings could be used to design and provide nutrition interventions for this specific population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence of Malnutrition and Obesity Among Children and Adolescents From Immigrant Families Living in Korea
Seong-Woo Choi, So-Yeong Kim, Kyung-Ae Park
Journal of Korean Maternal and Child Health.2025; 29(1): 29. CrossRef - Fruit Consumption and Mental Health in Adolescents from Multicultural and Non-multicultural Families: Data from Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web Based Survey 2021
Soohyun Kim, Jeong-Hwa Choi, Young-Ran Heo
Human Ecology Research.2025; 63(2): 175. CrossRef - Identification of important features in overweight and obesity among Korean adolescents using machine learning
Serim Lee, JongSerl Chun
Children and Youth Services Review.2024; 161: 107644. CrossRef - Dietary Behaviors Associated with Health Perception of Korean Adolescents from Multicultural Families: based on data from the 2017 ~ 2019 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Surveys
YueRong Hu, SuJin Song
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(3): 192. CrossRef - Effects of heavy metal, vitamin, and curry consumption on metabolic syndrome during menopause: a Korean community-based cross-sectional study
Hai Duc Nguyen, Min-Sun Kim
Menopause.2021; 28(8): 949. CrossRef - Association between levels of thiamine intake, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases and depression in Korea: a national cross-sectional study
Hai Nguyen Duc, Hojin Oh, In Mo Yoon, Min-Sun Kim
Journal of Nutritional Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Antioxidant Vitamins, Curry Consumption, and Heavy Metal Levels on Metabolic Syndrome with Comorbidities: A Korean Community-Based Cross-Sectional Study
Hai Nguyen Duc, Hojin Oh, Min-Sun Kim
Antioxidants.2021; 10(5): 808. CrossRef - Study on the Dietary Behavior of Adolescents in Multicultural Families Using the Nutrition Quotient and Their Changes in the Nutrition Knowledge and the Dietary Attitudes after Nutrition Education
Yoo-Jin Jung, Sung Hee Min, Min June Lee
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2020; 30(3): 208. CrossRef
- Prevalence of Malnutrition and Obesity Among Children and Adolescents From Immigrant Families Living in Korea
- 1,819 View
- 7 Download
- 8 Crossref

- [English]
- The Effect of Consumers' Factors of Food Choices on Replacing Soft Drinks with Carbonated Water
- Seoyoung Park, Dongmin Lee, Jaeseok Jeong, Junghoon Moon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(4):300-308. Published online August 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.4.300
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This research was conducted to identify the consumers' food choice factors that affect the consumers' replacement of soft drinks with carbonated water.
METHODS
The present study used secondary data from a consumer panel survey conducted by the Rural Development Administration of Korea, and the data included the panel members' purchase records based on their monthly spending receipts. The survey asked the participants about their food choice factors and their personal responsibility for their health. This survey included independent variables for the consumers' food purchase factors. As a dependent variable, two types of groups were defined. The replacement group included those people who increased their purchase of carbonated water and decreased their purchase of soft drinks. The non-replacement group included those people who did not change their purchase patterns or they increased their purchase of soft drinks and they decreased their purchase of carbonated water. Logistic regression analysis was conducted to determine the consumers' food choice factors that were associated with replacing soft drinks with carbonated water.
RESULTS
The replacement group was significantly associated with (1) a younger age (OR=0.953), (2) being a housewife (OR=2.03), (3) higher income (OR=1.001) and (4) less concern about price (OR=0.819) when purchasing food. This group also showed (5) higher enjoyment (OR=1.328) when choosing food and (6) they took greater responsibly for their personal health (OR=1.233).
CONCLUSIONS
This research is the first study to mainly focus on soft drinks and carbonated water. The result of this research showed that young, health-conscious consumers with a higher income and who are more interested in food have more possibilities to replace soft drinks with carbonated water. These research findings may be applied to consumers who have characteristics that are similar to the young health-conscious consumers and the results can help to suggest ways to reduce sugar intake and improve public health. However, this research has a limitation due to the application of secondary data. Therefore, a future study is needed to develop detailed survey questions about food choice factors and to extend these factors to all beverages, including soft drinks made with sugar substitutes, so as to reflect the growth of alternative industries that use artificial sweeteners or different types of sugar to make commercially available drinks. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of the Dietary Behavior-Related Consumer Competency on the Purchase Satisfaction of Fresh Food via Early-Morning Delivery Service
Soon-Ok Lee, Ji-Young Kim, Seung-Min Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2021; 50(6): 612. CrossRef
- Effects of the Dietary Behavior-Related Consumer Competency on the Purchase Satisfaction of Fresh Food via Early-Morning Delivery Service
- 1,499 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- The Effect of Personality Type and Job Performance on Emotional Exhaustion and Job Satisfaction - Staff of the Center for Children's foodservice management -
- Kyung Min Lee, Min Sun Jeon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(6):496-505. Published online December 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.6.496
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study examined the relationship between the personality traits and job performance of Centers for Children's Foodservice Management (CCFSM) staff on emotional exhaustion and job satisfaction. In addition, the characteristics of the center organization were examined to provide practical guidelines for the operation of the center. The aim was to determine management implications with an important meaning in human resource management to enhance the efficiency of the operation of Centers for Children's Foodservice Management (CCFSM).
METHODS
Out of 207 centers, there were 1,057 employees at 173 centers who agreed to participate in the study, the questionnaire was mailed on February 17, 2017 and collected by mail on March 31, 2017. Finally, 81 centers (46.82%) participated in the survey and 493 questionnaires were used.
RESULTS
Neuroticism among the five personality factors had a positive (+) influence on ‘cynicism’ and ‘exhaustion’ among the three subordinate factors of emotional exhaustion, negative (−) effects on the ‘job’ among the six subscales of job satisfaction. In addition, openness showed a negative (−) effect on ‘loss of professional confidence’ of emotional exhaustion and positive (+) relationship with the ‘job’ of job satisfaction. Agreeableness appeared to have a negative (−) effect on all factors of emotional exhaustion and a positive (+) influence on all factors of job satisfaction. As a result of analyzing the effects of job performance on emotional exhaustion and job satisfaction, the planning and operations management team showed a positive (+) influence on all factors of emotional exhaustion and negative (−) influence on all factors of job satisfaction. On the other hand, the nutrition management team showed a negative (−) influence on all emotional exhaustion factors and a positive (+) influence on the factors of job satisfaction. The hygiene management team showed a positive (+) relationship with ‘Emotional exhaustion’ among the subordinate factors of emotional exhaustion and a negative (−) influence on the ‘Educational opportunity’ of job satisfaction.
CONCLUSIONS
The personality type and job performance of Centers for Children's foodservice management (ccfsm) staff significantly affected the emotional exhaustion and job satisfaction. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Study on the relationship between employee perception of overqualification, job burnout, and impulsive buying behavior
Li Chaoyang, Fang Yuanhan, Yu Zengyuan, Li Huitao
Current Psychology.2025; 44(6): 5238. CrossRef
- Study on the relationship between employee perception of overqualification, job burnout, and impulsive buying behavior
- 1,043 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Perception on Optimal Diet, Diet Problems and Factors Related to Optimal Diet Among Young Adult Women Using Focus Group Interviews: Based on Social Cognitive Theory
- Hye Jin Kim, A Reum Lee, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(4):332-343. Published online August 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.4.332
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Study purpose was to investigate perception on diet, diet problems and related factors among young adult women using focus group interviews (FGI) based on the Social Cognitive Theory (SCT).
METHODS
Eight groups of FGI were conducted with 47 female undergraduate or graduate students. Guide for FGI included questions regarding perception on optimal diet, diet problems and cognitive, behavioral, and environmental factors of SCT. FGI were video, audio-taped, transcribed and analyzed by themes and sub-themes.
RESULTS
Subjects showed irregular eating habits (skipping breakfast, irregular meal time) and selection of unhealthy foods as the main diet problems. Regarding cognitive factors related to optimal diet, subjects mentioned positive outcome expectations (e.g., health promotion, skin health, improvement in eating habits, etc.) and negative outcome expectations (e.g., annoying, hungry, expensive, taste). Factors that promoted optimal diet were mainly received from information from mobile or internet and access to menu or recipes. Factors that prevented optimal diet included influence from friends, lack of time and cooking skills. Behavioral factors for optimal diet included behavioral capability regarding snacks, healthy eating and smart food selection. Subjects mentioned mass media (mobile, internet, TV) as the influential physical environment, and significant others (parents, friends, grandparents) as the influential social environment in optimal diet. For education topics, subjects wanted to learn about healthy meals, basic nutrition, disease and nutrition, and weight control. They wanted to learn those aspects by using mobile or internet, lectures (cooking classes), campaign and events.
CONCLUSIONS
Study results might be used for planning education regarding optimal diet for young adult women. Education programs need to focus on increasing positive outcome expectations (e.g., health) and behavioral capability for healthy eating and food selection, reducing negative outcome expectations (e.g., cost, taste) and barriers, making supportive environments for optimal diet, and incorporating topics and methods found in this study. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors affecting sugar intake in adults based on the social cognitive theory
Kilye Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(1): 120. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Need for Obesity Prevention Education Programs through Analysis of Factors Affecting Student Obesity Factors in Seoul during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Seoung Hi Kim, Seonyeong Baek, Min Jeong Choi, Sunny Ham
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2022; 32(3): 214. CrossRef - Focus Group Interviews with U.S. Americans with Respect to Recipe and Sensory Characteristics of Seolgitteok (Korean Rice-Flour Cake)
Han-Seok Seo, Sungeun Cho
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2018; 34(1): 15. CrossRef - Meal Types by Cooking Method Consumed by Korean Adults according to Meal Provision Place: Using 2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Mi-Kyung Choi
Korean Journal of Food & Cookery Science.2017; 33(3): 264. CrossRef - Utilization of Internet Dietary Information by University Students in Seoul and Gyeonggi Area
Young Eun Kang, Sim Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2016; 25(6): 811. CrossRef
- Factors affecting sugar intake in adults based on the social cognitive theory
- 1,420 View
- 6 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Evaluation of Nutrition Quotient and Related Factors in Preschool Children
- Yeon Hyang Jung, Jung Hee Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(1):1-11. Published online February 29, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to evaluate the nutrition quotient (NQ) by gender and understand which factors influence NQ in preschool children.
METHODS
Subjects were 245 children (110 boys, 135 girls) aged 4-6 years and their parents. The questionnaire composed of demographic characteristics, eating behavior factors and the NQ questions. The NQ consisted of 19 food behavior checklist items and all items were grouped into 5 factors: balance, diversity, moderation, regularity, and practice. Inbody J05, a measurement device that measures individual's body composition was used to measure children's anthropometric data. All data were statistically analyzed by SPSS program (Ver. 20) and the statistical differences in variables were evaluated by Student t-test, chi2-test, One-way ANOVA and Duncan's multiple range test.
RESULTS
The total NQ score of the subjects was 65.3. The NQ score of girls (67.0) was significantly higher than that of the boys (63.2) (p<0.01). The girls' average scores of NQ factors including diversity (p<0.01) and practice (p<0.05) were higher than those of the boys. The analysis of related-factors influencing NQ scores showed that there was a significant difference among the groups according to feeding methods during infancy (p<0.05), breast feeding group being the highest. Furthermore, the NQ score showed a significant difference depending on how to correct children's unbalanced diet as well as parents' nutrition knowledge. The NQ score of obesity group tended to be lower than that of underweight group although there was no significant difference.
CONCLUSIONS
Overall results indicated that the girls had better quality of diet and eating habits than the boys. Children and their parents need proper nutrition education and counseling to correct children's eating habits and to improve diet quality in kindergartens and in children care centers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk assessment of four polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in South Korean sesame oil products
Da Eun Hong, Da-Hyun Jeong, Sungmok Kim, Hee-Seok Lee
Food Science and Biotechnology.2026; 35(1): 297. CrossRef - Analysis of the factors that influence preschool children eating behavior by applying the health belief model: Seoul and Gyeonggi Province
Sung-Mi Cha, Soo-Youn Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(3): 541. CrossRef - Dietary Behavior and Related Factors of Preschool Children in Seocheon-gun, Korea
Seung-Lim Lee, Sun-Im Won
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2022; 32(1): 34. CrossRef - Evaluation of dietary behaviors of preschool children in Seoul and Gyeonggi-do associated with the level of parents' health consciousness: using nutrition quotient for preschoolers (NQ-P)
Soo-Youn Kim, Sung-Mi Cha
Nutrition Research and Practice.2021; 15(2): 248. CrossRef - Development of nutrition quotient for elementary school children to evaluate dietary quality and eating behaviors
Jung-Sug Lee, Ji-Yun Hwang, Sehyug Kwon, Hae-Rang Chung, Tong-Kyung Kwak, Myung-Hee Kang, Young-Sun Choi, Hye-Young Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(6): 629. CrossRef - Evaluation of dietary behavior and investigation of the affecting factors among preschoolers in Busan and Gyeongnam area using nutrition quotient for preschoolers (NQ-P)
Soo-Youn Kim, Sung-Mi Cha
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(6): 596. CrossRef - Assessment of dietary behaviors among preschoolers in Daejeon: using Nutrition Quotient for Preschoolers (NQ-P)
Hye-Jin Lee, Jin Hee Kim, SuJin Song
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(2): 194. CrossRef - Analysis of the types of eating behavior affecting the nutrition of preschool children: using the Dietary Behavior Test (DBT) and the Nutrition Quotient (NQ)
Hyeon Mi Sim, Youngshin Han, Kyung A Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(6): 604. CrossRef - Evaluation of Dietary Behavior among Preschooler in Jecheon Area Using Nutrition Quotient for Preschoolers
Sung Hee Min
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2018; 34(4): 413. CrossRef - Evaluation of Dietary Behavior of Infants and Toddlers in Ganghwa County by Using Nutrition Quotient (NQ)
Eun-mi Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2017; 27(1): 17. CrossRef - Nutritional status of 3~5 year old children attending kindergarten and childcare facilities: Using data from the 2010 and 2014 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
Mi Yeon Park, Pil Sook Park
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(4): 361. CrossRef - The Infant and Child Growth Assistance System Based on a Smartphone
Ki-Won Byun, Joon-Gyu Kang
Journal of the Korea Society of Computer and Information.2016; 21(8): 95. CrossRef
- Risk assessment of four polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in South Korean sesame oil products
- 1,773 View
- 8 Download
- 12 Crossref

- [English]
- The Prevalence of Hypertension and Related Nutritional Risk Factors of Elderly Living in a Rural Area
- Mee Sook Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(4):291-300. Published online August 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.4.291
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The prevalence of hypertension in Korean rural elderly was significantly higher than that of the general population. Determining the potential risk factors of hypertension would be useful for managing and improving the treatment and prevention of hypertension in rural areas.
METHODS
We studied 336 elderly individuals 110 males, 226 females) aged between 65 years and 95 years residing in the rural area, S-gun Jeonbuk. Health-related habits, frequency of intake of food groups, nutrient intakes, anthropometric and biochemical measurements were assessed. Subjects were defined as hypertensive if SBP was > or = 140 mmHg or if DBP was > or = 90 mmHg or take an antihypertensive drug.
RESULTS
The rate of prevalence of hypertension in the study group was 51.8% (male 40.0%, female 57.5%). The risk of occurrence of hypertension was higher among females (OR, 1.98), 75 years old or older (OR, 1.62), BMI > or = 25 kg/m2 (OR, 2.84), acceptable range (upper end) of body fat (OR, 2.29) and unhealthy (too high) range of body fat (OR, 3.28), hypertriglyceridemia (OR, 2.17) and hypercholesterolemia (OR, 5.42), low protein intakes (OR, 1.78). However, health related habits, frequencies of intake of food groups and most nutrient intakes except for protein did not show any significant relationship with the occurrence of hypertension.
CONCLUSIONS
To reduce the risk of occurrence of hypertension among elderly individuals in rural areas, it is needed to avoid increase of body fat, 25 or higher BMI (kg/m2) and hyperlipidemia and low intake of proteins. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health-related Behavior Affecting Hypertension in the Elderly Using Data from the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jongsuk LEE
Korean Journal of Clinical Laboratory Science.2024; 56(2): 163. CrossRef
- Health-related Behavior Affecting Hypertension in the Elderly Using Data from the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,279 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Survey on Health-related Factors, Nutrition Knowledge and Food Habits of College Students in Wonju Area
- Seung Lim Lee, Sun Hee Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(2):96-108. Published online April 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.2.96
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was performed to investigate health-related factors, nutrition knowledge and food habits of college students in Wonju.
METHODS
A total of 442 (male: 221, female: 221) college students were recruited and a questionnaire-based survey was conducted. The general characteristics, health-related factors, nutrition knowledge, and food habits were investigated and data were analyzed using SPSS WIN (ver 21.0).
RESULTS
The body mass index (22.9 kg/m2 vs 20.9 kg/m2, p < 0.001) was significantly higher in the males. The ratio of weight (p < 0.001) was significantly different between males and females. Health-related factor scores 'Exercise (p < 0.001)', 'Number of exercise (p < 0.001)', 'Times of exercise (p < 0.01)', 'Concerns about health (p < 0.05)', 'Health condition (p < 0.001)' were significantly higher in the males. 'Type of exercise (p < 0.001)' was significantly different between males and females. Score on 'Watching TV & computer games (p < 0.01)' was significantly higher in the females. Smoking (p < 0.001) was significantly higher in the males. Type of beverages consumed (p < 0.001) was significantly different between males and females. Nutrition knowledge score (11.8 vs 12.9, p < 0.05) was significantly higher in the females. Scores on 'Iron deficiency is leading to anemia (p < 0.01)' and 'carbonated beverages, such as coke, have no calorie (p < 0.05)' were significantly higher in the females. Food habits score (56.4 vs 53.7, p < 0.01) was significantly higher in the males. Scores on 'I have three meals a day (p < 0.01)', 'I have breakfast regularly (p < 0.001)', 'I have meals on time (p < 0.001)', 'I do exercise every day (p < 0.001)', 'I don't eat junk food often (p < 0.05)', 'I don't eat sweet food often (p < 0.05)', and 'I don't eat out often (p < 0.05)' were significantly higher in the males.
CONCLUSIONS
Nutritional education for college students is needed in order to improve their health and nutritional education program should be tailored to meet various needs of these students. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Coffee Consumption Patterns According to Health Behavior and Dietary Factors among Young Adults : From the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2021
Hyun-Ju Jo, Hyun-Kyoung Bang
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2025; 35(4): 369. CrossRef - Which factor, food literacy or health promotion literacy, predicts women’s healthy eating habits better? Results of a study in western Iran
Serajeddin Mahmoudiani
Biodemography and Social Biology.2024; 69(4): 218. CrossRef - Usage and Quality Satisfaction of Convenience Food at Convenience Stores according to the Eating Behavior of University Students in Southern Gyeonggi Province
Se-In Oh, Ok-Sun Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2023; 33(6): 492. CrossRef - Dietary habits and nutrient intake status of university students according to obesity risk based on body mass index and percent body fat
Chae Hong Lee, Kyung A Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(6): 714. CrossRef - Life stress, dietary attitudes, and frequency of snack intake for college students in Seoul and Gyeonggi area: the difference between male and female students
Hyun Seung Oh, Yu bin Kim, Soyoung Park, Kyunghee Song
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(1): 91. CrossRef - The Relationships between Food Literacy, Health Promotion Literacy and Healthy Eating Habits among Young Adults in South Korea
Yoojin Lee, Taehee Kim, Hyosun Jung
Foods.2022; 11(16): 2467. CrossRef - Use of Weight-control or Health Functional Foods, Associated Weight-control Behavior and Perception among University Students in Cheongju
Gayong Kim, Munkyong Pae
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(1): 23. CrossRef - Analysis of Usage, Preference, and Satisfaction for Convenience
Store Dessert among University Students in Chungbuk Area
Go Eun Lee, Hye-In Yang, Yun-Jung Bae
Journal of Biotechnology and Bioindustry.2021; 9: 63. CrossRef - Nutrition Knowledge and Eating Behaviors among College Students in the Pyeongtaek Area
Seo Hyeon Ahn, Seong Yeong Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2020; 30(3): 235. CrossRef - Sleep Quality and Its Association with the Dietary Behavior and Lifestyle of University Students in Cheongju
Sewhan Jin, Munkyong Pae
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(5): 395. CrossRef - Development of a Lifelogs-Based Daily Wellness Score to Advance a Smart Wellness Service
Ki-Hun Kim, Kwang-Jae Kim, Chiehyeon Lim, Jun-Yeon Heo
Service Science.2018; 10(4): 408. CrossRef - Recognition and Propagation for Temple Food among University Students with Food-related Majors
In-Joon Huh, Sim-Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(2): 137. CrossRef - Lunch Eating Patterns and Dietary Habits of University Students according to Major Lunch Place
Hyunji Kim, Hongmie Lee
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2016; 22(4): 261. CrossRef - Survey on Health Status and Food Habits of Male College Students in Wonju Area According to Drinking Behavior
Seung-Lim Lee
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2016; 22(1): 41. CrossRef - A Study on Weight Control Behaviour, Eating Habits and Health-related Life Habits According to Obesity Degree of University Students in Jeonbuk
Hye-Soon Chang
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2016; 25(1): 73. CrossRef - Dietary Habits and Perception Toward Food Additives according to the Frequency of Consumption of Convenience Food at Convenience Stores among University Students in Cheongju
Munkyong Pae
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(2): 140. CrossRef - Studies on Dietary Habits and Residence Students’ Satisfaction with University Dormitory Foodservice in Jeollabuk-do Iksan Area
Kyung-Jin Min, Il-Sook Choi
Journal of The Korean Society of Food Culture.2016; 31(5): 442. CrossRef - Relationship between Eating Style and Food Intake of Healthy Female College Students during Chuseok Holidays
Seok-Young Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(2): 131. CrossRef - Dietary Habits, Dietary Behaviors, Depression and Stress according to Self-Rated Health of University Students in Kyungnam Province
Kyung-Ae Park
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2016; 22(4): 272. CrossRef - Comparisons of Health Related Lifestyle and Dietary Behaviors according to Gender, Ethnicity and Residence Type of University Students in Yanbian, China
Kyung Hee Hong, Unju Hwa Oh
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(4): 486. CrossRef - Health-related Factors, Nutrition Knowledge and Dietary Habits among Nursing and Allied Health College Students
Su Ol Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of School Health.2015; 28(3): 158. CrossRef - A Study on Sodium-related Dietary Attitude and Behaviors According to Sodium-related Nutrition Knowledge of University Students
Mi-Hyun Kim, Jee-Young Yeon, Jong Wook Kim, Jae-Eon Byun, So-Young Bu, Mi-Kyeong Choi, Yun-Jung Bae
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(5): 327. CrossRef - Nutrition Knowledge, Food Habit Problems and Dietary Attitudes of Nursing Students
Su-Ol Kim, So-Myeong Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2015; 21(4): 466. CrossRef
- Coffee Consumption Patterns According to Health Behavior and Dietary Factors among Young Adults : From the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2021
- 1,733 View
- 8 Download
- 23 Crossref

- [English]
- An Evaluation of Chronic Disease Risk Based on the Percentage of Energy from Carbohydrates and the Frequency of Vegetable Intake in the Korean Elderly: Using the 2007-2009 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Yoon Suk Suh, Min Seon Park, Young Jin Chung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(1):41-52. Published online February 28, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.1.41
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Korean elderly people are known to consume diets high in carbohydrates low in vegetables compared to other age groups. This study evaluated the chronic disease risks and nutritional status in this group based on the percentage of energy from carbohydrates and the frequency of vegetable intake.
METHODS
Using the 2007~2009 Korean National Health Nutrition Examination Survey data, except those who were undergoing treatment for chronic disease, final 1,487 subjects aged 65 and older were divided into 4 groups: moderate carbohydrate energy ratio of 55~70% and low frequency of vegetable intake defined as less than 5 times per day (MCLV), moderate carbohydrate ratio and high frequency of vegetable intake more than 5 times (MCHV), high carbohydrate energy ratio above 70% and low frequency of vegetable intake less than 5 times (HCLV), and high carbohydrate ratio and high frequency of vegetable intake more than 5 times (HCHV). All data were analyzed after the application of weighted value, using a general linear model or logistic regression.
RESULTS
More than half of Korean elderly consumed diets with HCLV, and this group showed poor nutritional status and lower frequency of intake of most food items, but with no risk of chronic disease such as diabetes, obesity, hypertension, cardiovascular disease or anemia probably due to low intake of energy. On the contrary, MCHV group with a high percentage of energy from fat and protein showed the highest intake of energy and most nutrients, the highest frequency of intake of most of food items and a tendency of high risk of abdominal obesity, being followed by the MCLV group. Meanwhile, HCHV group showed a tendency of high risk of hypertension, followed by HCLV group with low frequency of intake of vegetables compared with the two moderate carbohydrate groups.
CONCLUSIONS
The results suggested that the percentage of energy from carbohydrate and the frequency of vegetable intake affected the nutritional status, but not significantly affected the risk of chronic disease in Korean elderly. Further studies using more detailed category of % energy from carbohydrates and of type and amount of vegetables with consideration of individual energy intake level, excessive or deficient, are needed to confirm the results. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of Dietary Quality with Subjective Health-Related Perception and Chronic Diseases According to Age Segmentation of Korean Elderly
Sojeong Lee, Seungmin Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 363. CrossRef - Energy big data acquisition and application based on service portfolio quality
Pingping Sun, Lingang Gu
Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments.2021; 45: 101134. CrossRef - Health and Nutrition Status of Elderly People with Multimorbidity: A Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2013~2015)
Na-Gyeong Oh, Jung-Sook Seo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(6): 502. CrossRef - Analyzing the Relative Importance for the Development Plan of the Public Health Care System
You Ho Kim
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2018; 43(4): 300. CrossRef - The Quality of a Traditional Dietary Pattern in Relation to Metabolic Syndrome in Elderly South Koreans
Chorong Oh, Jaekyung No
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2018; 27(4): 254. CrossRef - Development of a Food Exchange Table and Food Pattern for Nutritionally Balanced Menu Planning
Yun Ahn, Ikhyun Yeo, Sangyun Lee, Kisun Nam
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(5): 411. CrossRef - Estimation of Usual Intake and Assessment of Nutrient Intake for Korean Adolescents: Analysis of the 2010-2012 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Meeyoung Kim, Jihyun Yoon
Family and Environment Research.2017; 55(4): 385. CrossRef
- Association of Dietary Quality with Subjective Health-Related Perception and Chronic Diseases According to Age Segmentation of Korean Elderly
- 1,341 View
- 0 Download
- 7 Crossref

- [English]
- The Development and Validation of Eating Behavior Test Form for Infants and Young Children
- Youngshin Han, Su An Kim, Yoonna Lee, Jeongmee Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(1):1-10. Published online February 28, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to develop and validate Eating Behaviors Test form (EBT) for infants and young children, including eating behaviors of their parents and parental feeding practices.
METHODS
Draft version of EBT form was developed after a pretest on 83 mothers. It was consisted of 42 questions including 3 components; eating behavior of children, eating behavior of parents, and parental feeding practices. Using these questionnaires, the first survey was conducted on 320 infants and children, 1 to 6 year old, for exploratory factor analysis, and the second survey was collected on 731 infants and children for confirmatory factor analysis.
RESULTS
Exploratory factor analysis on 42 questions of EBT form resulted in 3 factor model for children's eating behavior, 3 factor model for parents' eating behavior, and 1 factor model for parental feeding practices. Three factors for children's eating behavior could be explained as follows; factor 1, pickiness (reliability alpha=0.89; explanation of variance=27.79), factor 2, over activity (alpha=0.80, explanation of variance=16.51), and factor 3, irregularity (alpha=0.59, explanation of variance=10.01). Three factors for mother's eating behavior could be explained as follows; factor 1,irregularities (alpha=0.73, explanation of variance=21.73), factor 2, pickiness (alpha=0.65, explanation of variance= 20.16), and factor 3, permissiveness (alpha=0.60, explanation of variance=19.13). Confirmatory factor analysis confirmed an acceptance fit for these models. Internal consistencies for these factors were above 0.6.
CONCLUSIONS
Our results indicated that EBT form is a valid tool to measure comprehensive eating and feeding behaviors for infants and young children. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Parents' needs and perceptions of dietary and nutrition education in early childhood education institutions in South Korea: a mixed methods study
Jounghee Lee, Sookyung Choi, Minseo Kim, Seonghyun Lim, Jeong-Weon Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(6): 441. CrossRef - A study on the factors affecting the omnivorous diet of adolescents and the typology: focusing on inherited and acquired cultural capital
Hyewon Lee, Rando Kim
Journal of Families and Better Life.2024; 42(1): 81. CrossRef - Assessment of Dietary Characteristics and Eating Behavior in Children Using a Dietary Screening Test
Sun-Im Won
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(6): 557. CrossRef - Associations between maternal comprehensive feeding practices and dietary practices in preschool children
Myeongil Cho, Seunghee Kye
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(1): 141. CrossRef - The effect of the mother's modeling and feeding practices on the eating behavior of young children
Hyeonmi Sim, Youngshin Han, Kyung A Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(2): 296. CrossRef - The influence of parental eating behaviors, child-feeding practices, and infants’ temperaments upon infants’ eating behaviors
Goh Woon Lim, Kyoung Min Shin
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics.2022; 65(9): 466. CrossRef - The status of food allergy and parental burden of preschoolers in Jeju area
Jeong Eun Oh, Eunyoung Kim, Yunkyoung Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(6): 664. CrossRef - MAMAS: Supporting Parent--Child Mealtime Interactions Using Automated Tracking and Speech Recognition
Eunkyung Jo, Hyeonseok Bang, Myeonghan Ryu, Eun Jee Sung, Sungmook Leem, Hwajung Hong
Proceedings of the ACM on Human-Computer Interaction.2020; 4(CSCW1): 1. CrossRef - Analysis of the types of eating behavior affecting the nutrition of preschool children: using the Dietary Behavior Test (DBT) and the Nutrition Quotient (NQ)
Hyeon Mi Sim, Youngshin Han, Kyung A Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(6): 604. CrossRef - The Infant and Child Growth Assistance System Based on a Smartphone
Ki-Won Byun, Joon-Gyu Kang
Journal of the Korea Society of Computer and Information.2016; 21(8): 95. CrossRef - Evaluation of a Nutrition Education Program Designed to Reduce Sugar Intake in Preschool Children
Ma-Young Yeom, Youn-Ok Cho
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2016; 22(3): 179. CrossRef - The Development of Sugar Intake Reduction Test for Young Children
Nam-Hee Kim, Jee-Young Yeon, Mi-Hyun Kim
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(5): 818. CrossRef
- Parents' needs and perceptions of dietary and nutrition education in early childhood education institutions in South Korea: a mixed methods study
- 1,443 View
- 5 Download
- 12 Crossref

- [English]
- Blood Pressure and Dietary Related Risk Factors Associated with High Sodium Intake Assessed with 24-hour Urine Analysis for Korean Adults
- Yeon Seon Jeong, Hwa Jae Lim, Sook Bae Kim, Hee Jun Kim, Sook Mee Son
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(6):537-549. Published online December 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.6.537
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to examine blood pressure and other characteristics of a high sodium intake group assessed with 24-hr urine analysis and the dietary factors related to the risk of high sodium intake among Korean adults.
METHODS
A cross-sectional study was conducted with adults aged 20-59 years. Subjects who completed 24-hr urine collection (N = 205) were divided into 3 groups (tertile) according to the sodium intake estimated with 24-hour urine analysis. We compared the blood pressure, BMI and dietary related factors of the 3 groups (low, medium, high sodium intake group) with General Linear Model (GLM) and Duncan's multiple range test (p < 0.05). The risk factors related to high sodium intake were assessed with odds ratio (p < 0.05).
RESULTS
The sodium intake (mg/day) of the 3 groups were 3359.8 +/- 627.9, 4900.3 +/- 395.1 and 6770.6 +/- 873.9, respectively, corresponding to daily salt intake (g/day) 8.5, 12.4 and 17.2, respectively. High sodium group showed significantly elevated age, BMI and systolic/diastolic blood pressure. Being male gender was associated with significantly increased risk of sodium intake (OR = 1.972; 95%CI: 1.083-3.593). The other factors related to high sodium intake were higher BMI (> or = 25) (OR = 2.619; 95% CI: 1.368-5.015), current alcohol consumption (OR = 1.943; 95%CI: 1.060-3.564), and having salty soybean paste with salt percentage > 14% (OR = 3.99; 95% CI: 1.404-6.841). The dietary attitude related to increased risk of high sodium intake included 'enjoy dried fish and salted mackerel' (p < 0.001) and 'eat all broth of soup, stew or noodle' (p < 0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
Because high sodium intake was associated with higher blood pressure, nutrition education should focus on alcohol consumption, emphasis on related dietary factors such as using low salt soybean paste, improvements in the habit of eating dried fish and salted mackerel or eating all broth of soup, stew or noodle. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of fermented soybean on metabolic outcomes, anthropometric indices, and body composition: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials
Fatemeh Maleki Sedgi, Nazanin Mozaffari, Mohammad Reza Pashaei, Fatemeh Hajizadeh-Sharafabad
Food & Function.2025; 16(2): 389. CrossRef - Comparison between 24-hour diet recall and 24-hour urine collection for estimating sodium and potassium intakes and their ratio among Korean adults
Taisun Hyun, Mi-Kyeong Choi, Young-Ran Heo, Heekyong Ro, Young-Hee Han, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(2): 284. CrossRef - Development and application of the sodium index to estimate and assess sodium intake for Korean adults
Yeon-Kyung Lee, Taisun Hyun, Heekyong Ro, Young-Ran Heo, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Nutrition Research and Practice.2022; 16(3): 366. CrossRef - Comparison of Sodium-Related Dietary Behavior and Low-Salt Dietary Attitude Based on the Gender and Salty Taste Assessment of Chinese International Students in the Jeonbuk Area
Qi Li, Ji Eun Lee, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2021; 31(2): 91. CrossRef - Estimation model for habitual 24-hour urinary-sodium excretion using simple questionnaires from normotensive Koreans
Ji-Sook Kong, Yeon-Kyung Lee, Mi Kyung Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi, Young-Ran Heo, Taisun Hyun, Sun Mee Kim, Eun-Soon Lyu, Se-Young Oh, Hae-Ryun Park, Moo-Yong Rhee, Hee-Kyong Ro, Mi Kyung Song, Tatsuo Shimosawa
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(2): e0192588. CrossRef - Relationship of sodium consumption with obesity in Korean adults based on Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2010~2014
Se Young Cheon, Hye Won Wang, Hwa Jung Lee, Kyung Mi Hwang, Hae Seong Yoon, Yoon Jung Kang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(1): 64. CrossRef - Study of the characteristics of dietary behavior and the effects of nutrition education for sodium reduction according to the stages of behavioral change in sodium reduction of male adult subjects in Gwangju·Jeonnam regions
Young Ran Heo, Hyun Young Oh, Hee Kyong Ro
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(5): 472. CrossRef - Correlation analysis of sodium-related knowledge, dietary behavior, attitudes towards a low-salt diet and meal attitude guidance for elementary school teachers in Jeonbuk area
Hyun Ok Moon, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(2): 180. CrossRef - Verification of Utility of Simple Mensuration of Cl-from Urine to Estimate the Amount of Sodium Intake
Sung-Ho Lee, Chae-Joon Lee, Sung-Mi Ju, Hyun-Joo Lee, Wang-Yeon Ra, Soon-Ok Kim
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(1): 27. CrossRef
- Effect of fermented soybean on metabolic outcomes, anthropometric indices, and body composition: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials
- 1,633 View
- 2 Download
- 9 Crossref

- [English]
- Association of Whole Grain Consumption with Nutrient Intakes and Metabolic Risk Factors in Generally Healthy Korean Middle-Aged Women
- Ye Jin Kim, Jin Hee Yum, Seungmin Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(2):176-186. Published online April 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.2.176
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Epidemiological studies have suggested that a higher consumption of whole grain foods can significantly reduce the risk of chronic diseases including cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes and obesity. The objective of the current study was to examine associations among the consumption of whole grains and nutrient intakes and biochemical indicators associated with chronic diseases among generally healthy middle-aged Korean women.
METHODS
Using 24-hour recall data from the 2008-2009 National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys, whole grain intake (g/day) was calculated for a total of generally healthy 1,953 subjects. The subjects were divided into three groups by the level of whole grain consumption (0 g/day, > 0 and < 20 g/day or > or = 20 g/day). Mean values or proportions of various nutrient intakes and metabolic risk factors were compared according to the level of whole grain consumption. All statistical analysis was conducted using SAS software version 9.2.
RESULTS
We observed that the overall consumption of whole grains was quite low. Specifically, 58.2% of subjects reported no whole grain consumption on the day of the survey, and the mean whole grain intake was only 15.3 g/day. The whole grain consumption was positively associated with intakes of various macro and micronutrients, namely, plant proteins and fats, dietary fiber, calcium, plant iron, potassium, zinc, vitamin A, beta-carotene, thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, vitamin B6 and folic acid. In addition, we found significantly decreasing trends in abdominal obesity and hypertriglyceridemia as whole grain intake levels increase.
CONCLUSIONS
The study findings suggested the importance of promoting whole grain consumption as an efficient tool for improving various dietary aspects and preventing chronic diseases.
- 1,135 View
- 5 Download

- [English]
- An Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Nutrition Counseling for Adults with Risk Factors for Dyslipidemia
- Tae Young Nam, Jung Hee Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(1):27-40. Published online February 28, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.1.27
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Dyslipidemia is a component of the metabolic syndrome and a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. Nutrition counseling is important to improve dyslipidemia. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of nutrition counseling in adults with risk factors for dyslipidemia diagnosed by the national health screening program. The nutrition counseling for adults with risk factors for dyslipidemia was carried out at a public health center in Gyeonggi-do. Thirty four patients out of forty five participants in the program completed the nutrition counseling program. The nutrition counseling was provided 3 times during a 12-week period. Individualized nutrition counseling to improve dietary habits was conducted after examining participants' dietary intake through questionnaires about dietary habits and whether they practice dietary guidelines. Data about serum lipid profiles, body composition, nutrition knowledge, the practice of dietary guidelines, and dietary behavior were collected before and after nutrition counseling to evaluate the effectiveness of nutrition counseling. All data were statistically analyzed by SPSS program (Korea ver.18.0) and significant difference was evaluated by paired t-test and chi(2)-test. Body weight, body fat and WHR were significantly decreased after nutrition counseling. Total-cholesterol, TG, and LDL-cholesterol were significantly decreased but HDL-cholesterol did not show significant changes. Both scores of nutrition knowledge and the practice of dietary guidelines improved significantly (p < 0.001). This study shows that nutrition counseling helps to encourage healthy eating practices and to improve serum lipid profiles of adults with risk factors for dyslipidemia. Overall, results indicated that nutrition counseling resulted in positive changes to lower the reliance on medications. Therefore, nutrition counseling should be considered for the initial treatment of dyslipidemia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Facilitators and barriers to achieving dietary and physical activity goals: focus group interviews with city bus drivers and counseling dietitians
Yongmin Jo, Suhyeun Cho, Young-Hee Han, Taisun Hyun
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(5): 376. CrossRef - Comparison of Health Behaviors and Nutritional Status related to Dyslipidemia in Korean Middle-Aged Adults - From the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys, 2007~2010 -
Myung-Gon Shin, Ki-Hong Yoon, Mi-Young Song
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(5): 724. CrossRef - Development of Job Standards for Clinical Nutrition Therapy for Dyslipidemia Patients
Min-Jae Kang, Jung-Sook Seo, Eun-Mi Kim, Mi-Sun Park, Mi-Hye Woo, Dal-Lae Ju, Gyung-Ah Wie, Song-Mi Lee, Jin-A Cha, Cheong-Min Sohn
Clinical Nutrition Research.2015; 4(2): 76. CrossRef - Short-term Effects of a Lifestyle Intervention Program on Eating Behaviors, Physical Activity and Cardiovascular Risks in Korean Adults
Jiyeon Park, Hyekyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2014; 31(4): 37. CrossRef
- Facilitators and barriers to achieving dietary and physical activity goals: focus group interviews with city bus drivers and counseling dietitians
- 1,319 View
- 0 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Evaluation of the Quality Attribute and Satisfaction on School Foodservice in 2010
- Il Sun Yang, Bo Sook Yi, Moon Kyung Park, Seung Hee Baek, Yoo Sun Chung, Jin Yi Jeong, Yoon Ji Kim, Hye Young Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(5):491-504. Published online October 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.5.491
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purposes of this study were to analyze the quality attributes, quality factors and customer satisfaction in school foodservice and to provide suggestions for improving school foodservice environments. The survey was distributed to different respondents (5,771 students, 2,045 parents, and 1,981 faculty members) at different types of schools (elementary school, middle school, and high school) on September 2010 in 16 cities and provinces. The data were analyzed using SPSS for descriptive analysis, one-way ANOVA, t-test and multiple linear regression analysis. First, all foodservice quality attributes were significant different by respondents and the faculty had higher scores than parents and students. A comparison of scores by respondents and distribution place demonstrated that classroom of student and parents had a higher score for quality attributes. The overall satisfaction with school foodservice was significant different by respondents and higher for classroom than for dining hall for student and parents. In comparison of annual data, there was decreased overall satisfaction and quality attributes in student and parents. Second, in the regression results, which showed the effects of the foodservice quality attributes on overall satisfaction by respondents and distribution place, improvements of 'food taste', 'pleasant foodservice environment', and 'kindness of employee' would increase satisfaction in most of the respondents. Third, the overall satisfaction with school foodservice was higher for nutrition teachers than dietitians for students and faculty. Therefore, the operators will need to make different efforts based on each customer needs to improve the overall satisfaction on school foodservice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Acceptability of School Menus: A Systematic Review of Assessment Methods
Síntia Almeida Santana, Sueny Andrade Batista, Dayanne da Costa Maynard, Verônica Cortez Ginani, Renata Puppin Zandonadi, Raquel Braz Assunção Botelho
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(3): 2242. CrossRef - School Foodservice Employees’ Perception on Food Waste Generation and Needs to Improve Foodservice for Plate Waste Reduction in Gyeonggi Province
Kyung-Eun Lee, Jiyeon Choi
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2019; 29(5): 408. CrossRef - Development of Model for 「The Survey on School Foodservice Program」
Hae-Young Lee, Bo-Sook Yi, Jina Cha, Sun-Ok Ham, Moon-Kyung Park, Mi-Nam Lee, Hye-Young Kim, Haeng-Hwa Kang, Jin-Wook Kwon, Yun-Hui Jeong
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(1): 60. CrossRef - Perception of Use of Environment-friendly Agricultural Products during School Foodservice of Mothers of Elementary School Students in Gyeonggi
Young-Un An, Myung-Hee Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi, Mi-Hyun Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(3): 234. CrossRef - Effects of students' satisfaction with school meal programs on school happiness in South Korea
Sooyoun Kwon, Oksun Kim, Youngmi Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2018; 12(4): 342. CrossRef - Improving Perception and Satisfaction on Middle and High School Foodservice: The Role of Student Participation Program in Serving School Meals
Jeong-Eun Park, Kyung-Suk Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(3): 243. CrossRef - Exploratory study on effect of eco-friendly program in high school foodservice on adolescents' dietary behavior and satisfaction with foodservice
Seyoung Ju, Deokhee Song, Hyeja Chang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(5): 494. CrossRef - Analysis of Perception and Satisfaction of Military Foodservice that are Provided According to the Ranks of the Soldiers
Jun-Hee Kim, Se-Jeong Bae
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(1): 53. CrossRef - Dietary Habits and Satisfaction of School Foodservice by High School Type in Chungnam Area
Myung-Hee Kim, Su-Mi Lim, Jee-Young Yeon
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2015; 25(2): 213. CrossRef - Evaluation of Foodservice Hygiene in Middle School Students by Meal Service Area in Busan
Yeo Kyeong Kim, Hee Sun Choi, Eun Soon Lyu
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2015; 44(1): 145. CrossRef - Students’ Satisfaction of School Lunch According to the Dietary Habit and Educational Experience of Nutrition and Food
Sung Hee Park, Young Chan Choe
Family and Environment Research.2015; 53(4): 425. CrossRef - Use and Assessment of Home-Delivered Meal Service for Children from Low-Income Families
Jeong-A Moon, Chang-Hee Yoo, Kyung-Eun Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2015; 44(6): 935. CrossRef - A Study on the Foodservice Quality Factors and Satisfaction of Community Children Center
Seong Hee Ko, Kyung-Yeoun Lee
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2014; 27(5): 914. CrossRef - Perception and Satisfaction of Free Foodservice in Male Middle School Students in Chungnam
Yu-Rin Kim, Eun-Jin Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2014; 20(2): 87. CrossRef
- Acceptability of School Menus: A Systematic Review of Assessment Methods
- 1,448 View
- 3 Download
- 14 Crossref

- [English]
- Health-related Factors and Nutritional Status in Shift-workers at Coffee Shops: Focused on Single Women in Twenties in Seoul
- Seung Lim Lee, Soo Jin Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(5):467-477. Published online October 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.5.467
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study examined the health-related factors and nutritional status of 89 single women workers in their 20's who work night and day shift at the take-out coffee shops and the 89 single women office workers. The results of the study are summarized as follows: The shift-workers showed lower rate of office tenure (p < 0.001), income (p < 0.001), job satisfaction (p < 0.05), weight (p < 0.05), and higher rate of weight change (p < 0.001) than the non shift-workers. The shift-workers showed lower rate of of exercise (p < 0.001), sleeping hours (p < 0.01), and good health condition (p < 0.01), and higher rates of smoking (p < 0.001), presence of disease (p < 0.001), gastric and intestinal illnesses (p < 0.001) than the non shift-workers. More than 88.8% of the shift workers answered that they ate alone (p < 0.001). The shift workers showed lower rate of regularity of meal (p < 0.001), balanced diet (p < 0.001), and mealtime (p < 0.001), and higher rate of skipping breakfast (p < 0.001), consumption of salty and spicy food (p < 0.001), and overeating (p < 0.01) than the non shift-workers. The shift workers consumed (p < 0.001) less frequently rice, soup and side dishes, and more frequently noodles and snack, bread than the non-shift-workers. The shift workers showed lower rate of consumption of beer (p < 0.01), and higher rate of consumption of coffee (p < 0.001), tea (p < 0.01) and soju (p < 0.001) in once a week or more intakes than the non-shift-workers. The shift workers showed higher rate of consumption of carbohydrates (p < 0.05), and calcium (p < 0.05) and lower rate of consumption of protein (p < 0.05), fiber (p < 0.05), vitamin C (p < 0.05), and folate (p < 0.05) intakes than the non-shift-workers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Qualitative Study of the Awareness and Influencing Factors of the Dietary Habits of the Male and Female Workers' at a Manufacturing Facility in Gwangju
Ji Suk Yim, Young-Ran Heo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(1): 12. CrossRef - Diet Pattern and Nutritional Status of Women Working in Call Centers of India
Meenakshi Mathur, Monika Harsh, Sumita Mathur
ETP International Journal of Food Engineering.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationships between dietary behavior and health related factors according to shift work in nurses
Ji-Myung Kim, Bok-Hee Kang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2014; 47(6): 416. CrossRef
- A Qualitative Study of the Awareness and Influencing Factors of the Dietary Habits of the Male and Female Workers' at a Manufacturing Facility in Gwangju
- 1,266 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Factors Associated with Bone Mineral Density in Korean Postmenopausal Women Aged 50 Years and Above: Using 2008-2010 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Son Ok Mun, Jihye Kim, Yoon Jung Yang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(2):177-186. Published online April 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.2.177
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to investigate factors associated with Bone Mineral Density (BMD) in Korean postmenopausal women. The data from 2008-2010 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) were used for data analysis. Subjects were 2,701 postmenopausal women aged > or = 50 years. BMDs at whole body, total femur, femoral neck, and lumbar spine were measured by Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA). Dietary data from 24-hour dietary recall and a food frequency questionnaire containing 63 food items were used. The proportions of osteopenia at total femur, femoral neck, and lumbar spine were 37.4%, 54.5%, and 45.4%, respectively. The proportions of osteoporosis at total femur, femoral neck, and lumbar spine were 6.2%, 25.6%, and 34.3%, respectively. Age, anthropometric index including height, weight, and Body Mass Index (BMI), parathyroid hormone, and physical activity were related to BMD, but the relationships were site specific. Total femur BMD was explained by age, weight, parathyroid hormone and intakes of carbohydrate and fruits. Femoral neck BMD was related to age, weight, parathyroid hormone and intakes of riboflavin and fruits. Lumbar spine BMD was associated with age, weight, milk and dairy products, calcium intake, and exercise. These results indicated that adequate intakes of milk and dairy products, fruits, carbohydrate, calcium, riboflavin and exercise as well as weight maintenance might play an important role in maintaining optimum bone health in Korean postmenopausal women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Estimation of Bone Mineral Density in the Femoral Neck and Lumbar
Spine using Texture Analysis of Chest and Pelvis Computed Tomography
Hounsfield Unit
Young-Kyung Min, Dong-Ha Lee, Jae-Heung Yoo, Man-Jun Park, Jung-Wook Huh, MinWoo Kim
Current Medical Imaging Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Milk Consumption and Bone Mineral Density in Adults: Using Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008–2011
Ji Soo Kim, Seung-Won Oh, Jiwoo Kim
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2021; 42(4): 327. CrossRef - Dietary behaviors and nutritional status according to the bone mineral density status among adult female North Korean refugees in South Korea
Su-Hyeon Kim, Soo-Kyung Lee, Sin-Gon Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(5): 449. CrossRef - Nutrient Intake in Postmenopausal Rheumatoid Arthritis Women with Osteoporosis: Results from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yeon Soo Baik, Jee Won Park, Jihye Kim, Won Gyoung Kim, Sohee Oh, Sung-il Cho, Yeong Wook Song, Kichul Shin
Journal of Rheumatic Diseases.2017; 24(1): 35. CrossRef - Association between Hemoglobin Level and Bone Mineral Density in Korean Adults
Yun Hwan Oh, Ji Hyun Moon, Belong Cho
Journal of Bone Metabolism.2017; 24(3): 161. CrossRef - Association of serum vitamin D with osteosarcopenic obesity: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008–2010
Jinhee Kim, Yunhwan Lee, Seunghee Kye, Yoon‐Sok Chung, Okhee Lee
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2017; 8(2): 259. CrossRef - The Factors Influencing the Bone Mineral Density in Korean Adult Men : Based on Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2010~2011 Data
Hye-Sang Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(2): 136. CrossRef - Prevalence of Osteopenia/Osteoporosis and Related Risk Factors of Men Aged 50 Years and Older: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2010~2011 Data
Hye-Sang Lee
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2016; 22(2): 106. CrossRef - Bone mineral density and nutritional state according to milk consumption in Korean postmenopausal women who drink coffee: Using the 2008~2009 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Sun-Hyoung Ryu, Yoon Suk Suh
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2016; 49(5): 347. CrossRef - Sex- and age group-specific associations between intakes of dairy foods and pulses and bone health in Koreans aged 50 years and older: Based on 2008~2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hyun-Bi Seo, Young-Sun Choi
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2016; 49(3): 165. CrossRef - Nutrition Diagnostic Analysis for Nutrition Care Process Model in Adults of a Health Screening & Promotion Center
Hye Seung Lee, Ji Ho Chang, Hyeon Jeong Lee, So Jeong Park, Eun Hee Kang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(1): 61. CrossRef - Problems with Bone Health and the Influencing Factors of Bone Mineral Density in Women across the Life Cycle
Nami Chun, Hyunju Chae
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2015; 21(1): 43. CrossRef - A Study on the Correlation between Menopausal Rating Scale and Bone Mineral Density for Menopausal Osteoporosis Patients※
Kyu In Kwak, Jae Hui Kang, Yun Joo Kim, Hyun Lee
The Acupuncture.2014; 31(3): 25. CrossRef - Various Factors Affecting the Bone Mineral Density in Korean Young Adult Women: Data from the Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES V), 2010~2011
Kwang-Hyun Jho, Soon-Nam Choi, Nam-Yong Chung
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2014; 20(2): 110. CrossRef - Association of Anthropometric and Biochemical Factors with Bone Mineral Density in Korean Adult Women Data from the Fourth (2008~2009) and Fifth (2010~2011) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (KNHANES IV & V)
Soon-Nam Choi, Kwang-Hyun Jho, Nam-Yong Chung
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2014; 20(3): 157. CrossRef - Analysis of Bone Mineral Density, Biochemical Index and Nutrient Intakes of 30-70 Years Old Women: Based on 2011 KNHANES
Jae Ok Koo, Myung Sook Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(4): 328. CrossRef
- Estimation of Bone Mineral Density in the Femoral Neck and Lumbar
Spine using Texture Analysis of Chest and Pelvis Computed Tomography
Hounsfield Unit
- 1,488 View
- 5 Download
- 16 Crossref

- [English]
- A Study on Relationship between Socio-demographic Factors and Food Consumption Frequencies among Adolescents in South Korea: Using the Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey from 2011
- Ji Eun Jo, Hae Ryun Park, Soo Bin Jeon, Jin Sil Kim, Go Eun Park, Yang Li, Young Suk Lim, Jinah Hwang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(2):165-176. Published online April 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.2.165
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The objective of this study was to analyze the influence of socio-demographic factors on food consumption frequencies among adolescents in Korea. Data were obtained from the Seventh Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey (2011 KYRBS), a nationwide representative sample of 75,643 (37,873 males and 37,770 females) middle and high school students. It was carried out as a self-administered on-line survey. The frequency of eating breakfast was 4.8 times per week for middle school students and 4.6 times per week for high school students (p < 0.001). Higher levels of perceived household economic status, family affluence scale (FAS) and education attainment of mother were associated with more frequent breakfast eating. The frequencies of consumption of vegetables and milk were higher in males than in females (p < 0.001). The frequency of consumption fruits was higher in females than in males (p < 0.01). Higher levels of perceived household economic status, FAS and education attainment of mother were associated with more frequent consumption of vegetable, fruits and milk. The frequencies of consumption of soda, fast food and instant noodls were higher in males than in females (p < 0.001). The frequency of consumption of snacks was higher in females than in males. Adolescents with lower levels of FAS and education attainment of mother were at risk for skipping breakfast and consuming of soda, fast food and instant noodls more frequently. Whereas, adolescents with higher levels of FAS, education attainment of mother were more likely to be frequent consumers of vegetable, fruits and milk. These findings demonstrated that being high school students and belonging to lower level of socio-economic status (SES) were associated with undesirable food habits.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mediating Effects of Mukbang and Cookbang Viewing on the Association Between SNS Use and Adolescents’ Food-Related Lifestyle
Soo Jin Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2025; 54(11): 986. CrossRef - Changes in eating behaviors according to household income in adolescents during the COVID-19 pandemic: findings from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hye Ah Lee, Ho Jung Lee, Bomi Park, Yoonhee Shin, Hyunjin Park, Hyesook Park
Epidemiology and Health.2022; 44: e2022102. CrossRef - Biochemical Characteristics and Dietary Intake according to Household Income Levels of Korean Adolescents: Using Data from the 6th (2013 ~ 2015) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yu-Kyeong Kwon, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(6): 467. CrossRef - Trends in Beverage Consumption and Related Demographic Factors and Obesity among Korean Children and Adolescents
Su Bin Hwang, SoHyun Park, Guang-Ri Jin, Jae Hyun Jung, Hyeon Ju Park, Su Hyun Lee, Sangah Shin, Bog-Hieu Lee
Nutrients.2020; 12(9): 2651. CrossRef - Convenience Store Use and the Health of Urban Adolescents in Seoul, South Korea
Nan-He Yoon, Changwoo Shon
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(18): 6486. CrossRef - Factors influencing the consumption of convenience foods among Korean adolescents: analysis of data from the 15th (2019) Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey
Seul Ki Park, Ji Hyun Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(3): 255. CrossRef - Development of NQ-A, Nutrition Quotient for Korean Adolescents, to assess dietary quality and food behavior
Hye-Young Kim, Jung-Sug Lee, Ji-Yun Hwang, Sehyug Kwon, Hae Rang Chung, Tong-Kyung Kwak, Myung-Hee Kang, Young-Sun Choi
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(2): 142. CrossRef - Gender Differences in Adolescents' Dietary Perceptions and Practices
Taejung Woo, Hye-Jin Lee, Kyoung Ae Lee, Seung Min Lee, Kyung-Hea Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(2): 165. CrossRef - Study on Nutritional Knowledge and Food Consumption Differences of Middle School Students living in Rural and Urban Areas of Inner Mongolia
Ying Li, Youngmi Lee, Nari Park, Haeryun Park
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2015; 25(6): 933. CrossRef - Analysis of consumption frequencies of vegetables and fruits in Korean adolescents based on Korea youth risk behavior web-based survey (2006, 2011)
Yangsuk Kim, Yong-Suk Kwon, Young-Hee Park, Jeong-Sook Choe, Jin-Young Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2015; 9(4): 411. CrossRef
- Mediating Effects of Mukbang and Cookbang Viewing on the Association Between SNS Use and Adolescents’ Food-Related Lifestyle
- 1,538 View
- 3 Download
- 10 Crossref

- [English]
- Characteristics of the Health Factors in 45~60 Year Old Korean Women related to Menopausal Stages: Based on 2008~2009 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Hye Jin Lee, Kwang Hyun Cho, Kyung Hea Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2012;17(4):450-462. Published online August 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.4.450
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We analyzed data from the combined 2008~2009 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) to compare the health factors related to menopausal stages in 45~60 year old Korean women. In this study, we classified the subjects into a premenopausal group (n = 439) and a postmenopausal group (n = 683). In the postmenopausal group, age was higher (p < 0.001), monthly income (p < 0.01) and education levels (p < 0.001) were significantly lower than in the premenopausal group. Body fat % and waist circumferences were also higher in the postmenopausal group than in the premenopausal group. The serum glucose (p < 0.05), total cholesterol (p < 0.001), LDL-cholesterol (p < 0.001), triglyceride (p < 0.001), GOT (p < 0.001), GPT (p < 0.001) in the postmenopausal group were higher than in the premenopausal group. The postmenopausal group showed a significantly lower quality of life compared to the premenopausal group (p < 0.01). With regard to dietary quality, nutrient adequacy ratio (NAR) of vitamin A, vitamin B1, vitamin B2 and niacin in the postmenopausal group were significantly lower than in the premenopausal group. The levels of glucose, total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, and triglyceride showed a significantly positive correlation with age, waist circumferences, body fat % and BMI. The 45~60 year old Korean women in this study showed high levels of obesity and serum lipids. Also, intakes of the vitamins and minerals of the women did not meet the level of Dietary reference intakes for Koreans. Therefore, nutritional risk may be high in the women, especially in postmenopausal women. In order to prevent the health risk, women's health care including the quality of the meal should be considered.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Physical Characteristics and Nutrient Intakes according to Menopause and Number of Years Passed Using National Health and Nutrition Survey (2013-2019) Data
Su Gyung Kim, Bok-Mi Jung
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2023; 34(2): 235. CrossRef
- Analysis of Physical Characteristics and Nutrient Intakes according to Menopause and Number of Years Passed Using National Health and Nutrition Survey (2013-2019) Data
- 1,361 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Nutrient Intake, Lifestyle Factors and Prevalent Hypertension in Korean Adults: Results from 2007-2008 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Sle Koo, Youngok Kim, Mi Kyung Kim, Jin Sook Yoon, Kyong Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2012;17(3):329-340. Published online June 30, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.3.329
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hypertension is a well-known risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Previous studies have shown that changes in diet and lifestyle factors can prevent the development of hypertension, but the combined effects of these modifiable factors on hypertension are not well established. The objective of this study is to investigate associations of diet and lifestyle factors, evaluated both individually and in combination, with prevalent hypertension among Korean adults. We analyzed data obtained from the 2007-2008 Korean National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey, a nationwide cross-sectional study using a stratified, multistage probability sampling design. The associations of 12 nutrient intakes and lifestyle factors with risk of hypertension were explored using restricted cubic spline regression and logistic regression models among 6,351 adults. Total energy and several nutrients and minerals, including, calcium, vitamin A, vitamin C, and sodium, showed non-linear relationships with the risk of prevalent hypertension. In multivariate logistic regression models, dietary score, obesity and alcohol intake were independently associated with the risk of prevalent hypertension, but smoking and physical activity were not. Overall, participants whose dietary habits and lifestyle factors were all in the low-risk group had 68% lower prevalence of hypertension (OR: 0.32, 95 CI: 0.14-0.74) compared to those who were at least one in the high-risk group of any dietary or lifestyle factors. The result suggests that combined optimal lifestyle habits are strongly associated with lower prevalence of hypertension among Korean adults.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Genetic Variations in Thiamin Transferase SLC35F3 and the Risk of Hypertension in Koreans
Ja-young Seo, Jeong-Hwa Choi
Clinical Nutrition Research.2021; 10(2): 140. CrossRef - Association of Soybean Food Intake and Cardiometabolic Syndrome in Korean Women: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2007 to 2011)
Sook-Hyun Jun, Woo-Kyoung Shin, Yookyung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 143. CrossRef - How Much Intake of Sodium Is Good for Frailty? : The Korean Frailty and Aging Cohort Study (KFACS)
S. Kim, M. Kim, J. Min, J. Yoo, M. Kim, J. Kang, Chang Won Won
The Journal of nutrition, health and aging.2019; 23(6): 503. CrossRef - Nutritional Status of Hypertensive Men in Gyeongnam Area
Hae-Jin Park, Ye-Ji Choi, Sung-Hee Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2016; 26(4): 297. CrossRef - Nutrition knowledge, eating attitudes, nutrition behavior, self-efficacy of childcare center foodservice employees by stages of behavioral change in reducing sodium intake
Yun Ahn, Kyung Won Kim, Kyungmin Kim, Jinwon Pyun, Ikhyun Yeo, Kisun Nam
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(5): 429. CrossRef - Prevalence of Osteoarthritis and Related Risk Factors in the Elderly: Data from the Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES V), 2010~2012
Hye-Sang Lee
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2014; 20(2): 99. CrossRef - Excessive Sodium Intake and Related Factors According to Energy Intakes Among Korean Elderly: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study
Young-Jin Tak, Jeong-Gyu Lee, Yun-Jin Kim, Sangyeoup Lee, Dong-Wook Jung, Yu-Hyeon Yi, Young-Hye Cho, Eun-Jung Choi, Seung-Hun Lee, Hye-Lim Hwang, A-Ra Cho
Journal of the Korean Geriatrics Society.2014; 18(4): 185. CrossRef - The relationship of dietary sodium, potassium, fruits, and vegetables intake with blood pressure among Korean adults aged 40 and older
Mi Kyung Kim, Kirang Kim, Min-Ho Shin, Dong Hoon Shin, Young-Hoon Lee, Byung-Yeol Chun, Bo Youl Choi
Nutrition Research and Practice.2014; 8(4): 453. CrossRef - An Analysis of Food Consumption Patterns of the Elderly from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES Ⅴ-1)
Eun Mi Kim, Mi-Kyung Choi
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2013; 42(5): 818. CrossRef - Prevalence of Hypertension and Related Risk Factors in the Elderly: Data from the 4th Korean National Health & Nutrition Examination Survey, 2007~2009
Hye-Sang Lee
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2013; 19(1): 14. CrossRef - Association of Bone Mineral Density and Blood Pressure, Calcium Intake among Adult Women in Seoul · Kyunggi Area - Based on 2011 KNHANES -
Jae Ok Koo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(3): 269. CrossRef
- Genetic Variations in Thiamin Transferase SLC35F3 and the Risk of Hypertension in Koreans
- 1,351 View
- 1 Download
- 11 Crossref

- [English]
- Association of Plasma Osteoprotegerin with Adiponectin and Difference according to Obesity in Men with Metabolic Syndrome
- Woori Na, Cheongmin Sohn
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(6):762-770. Published online December 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.6.762
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Osteoprotegerin (OPG) plays a core role in bone reformation by antagonizing the effect of receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand (RANKL), and mediates vascular calcification in cardiovascular disease patients. Thus, we aimed to examine the relationship between serum OPG levels and cardiovascular factors and inflammatory markers in metabolic syndrome patients (MS). This cross-sectional study included 96 men who visited the diet clinic between May and July 2011. Patients were classified into 2 groups based on NCEP-ATP guidelines: normal and with MS (n = 50 and 46, respectively). Physical measurements, biochemical assay were measured. Serum OPG and IL-6, diponectin and hs-CRP were assessed. MS were aged 50.02 +/- 10.85 years, and normal patients 52.07 +/- 9.56 years, with no significant differences. Significant differences were not observed in BMI between the 2 groups. Moreover, significant differences were not observed in serum OPG, however, the serum OPG level (4.41 +/- 1.86 pmol/L) differed significantly between an overweight MS (BMI > 25) and normal patients. OPG was correlated to age (r = 0.410, p = 0.000), HDL-cholesterol (r = 0.209, p = 0.015), and log adiponectin (r = 0.175, p = 0.042). Multiple regression analyses using the enter method showed that age (beta = 0.412, p = 0.000) and BMI (beta = 0.265, p = 0.000) considerably affected OPG. In conclusion, out study showed that serum OPG levels are correlated with cardiovascular risk factors, such as BMI, HDL-cholesterol and adiponectin in MS and adiponectin, suggesting that serum OPG has potential as a cardiovascular disease indicator and predictor.
- 1,024 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Influencing Factors on the Dietary supplements Consumption among Children in Korea
- Jeeyeon Lee, Dohee Kim, Yoonna Lee, Eunmi Koh, Youngsoo Jang, Hyeyoung Lee, Youngae Jang, Cho il Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(6):740-750. Published online December 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.6.740
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - With a recent increase in dietary supplements (DS) consumption among children in Korea, this study was performed to examine the influencing factors on children's DS consumption. A nationwide survey was conducted employing 3 representative samples of children for summer & fall of 2008 and spring of 2009 by stratified multistage sampling of 120 survey sites per season based on the 2005 census population. Approximately 30 households from each survey site were screened for residing children of 0-19 years and about 1,700 households remained as eligible samples per season. Trained dietitians visited households to perform face-to-face interview to children and/or parents regarding DS consumption including health functional foods (HFF), vitamins/minerals (V/M) supplements and other food supplements during 1 month prior to interview. Out of 5,328 children responded, 18.7% reported DS consumption. Consumption rate was higher in boys (19.9% vs. 17.3% in girls, P < 0.05) and youngsters (22.8% compared to 15.0% in adolescents, P < 0.001). Children from higher income family (P < 0.001), those living in apartments (P < 0.001), those residing in metropolitan area (P < 0.001), and those of mothers with higher education (P < 0.001) were more likely to take DS. Also, mother's employment status and occupation were significantly associated with children's DS consumption. The most popular DS was HFF (72.1%), which was consumed more in children of higher income family. It is revealed that socioeconomic factors affect children's DS consumption significantly. Also it is necessary to estimate children's V/M intake from DS and foods together especially because there are tolerable upper limits set for V/M for safety purposes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Study on the Dietary Behavior of Korean Adults: Focus on Dietary Supplement Intake, Household Size, and COVID-19
Jinkyung Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(6): 468. CrossRef - Use of vitamin and mineral supplements and related variables among university students in Seoul
Jung-Hwa Choi, Youjin Je
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(4): 352. CrossRef - The Status of Dietary Supplements Intake in Korean Preschool Children: Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2010-2012
Dong Soo Kang, Kun Song Lee
Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition.2014; 17(3): 178. CrossRef - A Survey on the Usage Patterns of Vitamin and Mineral Supplements as Over-The-Counter Drugs among Korean Adolescents
Ji Hye Han, Hyun Sook Lee, Sun Hyo Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Culture.2014; 29(4): 364. CrossRef - Dietary Supplements Use and Related Factors of Preschoolers in 3 Korean Cities
Hye Sil Kim, Hye Young Lee, Mi Kyung Kim
Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition.2013; 16(2): 104. CrossRef
- A Study on the Dietary Behavior of Korean Adults: Focus on Dietary Supplement Intake, Household Size, and COVID-19
- 1,553 View
- 2 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Dietary and Lifestyle Factors Associated with Hypertension in Korean Adolescents: Based on 2005 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Killye Kim, Sook Mee Son, Hye Kyeong Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(4):439-453. Published online August 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.4.439
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was performed to determine dietary and lifestyle factors associated with hypertension in Korean adolescents. Study subjects were 12~19 years (n = 521) adolescents who participated in the 2005 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES III). Subjects were divided into the hypertensive group (HG, n = 102) and normotensive group (NG, n = 419) by '2007 Korean children and adolescents growth standard' and the relationships between blood pressure and physical measurement, nutrients intakes, eating behaviors and health related factors were analyzed. HG showed significantly higher levels in weight, waist circumference and BMI than NG. The amount of nutrient intakes was not different between NG and HG. Index of nutritional quality (INQ) for phosphate was higher in HG compared with NG. In both male and female HG, INQ for iron was higher but INQ for vitamin B1 was lower than NG. HG revealed higher consumption frequencies of snack, yoghurt, and ice cream compared with NG. In eating and behavioral factors, 'dinner with family', 'eat proper amount', 'keep Korean traditional diet', alcohol drinking, and mean alcohol intake were significantly different between the two groups. By logistic regression method, risk factors for hypertension revealed in this study were gender (male), age (15~19 years), BMI (> or = 85 percentile), and not keeping Korean traditional diet. These results suggest that education program for hypertension prevention in adolescents should include eating habits improvement and lifestyle modification as well as weight control.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biochemical Characteristics and Dietary Intake according to Household Income Levels of Korean Adolescents: Using Data from the 6th (2013 ~ 2015) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yu-Kyeong Kwon, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(6): 467. CrossRef - Differences in SBP, BMI, and Stress with AUDIT Score in Adolescents
Mi-Kyoung Cho, Mi Young Kim
The Open Nursing Journal.2018; 12(1): 228. CrossRef - An analysis of long-term occurrence of renal complications following pediatric pyeloplasty
Hahn-Ey Lee, Kwanjin Park, Hwang Choi
Journal of Pediatric Urology.2014; 10(6): 1083. CrossRef - The Factors related to Dyslipidemia and Hypertension among Male Office Workers
Eun Kyung Lee, Ok Soo Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(4): 432. CrossRef - A Study on Classification of Obesity for Koreans based on the Articles in the Korean Journal of Community Nutrition - Articles Enlisted from 1996 to 2011 -
Youngnam Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(5): 525. CrossRef - Association of Bone Mineral Density and Blood Pressure, Calcium Intake among Adult Women in Seoul · Kyunggi Area - Based on 2011 KNHANES -
Jae Ok Koo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(3): 269. CrossRef
- Biochemical Characteristics and Dietary Intake according to Household Income Levels of Korean Adolescents: Using Data from the 6th (2013 ~ 2015) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,353 View
- 4 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [English]
- Association of Whole Grain Consumption with Socio-Demographic and Eating Behavior Factors in a Korean Population: Based on 2007-2008 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Seungmin Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(3):353-363. Published online June 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.3.353
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The objective of the current study was to examine associations of whole grain consumption with socio-demographic (i.e.: sex, age, household income, education, marriage status) and certain eating behavior factors (i.e.: dish source, eating place, meal type) among a generally healthy Korean population. Using twenty-four hour recall data from the 2007-2008 National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys, whole grain intake (g/day) was calculated for a total of 8,836 generally healthy Koreans aged 6 years and higher. The study subjects had very low whole grain intake. Specifically approximately 60% of the subjects reported no whole grain consumption on the survey day, and mean daily intake ranged from 8.0 g to 15.1 g in different gender and age groups. Living with a spouse was found to be a positive environment factor for whole grain consumption, especially among men. As household income levels increased, whole grain consumption status also improved. The proportion of non-consumer was lowest in a 6-19 year group, and mean intake amount was highest in middle-aged adults. Major dish sources for whole grain consumption included boiled rice with mixed grains, corn, boiled rice with brown rice, cereal products, and other types of boiled rice. It was found that whole grain consumption was highly affected by eating places rather than meal types. The best contributing eating place was home in each age and gender group. The study findings may be useful in planning nutrition education strategy and formulating dietary behavior guidelines for whole grain consumption improvement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Whole grain metabolite 3,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid is a beneficial nutritional molecule with the feature of a double-edged sword in human health: a critical review and dietary considerations
Waldemar Wagner, Katarzyna Sobierajska, Łukasz Pułaski, Anna Stasiak, Wojciech M. Ciszewski
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.2024; 64(24): 8786. CrossRef - Association between quality and quantity of dietary carbohydrate and pregnancy-induced hypertension: A case–control study
Fereshteh Sanjarimoghaddam, Fatemeh Bahadori, Farnush Bakhshimoghaddam, Mohammad Alizadeh
Clinical Nutrition ESPEN.2019; 33: 158. CrossRef - Three types of a high-carbohydrate diet are differently associated with cardiometabolic risk factors in Korean adults
SuJin Song, YoonJu Song
European Journal of Nutrition.2019; 58(8): 3279. CrossRef - Associations between Low-Carbohydrate Diets from Animal and Plant Sources and Dyslipidemia among Korean Adults
Seong-Ah Kim, Kyungjoon Lim, Sangah Shin
Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics.2019; 119(12): 2041. CrossRef - High-Carbohydrate Diets and Food Patterns and Their Associations with Metabolic Disease in the Korean Population
Yun Jung Lee, SuJin Song, YoonJu Song
Yonsei Medical Journal.2018; 59(7): 834. CrossRef - Association between dietary carbohydrate quality and the prevalence of obesity and hypertension
D.‐Y. Kim, S. H. Kim, H. Lim
Journal of Human Nutrition and Dietetics.2018; 31(5): 587. CrossRef - Analysis of Kimchi, vegetable and fruit consumption trends among Korean adults: data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (1998-2012)
Eun-Kyung Kim, Ae-Wha Ha, Eun-Ok Choi, Se-Young Ju
Nutrition Research and Practice.2016; 10(2): 188. CrossRef - Evaluation of Obesity and Nutritional Status by Age among Low-income Women aged over 20 -Using Data from the Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey-
Hee-Kyung Jang
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2015; 25(2): 246. CrossRef - A Study on the Kimchi Consumption of Korean Adults:Using Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2010~2012)
Eun-Kyung Kim, Yoo-Kyung Park, Se-Young Ju, Eun-Ok Choi
Journal of The Korean Society of Food Culture.2015; 30(4): 406. CrossRef - Associations between food insecurity and healthy behaviors among Korean adults
In-Ae Chun, So-Yeon Ryu, Jong Park, Hee-Kyung Ro, Mi-Ah Han
Nutrition Research and Practice.2015; 9(4): 425. CrossRef - An Evaluation of Dietary Habit and Nutritional Status by Household Income in Female Adults over the Age of 20 - Using Data from the Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey -
Hee-Kyung Jang
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2014; 27(4): 660. CrossRef - Relations of Whole Grain Consumption with Predisposing, Reinforcing, and Enabling Factors among Korean Adults
Da-Hae Chae, Jin-Hee Yum, Seung Min Lee
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2014; 20(2): 133. CrossRef - Effects of Green Whole Grain Mixed Diet on Body Weight and Waist Circumference in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Bo Kyung Han, Young Mi Kang, Sang Hyeon Ju, Min Young Shin, Ji Min Kim, So Young Rha, Kyong-Hye Joung, Ju Hee Lee, Koon Soon Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Bon Jeong Ku
The Korean Journal of Obesity.2014; 23(1): 41. CrossRef - Association of Whole Grain Consumption with Nutrient Intakes and Metabolic Risk Factors in Generally Healthy Korean Middle-Aged Women
Ye Jin Kim, Jin Hee Yum, Seungmin Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(2): 176. CrossRef - Quality Characteristics of Bakery Products with Whole Green Wheat Powder
Jin-Young Kim, Ki-Teak Lee, Jeung-Hee Lee
Korean journal of food and cookery science.2013; 29(2): 137. CrossRef - Nutritional Evaluation and Its Relation to the Risk of Metabolic Syndrome according to the Consumption of Cooked Rice and Cooked Rice with Multi-grains in Korean Adults: Based on 2007-2008 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Soo-Hyun Son, Hwa-Jung Lee, Kyong Park, Tae-Youl Ha, Jung-Sook Seo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(1): 77. CrossRef - Study on Food Culture of Koreans over 80-Years-Old Living in Goorye and Gokseong
Hae-Kyung Chung, Mi-Hye Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Culture.2012; 27(2): 142. CrossRef - Diet Quality and Food Patterns of Obese Adult Women from Low Income Classes -Based on 2005 KNHANES-
Jin-Sook Yoon, Heekyung Jang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2011; 16(6): 706. CrossRef
- Whole grain metabolite 3,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid is a beneficial nutritional molecule with the feature of a double-edged sword in human health: a critical review and dietary considerations
- 1,656 View
- 10 Download
- 18 Crossref

- [English]
- Association between Risk Factors for Health and Taste Perceptions of Middle-aged and Elderly People Living in Rural Areas
- Mee Sook Lee, Se In Oh, Chung Shil Kwak
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(1):145-154. Published online February 28, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.1.145
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to evaluate the relationship between taste perceptions and risk factors for health of Korean elderly living in rural areas. Recognition thresholds for four basic tastes, drug consumption, BMI, fasting blood glucose, serum total cholesterol, serum triglyceride, systolic blood pressure, and diastolic blood pressure were assessed in 176 males and 312 females aged between 50 and 88 years. For the recognition threshold of the four basic tastes, alcohol drinking did not influence their sensitivities, but the alcohol drinking group preferred a higher pleasant concentration of NaCl than did the non-alcohol drinking group. However, smoking significantly decreased sensitivities of the four basic tastes. For the pleasant concentration of NaCl, the smoking group tended to prefer a higher concentration than the non-smoking group. Drug consumption, fasting blood glucose, serum total cholesterol, and serum triglycerides did not have a significant correlation to the sensitivity of the four basic tastes and preference of salty solution. Systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure may have been positively correlated with the pleasant concentration of NaCl but did not correlate with the recognition thresholds of NaCl and sucrose. Further, systolic blood pressure was negatively correlated with the recognition thresholds of caffeine, whereas diastolic blood pressure was negatively correlated with the recognition thresholds of caffeine and citric acid. The finding that the risk factors for health correlated with taste perception has diagnostic and practical implications for health promotion for the elderly.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Study on Eating Out Behavior and Recognition of Salinity in Restaurant Food in Jecheon Area
Soojin Park, Sung Hee Min
Journal of The Korean Society of Food Culture.2015; 30(1): 20. CrossRef - Appetite and Related Factors among Community Elders in Korea
Soojin Park
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2014; 43(9): 1431. CrossRef
- A Study on Eating Out Behavior and Recognition of Salinity in Restaurant Food in Jecheon Area
- 1,345 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Factors Related to Eating Breakfast of Middle and High School Students in Seoul
- Yangsuk Kim, Jihyun Yoon, Haengran Kim, Sungok Kwon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2010;15(5):582-592. Published online October 31, 2010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to determine the factors related to eating breakfast for middle and high school students in Seoul using the Theory of Planned Behavior. Out of 2,280 questionnaires distributed to 22 schools, 2,060 were returned (90.4% response rate) and 1,899 were analyzed (83.3% analysis rate). Gender, self-perceived household income level and mother's working status were examined as demographic factors. "Attitude", "Subjective norm", "Perceived difficulty in access to breakfast", "Perceived time restriction" and "Self restriction to breakfast" were extracted as psychosocial factors as the results of factor analysis and reliability test using 17 items. In case of middle school students, boys were more likely to skip breakfast than girls. The students perceiving their household income level "low or middle low" were more likely to skip breakfast than those who perceived their household income level "high or middle high". The students whose mother had a job tended to skip breakfast than those whose mother had no job. In case of high school students, the students perceiving their household income level "low or middle low" tended to skip breakfast than those perceiving their household income level "high or middle high". The results of analysis of variance, all the psychosocial factors examined in this study-"Attitude", "Subjective norm", "Perceived difficulty in access to breakfast", "Perceived time restriction" and "Self restriction to breakfast"- were related to the frequencies of eating breakfast during weekdays in both the middle and high school students.
- 382 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- A Survey on Preference and Purchase Factors of Seaweed
- Yu Mi Hwang, Il Su Choi, Bok Mi Jung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2010;15(3):361-368. Published online June 30, 2010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was carried out to investigate preference and purchase factors of seaweed in some regional residents of Korea. Subjects were residents (n = 1,218) whose residential area was divided into inland and coastal region and the survey was done during December 2007. Especially, purchase factors of seaweeds was conducted only in married females (n = 353). The subjects are composed of 46.5% male and 53.5% female. Regional distribution of subjects was found to be 16~17%, with highest ratio in the age bracket of 20~29 years old. Proportion of students, at 29.8%, was the highest ranking occupation of the subjects. Preference score of seaweeds by region was highest for laver followed by brown seaweed and sea tangle. In terms of preference by gender, female subjects displayed higher preference score for green laver (p < 0.01), seaweed fusiforme, brown seaweed, sea tangle (p < 0.001) than the male subjects. Considerations being made when purchasing seaweeds for each region were in the order of freshness, taste and nutrition. In comparing the inland and coastal region, scores of freshness, convenience, design and color for the coastal region was higher, displaying significant difference.
- 304 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- A Study on the Consumer Perception and Factor Analysis of Food Tourism
- Eun Hae Kim, Min A Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2010;15(1):83-93. Published online February 28, 2010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study is to investigate consumer perception and importance of food tourism properties and performance of the properties in Sangju province of Gyeongsangbuk-do. The study has found that persons who have food tourism experiences (75 persons, 50.7%) had slightly more than not experience persons (72 persons, 48.6%). Additionally, most of the respondents were usually satisfied with the local foods. Also, it was found that food tourism had been taken 1-2 times per 6 months (48 persons, 64.0%) on average, and 135 persons (91.2%) had intention of experiencing food tourism. According to the result of Importance-Performance Analysis (IPA) on consumers' food tourism properties, high importance was on 'There are attractive landscapes.' (4.52 +/- 0.56), 'Accommodations with reasonable price.' (4.18 +/- 0.80), and 'The food of the area is famous.' (4.15 +/- 0.73); and the properties such as 'There are local specialty shops or markets selling local produce.' (3.03 +/- 0.83), 'The climate is temperate.' (3.03 +/- 0.87), and 'There are attractive landscapes.' (3.02 +/- 0.98) showed average performance. A factor analysis about consumers' importances to the food tourism properties shows that the factors were divided into four kinds and each of the factors were named as 'convenience-stable propensity', 'valued-oriented propensity', 'adventurous-aggressive propensity' and 'traditional-active propensity'. Variance ratios of each factor were 22.319%, 10.286%, 8.723% and 6.239%, respectively. According to the result of a reliability analysis, Cronbach's alpha value was 0.8621, implying that reliability of each item was very high. Therefore, it is considered that development of food tourism products and promotion strategies therefore should be designed based on the importance of food tourism properties hereafter.
- 416 View
- 7 Download

- [English]
- A Comparison of Cluster and Factor Analysis to Derive Dietary Patterns in Korean Adults Using Data from the 2005 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Yoon Ju Song, Hee Young Paik, Hyojee Joung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14(6):722-733. Published online December 31, 2009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to explore dietary patterns and compare dietary patterns using cluster and factor analysis in Korean adults. This study analyzed data of 4,182 adult populations who aged 30 and more and had all of socio-demographic, anthropometric, and dietary data from 2005 Korean Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Socio-demographic data was assessed by questionnaire and dietary data from 24-hour recall method was used. For cluster analysis, the percent of energy intake from each food group was used and 4 patterns were identified: "traditional", "bread, fruit & vegetable, milk", "noodle & egg", and "meat, fish, alcohol". The "traditional" pattern group was more likely to be old, less educated, living in a rural area and had higher percentage of energy intake from carbohydrates than other pattern groups. "Meat, fish, alcohol" group was more likely to be male and higher percentage of energy intake from fat. For factor analysis, mean amount of each food group was used and also 4 patterns were identified; "traditional", "modified", "bread, fruit, milk", and "noodle, egg, mushroom". People who showed higher factor score of "traditional" pattern were more likely to be elderly, less educated, and living in a rural area and higher proportion of energy intake from carbohydrates. In conclusion, three dietary patterns defined by cluster and factor analysis separately were similar and all dietary patterns were affected by socio-demographic factors and nutrient profile.
- 384 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- A Survey on Preferences for Vegetable Cooking Methods and Vegetable-aversion-related Factors among Elementary School Students in Kwangju and Chonnam Regions
- Yu Kyong Ahn, Hee Kyong Ro
- Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14(5):531-544. Published online October 31, 2009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was conducted to survey multiple factors of aversion to vegetables and preferences for vegetable-related recipes in school meal services among elementary school children in order to help develop various menus and recipes for school meal services. Questionnaire survey was carried out with the study subjects, who were 401 children in 6th grade attending elementary schools in Chonnam and Kwangju metropolitan regions. Results from the survey can be summarized as follows: 65.1% of respondents answered they try to eat vegetables and other namul side dishes served in school meal service for health. As for the frequency of taking vegetables and namul side dishes out of daily meals, 47.4% of respondents chose 'once or twice'. The reasons for aversion to vegetables in boys were taste and cooking method, while girls were taste and feeling between teeth. In boys there were no differences between regions of Kwangju and Chonnam but the tendency of aversion to vegetables was significantly high in girls. As for the aspects of vegetable aversion of subjects, 46.9% of respondents took up 'black & purple' in the unfavorable color of vegetables. 49.1% in 'bitterness' and 39.2% in 'greasiness''were in terms of the aversive taste of vegetables. The aversive vegetable recipes were 58.6% in 'raw &seasoned' and the unfavorable feeling of vegetables were 53.1% in 'squashiness'. There were differences between regions of Kwangju and Chonnam with boys in color and cooking method in girls. Results from the survey on their preferences for vegetable recipes showed that leafy vegetables like crown daisy (raw/slightly seasoned) and pak choi (broth/pot stew) fell to the most aversive category, while bean sprouts (broth/pot stew) were chosen as the most favorable one. Among root begetables bell-flowers were found to belong to the least preferred recipe, while potatoes were proven to be most preferable in terms of recipes. As for fruit vegetables and other vegetables, all respondents didn't like 'fatsia shoots' vegetable and it's cooking method and they preferred 'green pumpkins (broth/pot stew)'. In respect of mushrooms, enoki mushroom (broth/pot stew) was found most preferred and had high tendency of preferences in boys and girls in Kwangju compared with Chonnam region. The study results indicated that respondents did not show big differences in factors influencing them to be averse to vegetables and their preferences for vegetable recipes depending on regions. In order to have high preference and intake in children's diets, it needs to study in reform of menu about using namul or vegetables mixed with meats and fruits that children preferred or applying roasted and fried other less than namul.
- 397 View
- 3 Download

- [English]
- Age-related Circulating Inflammatory Markers and Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors in Korean Women
- Ho Kyung Kwak, Mi Joung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14(4):451-461. Published online August 31, 2009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to investigate the age-related changes of cardiovascular disease risk factors and inflammatory markers in non-obese Korean women. Subjects were 112 women over 20 years old with body mass index (BMI) less than 30 kg/m2 and were divided into 3 groups (< 40 years, 40~59 years, > or = 60 years). Mean weight and BMI in the oldest group were significantly higher than those in the other 2 younger groups (P <0.05). Mean total cholesterol, triglyceride, LDL-cholesterol and apolipoprotein B/apolipoprotein A1 ratio (BAR) in the oldest group were significantly higher than those in the youngest group (P <0.05), and mean HDL-cholesterol of the oldest group was significantly lower than that of the youngest group (P <0.05). The older-aged group showed significantly higher mean values of atherogenic index (AI) and LDL/HDL ratio (P <0.05) than the respective younger-aged group, and AI was significantly correlated with age, nitric oxide and thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (P <0.01). In addition, mean vascular cell adhesion molecule-l (VCAM-1) tended to be higher in the older-aged group than the younger group. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha, a proinflammatory maker, was significantly positively correlated with serum homocysteine, a cardiovascular disease risk factor (P <0.01). In addition, a significantly positive correlation was observed between C-reactive protein and BAR (P <0.01). Overall results suggested that the aging might affect the increase of cardiovascular disease risk factors including the serum lipid profiles, weight and BMI, and age-related increases of weight and BMI might play a role in changes in certain biomarkers of inflammation.
- 326 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Dietary and Non-dietary Factors Related to Bone Mineral Density in Female College Students
- Ji Hye Lim, Hyun Sook Bae, Seung Min Lee, Hong Seok Ahn
- Korean J Community Nutr 2008;13(3):418-425. Published online June 30, 2008
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to investigate correlations between bone mineral density (BMD) and dietary and nondietary factors in female college students. The BMD of the subjects (n = 38) was measured using DEXA (Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry) at lumbar spine and three femoral sites including femoral neck, ward's triangle, and femoral trochanter. Three-day 24-hour dietary recall data were collected from each subject to assess consumption levels of nutrients and food groups. The mean (+/- SD) values of age, age of menarche, height, weight, body mass index (BMI), waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), fat mass, and % body fat of the subjects were 21.34 (+/- 1.73) years, 13.1 (+/- 1.2) years, 161.3 (+/- 5.0) cm, 53.7 (+/- 7.2) kg, 20.6 (+/- 2.6) kg/m2, 0.80 (+/- 0.04), 15.4 (+/- 4.4) kg, and 28.2 (+/- 4.7), respectively. The BMD values of lumbar spine, femoral neck, ward's triangle, and femoral trochanter as T-value were 1.150 +/- 0.13 g/cm2, 0.932 +/- 0.11 g/cm2, 0.850 +/- 0.13 g/cm2, and 0.721 +/- 0.10 g/cm2, respectively. The daily mean energy intake of the subjects was 1660.6 kcal. The intake levels of carbohydrate, calcium, iron, vitamin C, and folic acid were lower than the KDRIs, while those of fat, phosphorus, sodium, vitamin A, and vitamin B6 were higher than the KDRIs. Significantly negative correlation were detected between consumption of fat and oils and the BMD of all sites measured (p < 0.05). Potato and starch intake was negatively correlated to the BMD of femoral neck and word's triangle (p < 0.05). The intake of cereals was found to be negatively correlated to the BMD of ward's triangle (p < 0.05). There was also negative correlation of intake of soybeans and products with the BMD of lumbar spine (p < 0.05). Weight and muscle mass were positively correlated to the BMD of both lumbar spine and femurs (p < 0.01). Significantly positive correlations between BMI, and fat mass and the BMD of lumbar spine were observed (p < 0.001). Additionally fat mass was positively correlated to the BMD of femoral neck. WHR and % body fat were positively correlated to the BMD of lumbar spine (p < 0.05). Negative correlation was found between a serum calcium level and the BMD of femoral neck (p < 0.05). In summary non-dietary factors generally showed significant correlations with the BMD of lumbar spine, while several dietary factors showed significant correlations with the BMD of femurs.
- 367 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Factors Influencing the Consumption and Purchase of Functional Foods in Gwangju
- Eun young Kim, Ki sang Ryu, Young Ran Heo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2007;12(6):782-789. Published online December 31, 2007
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study is to know about the consumption patterns of functional foods and their associated factors for contributing to the promotion of healthiness on Gwangju residents. The results obtained are summarized as follows: in terms of age, 35.9% of men (n = 78) and 52.3% of women (n = 128) are found in the age range of 45~54 which comprises the highest portion of age distribution. 49.5% of subjects had college education or more. In the occupation category, 33.3% of the men had business job positions, and 39.8% of women were in the unemployed (housewife) category. Stress relief was the most important factor to maintain good health. 76.2% of the subjects have experience in consuming functional foods. The main reason for taking functional foods was to maintain health. Information and reliability of effectiveness were considered when selecting functional foods. Purchasing functional foods was motivated by family members, relatives, and/or the subjects themselves. Functional foods were mainly purchased from pharmacies or health food stores. Regular exercise, drinking, periodical medical checkups, and eating score all are taken into consideration with the consumption of functional foods.77.9% of subjects recognized functions for functional foods purchased. 18.8% of subjects experienced side effects after intaking functional food. Therefore, functional foods should be managed by the government and nutrition education for consumers should be required to encourage them to choose functional foods more satisfactorily and safely.
- 326 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Nutritional Environment Influences Hypertension in the Middle-aged Korean Adults: based on 1998 & 2001 National Health and Nutrition Survey
- Hae Jeung Lee, Haeng Shin Lee, Yoonna Lee, Young Ai Jang, Jae Jin Moon, Cho il Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2007;12(3):272-283. Published online June 30, 2007
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was performed to delineate the relationship between lifestyle and nutritional risk factors associated with hypertension in representative middle-aged Korean population. Hypertension in this study is defined as hypertensive (SBP> or = 140 mmHg or DBP> or = 90 mmHg) adults without recognition of a disease state before a health exam. With data from the 1998 and 2001 National Health and Nutritional Survey, nutrient intakes of 6,112 adults, 40-64 years of age were calculated using food composition database and matched with health examination records by individual ID. After excluding those with extreme intake values, the number of final subjects included in the analysis was 5,200 (male 2,458, female 2,742). Using logistic regression method, socio-demographic data, lifestyle factors, and nutrient intakes were analyzed. Risky factors for hypertension revealed in this study were age, sex, BMI over 23, waist circumference, alcohol intake of more than 16 g (male) or 8 g (female). Regarding nutrient intakes, the intakes of highest quartile for energy (> or = 2363.0 kcal) and protein (> or = 90.2 g) were significantly associated with higher risk of hypertension after adjusting for age, sex, and other socio-demographic factors (OR = 1.312 (1.046-1.711), OR = 1.488(1.194-1.854), respectively)). Although high intakes of sodium (> or = 6604.0 mg) and phosphorus seemed to be risk factors of hypertension also before energy adjustment (OR = 1.278(1.034-1.581), OR = 1.280(1.024 -1.600), respectively), only high intakes of energy and protein remained significant after adjustment. This study revealed that modifying risky lifestyles and dietary patterns, especially high energy intake, high protein intake, and high alcohol drinking, in middle-aged Korean adults could result in a prevalence decrease and/or prevention of hypertension.
- 340 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- The Effects of Regular Exercise on Obesity Indices and Dietary Factors in Adult Males
- Kang Ok Cho, Hyun Joo Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2007;12(2):160-167. Published online April 30, 2007
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was performed to investigate the effects of regular exercise on dietary factors and obesity indices among 407 healthy adult males subjects. Subjects were classified into regular exercise group (REG) and irregular exercise group (IREG). Two hundred and thirteen subjects of REG excercised regularly 3 times (more than 30 minutes/time) per week during more than last 1 month or more. One hundred and ninety-four of IREG (n = 194) didn't regularly exercise during the last 1 month. Obesity indices were BMI (Body Mass Index), WHR (Waist Hip Ratio) and PIBW (Percentage of Ideal Body Weight). And the mean BMI, WHR and PIBW of REG were (22.1, 0.90 and 105.8) significantly lower than those of IREG (25.7, 0.98 and 117.7) respectively. The mean daily starches, seeds, meats, eggs, fish, milk, fats and processed food intakes of REG were significantly lower than those of IREG. And the mean daily vegetables, mushrooms and beverages intakes of the IREG were significantly lower than REG. Energy intake of REG and IREG were 1968.2 kcal and 1978.9 kcal respectively. Vitamin C intake of IREG was significantly lower than REG. But niacin and cholesterol intake of REG were significantly lower than the IREG. Exercise regularity was positively related with obesity indices and dietary factors. Therefore, it is necessary to exercise regularly to prevent obesity and cardiovascular disease in Korean adult males.
- 388 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Dietary Risk Factors Associated with Hypertension in Patients
- Sook Mee Son, Gwui Yeop Huh
- Korean J Community Nutr 2006;11(5):661-672. Published online October 31, 2006
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was performed to determine the dietary risk factors associated with hypertension. The hypertensive group were composed of 112 hypertensive patients (male 53, female 59) who first visited the hypertension clinic and had been diagnosed as having primary hypertension (SBP > or = 140 mmHg or DBP > or = 90 mmHg). The regular visitors or the subjects on special diets or medical therapies were excluded. The normal group consisted of as subjects (male 41, female 54) matched with age and socioeconomic levels. The subjects having higher intakes (above the 75 percentile) in energy, protein, iron, vitamin A or C showed significantly higher hypertension risk estimated with odds ratio after the covariance factors (age, sex and BMI) were adjusted. More than 2400 mg of sodium (6 g of salt) intake was associated with significantly higher risk of hypertension (odds ratio: 1.773, CI: 1.014 - 3.014 for SBP > or = 140 mmHg; odds ratio: 2.373, CI: 1.359 - 4.215 for DBP > or = 90 mmHg). Hypertensive group showed significantly increased intakes of vegetables and fish and shell fish compared to the normal group. When the vegetable intakes were classified into Kimchi, fresh vegetables and cooked vegetables with seasoning, the hypertensive group was observed as having higher intakes of Kimchi and cooked vegetables with seasoning. The intakes of highest quartile for vegetables (> or = 327 g/day)(odds ratio: 3.164, CI: 1.740 - 5.752), fish and their products (> or = 102 g/day)(odds ratio: 2.756, CI: 1.486 - 5.109), grains(> or = 311 g/day)(odds ratio 2.393, CI: 1.186 - 4.832), meats and their product (> or = 106 g)(odds ratio: 2.210, CI: 1.225 - 3.987) compared to the lower were significantly associated with the higher risk of hypertension estimated with DBP (> or = 90 mmHg) after covariance factors were adjusted. In conclusion, our findings confirm that higher intake of energy or sodium are associated with the increased risk of hypertension. Because increased intake of vegetable or fish was associated with the higher risk of hypertension, in contrast with the finding of western countries, choosing or preparation of vegetables or fish with reduced salt is recommended.
- 376 View
- 6 Download

- [English]
- Development of Performance Indicators Based on Balanced Score Card for School Food Service Facilities
- Tongkyung Kwak, Hyeja Chang, Jiyong Song
- Korean J Community Nutr 2005;10(6):905-919. Published online December 31, 2005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study raised the necessity of developing performance indicators for measuring the management efficiency and effectiveness of school food service, and as a means of helping its implementation, a balanced score card (BSC) approach developed by Norton and Kaplan was adopted. This study established BSC in seven phases through literature: Phase 1 Defining a school food service and the scope of working activities, Phase 2 Establishing the vision of a school food service, Phase 3 Setting strategic goals, Phase 4 Identifying critical success factors (CSFs), Phase 5 Developing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), Phase 6 Extracting cause and effect relationship, and Phase 7 Completing a preliminary BSC. The preliminary BSC was turned into a survey, which was administered to food service related people working at the Office of Education and School Food Service including 16 offices, 209 dietitians, 48 school administrators both from self-operated and contract-managed, and 9 experts in areas related to school food service. They were asked questions about strategics from 4 different perspectives, 12 CSFs, 39 KPIs, and the cause and effect relationships among them. As a result, among the CSFs based on 4 different perspectives, all factors other than "zero sum on profit/loss" from the financial perspective turned out to be valid. In terms of KPIs, manufacturing cost percentages, casualty loss count/reduction rates, school foodervice participation rates, and sales goal achievement rates were found to be valid from the financial perspective, while student satisfaction index, faculty satisfaction index, leftover ratio, nutrition educational performance count, index of evaluating nutrition education, customer claim count/reduction rate, handling customer claim count/reduction rate, and parent satisfaction index were found to be valid from the customers' perspective. Besides, nutritional requirement sufficient ratio, nutritional management score, food poisoning outbreak count, employee safety accident count, sanitary inspection assessment index, meals per labor hour (productivity index), computerization ratio, operational management index, and purchase management assessment index were also found to be valid from the perspective of internal business processes. From the perspective of innovation and learning, employee turnover ratio/rate of absenteeism, annual education and training count, employee satisfaction index, human resource management assessment index, annual menu-related customer feedback, food service information index for employees and parents/schools were also found to be valid. The significance of this study is to present indices for measuring overall performance of school lunch food service operations without putting any limitation on types of school food service management, and to help correctly assess the contribution of the current types of school food service management to schools and students.
- 353 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- A Study on Social Factors and Physical Health Status of the Long-Lived Elderly People in Ganghwa-gun Area
- Hye Kyoung Han, Sung Sook Choi, Myung Wha Kim, Sung Dong Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2005;10(1):111-121. Published online February 28, 2005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was to performed to assess social factors and physical health status. The subjects of the study were 103 elderly people of age over 85 years living in Ganghwa-gun area. The method of this research was based on the interview-survey with questionnaire. Chi-square test was the main data analysis method. The subject group was composed of 36 males and 67 females, the average age being 91.0 +/- 3.2 years old for the males and 91.1 +/- 3.4 years old for the females. The aged average height and weight were 161.0 +/- 7.9 cm and 54.6 +/- 7.8 kg in males, 141.0 +/- 8.2 cm and 42.2 +/- 7.9 kg in females which were lower than the Korean average standard but the mean BMIs of both male and female showed normal range. Their level of education was lower and they tended to be religious. The aged population might be economically poor. Their level of living standards tended to have been lower-middle and lower class. The mean age of their parents' death were 64.3 +/- 17.2 years in males, 59.0 +/- 14.9 years in females for the father and 70.9 +/- 15.5 years in males, 66.8 +/- 16.6 years in females for the mother. The rate of living together with their family or spouse in the female aged was 83.2% higher than in the male aged. They tended to have engaged in hobbies that require less movement. Of the kinds of hobby, "TV watching (47.8% in male and 44.9% in female) was the highest. Ratios of the drinking and the smoking elderly were 30.6%, 25.0% in male and 7.5%, 18.8% in female but they tended to have never drunken and smoked. Of the subjects, 42.9% spend 8~9 hours for sleeping in male and 35.8% spend 10 hours for sleeping in female. They tended to have not done any particular health behavior. The most common diseases were digestive disease in male, arthritis and hypertension in female. Most elderly males (47.3%) and females (61.2%) had 1~2 diseases.
- 429 View
- 2 Download

- [English]
- The Ecological Factors Related to Completion of Weight Reduction Program in the Obese Premenopausal Women
- Sangyeon Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2004;9(6):683-694. Published online December 31, 2004
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The objective of this study is to improve the health related quality of life through the efficient weight reduction by analyzing the ecological factors related to completion of weight reduction program in the obese premenopausal women aged 20-29 years. The factors influencing completion of obesity management programs in the obese women were the preferences of sweet and salt taste, health related quality of life (general health, role emotional), eating attitude scores, and regularity of mealtime scores. The finding that the completion of obese management programme were improved if the health-related quality of life was high and the physiological status related symptoms of stress, depress, and eating disorder were good has implications for the treatment of obesity. The questionnaire used this study can be available to develop the obesity assessment sheets which is required the exploration of the characteristics of obese women and the tailored multi-disciplinary obesity management program. Moreover, the obesity assessment sheets will make a contribution to determine types of the programs that is suitable for obesity women before starting an obesity management program.
- 343 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- A Study of the Frequency of Food Purchase for Snacking and Its Related Ecological Factors on Elementary School Children
- Seock Ah Kang, Joung Won Lee, Kyeung Eun Kim, Jae Ok Koo, Dong Yean Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2004;9(4):453-463. Published online August 31, 2004
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In order to investigate food purchase frequency of elementary school children and its related ecological factors, 4314th, 5th and 6th grade elementary school children and their mothers, living in Seoul and Daejon, small city and rural area of Chungnam Province, were participated in this study. The subjects and their parents were surveyed by a selfrecording questionnaire about food purchase frequency and some ecological factors. Average height and weight of the subjects by gender and grade were similar to or a little bit more than the 1998 Korean Growth Standard. According to relative body weight, 30.6% and 10.8% of the subjects belonged to under-weight and obesity categories, respectively. Of the subjects, 46.9% used PC telecommunication or internet, 53.8% of them used it for less than an hour per day, and 46.4% watched TV for 2 to 4 hours a day. About 42% of the subjects spent 500 Won or less daily to buy snacks. A half of the subjects took snacks once a day because of hunger. Mothers' nutrition knowledge score was averagely 8.16 out of 13 full score and the average attitude score was 43.22 out of 50 full score. Foods purchased more than once a week were milk and yoghurt, cookies, ice-cream, ramyun, and gum in order. Family income, parents' education level, mothers' nutrition knowledge and food attitude score, students' snacking frequency and TV watching time showed significant correlations with purchase frequencies of some individual food items. In conclusion, the elementary school children considered taste most important rather than nutrition in buying snacks and most frequently bought carbohydrate foods and concentrated sugars except milk. Ecological factors such as mothers' nutritional knowledge and food attitude, TV watching time and snacking frequency had influenced the children's food purchase frequency. Accordingly, it is necessary to educate both children and their mothers about good food purchase and the importance of snacking.
- 609 View
- 10 Download

- [English]
- Factors Associated with Breakfast Skipping in Elementary School Children in Korea
- Sang Jin Chung, Yoonna Lee, Sunja Kwon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2004;9(1):3-11. Published online February 29, 2004
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The objective of this study was to examine relationships between breakfast skipping and ecological factors related to eating practice. Participants were 537 children (male: 274, female: 263) from two elementary schools in Kyunggido (School A) and Seoul (School B). Analysis included cross-tabulation of demographics, factors related to eating practice and weight status, frequency of breakfast skipping and types of breakfast and the number of foods at breakfast by schools. Logistic regression were conducted to identify the factors associated with breakfast skipping. Children in school B showed higher socioeconomic status by living environment and the type of fathers' job than those in school A. Eighty six percent of children in school B and 75% in school A ate breakfast 5 times and more per week. School and father's occupation differences correlated with the frequency of breakfast, but not mother's employ status was not. After controlling school, type of father's job, mother's employ status, eating breakfast 5 times and more was associated with eating with other family members, feeling hungry before breakfast, normal weight status, eating Korean traditional meal type and number of food eaten at breakfast. The results stress the need for intervention programs aimed at decreased skipping breakfast among elementary school children. While programs need to reach all children skipping breakfast, approaches need to be suitable to in particular those from low socioeconomic backgrounds.
- 496 View
- 2 Download

- [English]
- Fast Food Consumption and Related Factors among University Students in Daejeon
- Kyung Won Kim, Yun Ahn, Hyung Mee Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2004;9(1):47-57. Published online February 29, 2004
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The study purpose was to investigate the factors related to fast food consumption of university students. Factors were identified using the Theory of Planned Behavior. Based on the pilot study, 18 behavioral beliefs, 7 normative beliefs and 19 control beliefs were identified. Data (n = 269) were analyzed using analysis of variance or chi-square tests. Subjects were categorized into non-users (27.9%), users (42%) and frequent users ( > or = 2 times/week, 30.1%). Regarding behavioral beliefs, users or frequent users responded more positively on advantages of eating fast foods including 'taste' (p < 0.001), 'making me feel full' (p < 0.001), 'diverse menus' (p < 0.05) than non-users. Compared to users, non-users responded more positively on the item that eating fast foods leads to eat vegetables less (p < 0.05), and negatively on 'making me eat more salt'(p < 0.05). Most of the referent groups, parents (p < 0.001), sisters/brothers (p < 0.01), relatives (p < 0.01), friends (p < 0.05), boy/girl friends (p < 0.05) were important sources of influence regarding subjects' fast food consumption. Users or frequent users felt less control over factors or situations that make it consume fast foods (9 out of 19 control beliefs). These factors included; availability issues (p < 0.001), 'not having other foods on hand'(p < 0.01), 'others eating together like fast foods', 'convenience', 'social increase in fast food use', 'easy to get fast foods anytime' (p < 0.05). In addition, users of fast foods were more likely to eat fast foods when they don't have time, when they do not like to cook, when they feel hungry (p < 0.05). These results suggest that interventions for university students include strategies to moderate fast food use by modifying behavioral beliefs, suggesting alternative menus and behavior modification techniques, increasing perception of control, and eliciting social support.
- 478 View
- 18 Download

- [English]
- Depression and Dietary Factors Related to Hyperlipidemia in Urban Living Elderly Female from Low Income Group
- Sook Mee Son, Jin Kyung Park, Hong Sup Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2003;8(6):938-950. Published online December 31, 2003
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We conducted a case-control study to examine the relationship of depression and dietary related factors with the hyperlipidemia for urban living elderly women from low income group. The case group consisted of 45 elderly females with hyperlipidemia (serum cholesterol > or = 240 mg/dl or serum TG > or = 250 mg/dl) and the control group of 95 age matched elderly women with serum cholesterol levels less than 240 mg/dl and serum TG less than 250 mg/dl. In a univariate analysis, vitamin C intake, the number of family members living with the subject, and their depression scores were significantly higher in the hyperlipidemic group than in the control group. In the logistic regression analysis, the vitamin C intake (> or = 75% Korean RDA), the number of family members living with the subject (> or = 1), depression scores (> or = 7), BMI (> or = 27), and subscapular skinfold thickness (> or = 18 mm) were associated with significantly higher (p < 0.05) risks of hyperlipidemia in the elderly women. However after adjustment for other covariables, the depression scores (Odds Ratio 2.48 for depression score > or = 7 ; 95%CI : 1.10 - 5.60) and subscapular skinfold thicknesses (Odds Ratio 5.69 for SBT > or = 18 mm ; 95%CI : 1.87 - 17.32) were the significant risk factors associated with hyperlipidemia in the elderly women.
- 356 View
- 0 Download


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



