Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [Korean]
- Effects of primary caregivers’ food literacy, social support, food environment, and household income on the nutritional status of school-aged children: a cross-sectional study
- Seyeon Park, Ji-Yun Hwang, Sohyun Park, Hyun Joo Ryou, Jieun Oh
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(5):352-363. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00248

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The dietary habits of school-aged children play a critical role in their growth and development, and are strongly influenced by the home environment. Household income is closely associated with caregivers’ food literacy, social support, and food environment. This directly affects the nutritional status of children. This study aimed to provide evidence to inform policies and educational programs for improving dietary habits in children, and to establish a foundation for tailored support strategies for low-income families.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 846 primary caregivers of school-aged children from 17 regions across Korea, recruited through an online survey. Household income, caregivers’ food literacy, social support, and food environment were assessed. Nutritional status in children was measured using the Nutrition Quotient for Children (NQ-C). Statistical analyses included descriptive statistics, chi-square tests, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), analysis of covariance (ANCOVA), correlation analyses, and multiple linear regression.
Results
Caregivers from higher income households demonstrated significantly greater food literacy and social support (P < 0.001). Children from these households showed high balance scores and a large proportion of these children were in the “high” NQ-C grade. The NQ-C score in children was positively correlated with food literacy (r = 0.425), social support (r = 0.471), and the food environment (r = 0.235) (P < 0.001). Multiple regression analysis showed that food literacy (β = 0.256) and social support (β = 0.348) were significant predictors of nutritional status in children.
Conclusion
This study confirmed that the nutritional status in children is not only determined solely by household income but is also mediated by caregivers’ food literacy, social support, and food environment. These findings highlighted the limitations of providing only economic support. The findings underscore the need for multifaceted interventions such as strengthening parental nutrition education, expanding social support networks, and improving access to healthy foods.
- 280 View
- 13 Download

- [English]
- Safety education status and needs priorities of Korean military food service personnel using the Borich Needs Assessment and the Locus for Focus model: a cross-sectional study
- Jeongeun Park, Eunsil Her
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(4):261-273. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00185

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Since the enactment of the Serious Accidents Punishment Act in Korea in 2021, the importance of safety management in food service facilities has increased. This study was conducted to examine the status of safety education and to identify educational needs for safety accident prevention among army food service personnel.
Methods
This study included 157 food service personnel from Army units located in Gyeongsangnam-do. Participants were divided into two groups based on the daily number of meals served. Demographic characteristics, the status of safety education, and priority for safety accident prevention education were evaluated.
Results
A total of 97.5% of participants received safety education, with 60.8% attending at least monthly. “Lecture” (63.4%) was the most commonly used educational method. The preferred educational methods were “Lecture” (23.5%) and “Counselling” (23.5%), showing significant group differences (P < 0.001). A total of 79.6% of participants reported applying the educational content in their performance. The mean importance score for safety accident prevention (4.78) was higher than the performance score (4.44), with significant differences between the two groups observed in the importance scores (P < 0.05). “Slip & burn” had the highest importance score, while “Electric shock and fire” had the highest performance score. The educational needs analysis revealed that the highest priority item for the < 100 meals group was “When moving heavy items, an assistive device or assistance from colleagues should be utilized”, while for the ≥ 100 meals group, it was “When using a vegetable cutter or grinder, use an exclusive stick.”
Conclusion
This study can serve as a foundational database for developing customized safety education programs tailored to Korean army food service personnel.
- 1,511 View
- 23 Download

- [English]
- The dietary factors associated with sleep duration in postmenopausal middle-aged women: a cross-sectional study using 2019–2023 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
- Eugene Shim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(3):197-213. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00052

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to analyze dietary factors associated with sleep duration in postmenopausal middle-aged women using data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), with particular emphasis on the postmenopausal period.
Methods
A total of 3,040 postmenopausal women aged 40–64 years from the 2019–2023 KNHANES were included. Sleep duration was classified into four categories: “appropriate sleep duration” (ASD; 7–9 hours), “short sleep duration” (6–7 hours), “very short sleep duration” (VSSD; < 6 hours), and “long sleep duration” (LSD; > 9 hours). Nutrient and food intake were compared among groups using analysis of covariance. Multinomial logistic and polynomial regression models assessed associations, adjusting for demographic and health covariates.
Results
The VSSD group had higher body mass index and waist circumference than the ASD group, despite lower total energy intake, and also consumed more snack energy and skipped breakfast and dinner more often. This group also had lower intakes of monounsaturated fatty acids and nuts and seeds. In the late menopausal group, greater consumption of cereal grains, fish and shellfish, and beverages was associated with elevated LSD risk. Conversely, higher folate intake in the early menopausal group was inversely associated with VSSD risk. Cholesterol intake was positively associated with LSD risk in both groups. A negative nonlinear association between sleep duration and dietary intake was observed in the early menopausal group when polyunsaturated fatty acid intake exceeded 19.86 g/day and riboflavin intake exceeded 1.76 mg/day. In the late menopausal group, riboflavin intake was strongly correlated with increased LSD risk (odds ratio = 4.776, P = 0.004). Sugar and beverage intake showed a positive linear relationship with sleep duration at average intake levels.
Conclusion
Dietary factors associated with sleep duration differed by postmenopausal period, with specific nutrients and food groups exhibiting variable associations with sleep duration above mean intake levels.meS
- 2,826 View
- 35 Download

- [English]
- Understanding the charactersitics and types of single-person households based on food purchase frequencies in Korea: a cross-sectional study using the 2023 Consumer Behavior Survey for Foods
- So-Yun Kim, Youngmin Nam, Jong-Youn Rha, Haerang Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):27-39. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00031

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated the differences in food purchase frequency among single-person households by gender and age group and explored the characteristics of single-person household groups according to their food purchase patterns.
Methods
Utilizing data from the 2023 Consumer Behavior Survey for Foods conducted by the Korea Rural Economic Institute, this study examined food purchase frequencies among 966 single-person households. Data were analyzed using Rao-Scott chi-square tests, ANCOVA, ANOVA, and K-modes hierarchical cluster analysis.
Results
Significant differences were observed in the food purchase frequencies of single-person households for fresh and convenient food. Women displayed higher purchase frequencies for fish, vegetables, and fruits, whereas men showed higher purchase frequencies for convenient foods (P < 0.005). Single-person households aged 39 years and younger exhibited lower purchase frequencies for vegetables (P < 0.005) and fish (P < 0.001) and substantially higher frequencies of convenient food purchases (P < 0.001). Additionally, this study identified three distinct single-person household groups based on food purchase pattern: the “nutrition-conscious” group, which exhibited high purchase frequency for fresh foods; the “convenience-seeking” group, which showed high purchase frequency for all types of convenient foods; and the “passive food consumer” group, which displayed relatively low purchase frequency for both fresh foods and convenient foods. The socio-demographic characteristics of single-person households differed significantly across these three groups, with the “passive food consumer” group and “convenience-seeking” group exhibiting lower healthy eating competency (MN(nutrition-conscious group) = 3.68, MP(passive-food-consumer group) = 3.40, MC(convenience-seeking group) = 3.52, P < 0.001), safe eating competency (MN = 3.87, MP = 3.57, MC = 3.77, P < 0.001), and satisfaction (MN = 3.36, MP = 3.23, MC = 3.25, P = 0.04) than the “nutrition-conscious” group.
Conclusion
This study underscores the need for targeted nutrition programs to address the unique needs of single-person households depending on their characteristics. Specifically, this study highlights the importance of targeted interventions for “convenience-seeking” and “passive food consumer” to promote dietary competency and encourage healthy dietary behavior. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Secular trends in dietary patterns among Korean adults: using data from the 2007–2022 Korea National health and nutrition examination survey
Eunyoung Tak, Juhae Kim, Heejin Lee, Minji Kang
Nutrition Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Secular trends in dietary patterns among Korean adults: using data from the 2007–2022 Korea National health and nutrition examination survey
- 8,276 View
- 75 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Effects of a multi-component program based on partially hydrolyzed guar gum (Sunfiber®) on glycemic control in South Korea: a single-arm, pre-post comparison pilot clinical trial
- Hyoung Su Park, A-Hyun Jeong, Hyejung Hong, Hana Jang, Hye-Jin Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):40-52. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00276
- Correction in: Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):173

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The aim of this study was to assess the impact of a multi-component program, including partially hydrolyzed guar gum (PHGG, Sunfiber®) supplementation, on glycemic control, gut health, and nutritional status to support diabetes prevention and management among Korean adults.
Methods
A single-arm trial was conducted with 29 adults (aged 20-55 years) with fasting plasma glucose (FPG) ≥ 100 mg/dL. Over a six-week period, participants engaged in a multi-component program that incorporated the supplementation of PHGG (Sunfiber®, 12.5 g/day), weekly nutritional coaching, and the use of continuous glucose monitoring devices. The program’s effectiveness was evaluated by measuring FPG and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels through blood tests conducted before and after the intervention. Improvements in gut health were gauged using the Korean Gut Quotient Measurement Scales, while enhancements in nutritional status were assessed using the Nutrition Quotient (NQ) and surveys that evaluated improvements in gut health and nutritional status.
Results
Participants’ average age was 43.89 years, with approximately 80% being male. Most participants (about 75%) were classified as overweight or obese. After six-weeks, 17 participants who adhered closely to the program (meeting certification criteria) exhibited significant reductions in key blood glucose markers. FPG levels decreased from 113.06 ± 23.16 mg/dL to 106.24 ± 16.33 mg/dL (P < 0.05), and HbA1c levels decreased from 6.08% ± 0.81% to 5.87% ± 0.53% (P < 0.05). The NQ evaluation revealed significant increases in comprehensive nutrition scores, and in the balance and practice domain scores for all participants (P < 0.05). Furthermore, in the gut health survey, approximately 82.1% of all participants reported experiencing positive changes.
Conclusion
Among adults with elevated FPG levels, a multi-component intervention program that included PHGG (Sunfiber®) supplementation, structured dietary management, and the use of health-monitoring devices showed significant benefits in improving glycemic control, overall nutritional status, and gut health. Trial Registration: Clinical Research Information Service Identifier: KCT0010049.
- 6,196 View
- 41 Download

- [Korean]
- Biochemical characteristics, nutrient intakes, and chronic disease risk according to the dietary fat energy ratio in middle-aged Korean: a cross-sectional study using data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Ga-Hyeon Jeong, Sook-Bae Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(6):528-540. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00304
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to examine health-related characteristics and chronic disease risk in middle-aged Koreans based on their fat energy intake ratio.
Methods
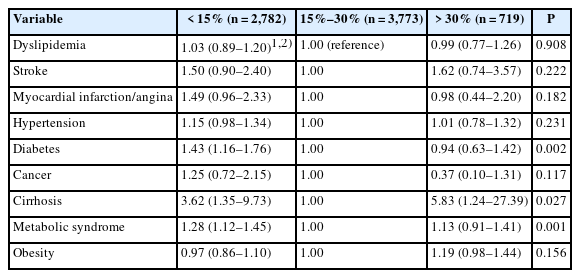
We analyzed data from 7,274 Koreans aged 40–64 years using the 7th (2016–2018) Koreans National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Participants were classified into three groups based on their fat energy intake ratio: insufficient (< 15%), adequate (15%–30%), and excessive (> 30%). We assessed their socio-demographic characteristics; lifestyle characteristics; biochemical characteristics; quantitative and qualitative nutrient intakes, measured using dietary reference intakes for Koreans and index of nutrition quality (INQ); and chronic disease risk.
Results
Significant differences were observed between the groups in age, gender, income, education, and residence region. The insufficient group had the highest proportion of older adults, male, lower income, rural residents, and lower education levels. The groups differed significantly in lifestyle characteristics, with the insufficient group having the highest rates of no walking, heavy drinking, smoking, and poor subjective health perception. Biochemical characteristics in the insufficient group exhibited the lowest levels for fasting blood glucose, hemoglobin A1c, and triglycerides. Significant differences were found in both the quantitative and qualitative intake of nutrients. The insufficient group had the lowest intake of most nutrients except fiber, whereas the excessive group had the lowest fiber intake. Based on the INQ, vitamin A and Ca were the lowest in the insufficient group, and vitamin C and folic acid were the lowest in the excessive group. The risk of diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome was highest in the deficient group, and the risk of liver cirrhosis was highest in the excessive group.
Conclusion
Insufficient or excessive fat energy intake ratio negatively affects nutrient intake and chronic disease risk. Fat energy intake of 15%–30% is important for improving nutrient intake and managing chronic diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, and liver cirrhosis. We suggest that education and an appropriate social environment are necessary to ensure this fat energy intake. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Study on the Optimization of Manufacturing Conditions for Traditional Potato Bugak Using Response Surface Methodology
Yu Hyeon Jo, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2025; 35(1): 60. CrossRef - Nutritional risk assessment using estimated usual nutrient intake in Korean adults: analysis of the 8th (2019–2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
Woojin Byeon, Cho-il Kim, Sung Ok Kwon, Jihyun Yoon, Linxi Huang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(5): 799. CrossRef
- Study on the Optimization of Manufacturing Conditions for Traditional Potato Bugak Using Response Surface Methodology
- 1,239 View
- 45 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Co-occurrence network and pattern of school lunch using big data and text-mining using data from the 2021–2023 school meal menu information on the NEIS open educational information portal: an exploratory study
- Hyeyun Kang, Jimi Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(6):514-527. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00297
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
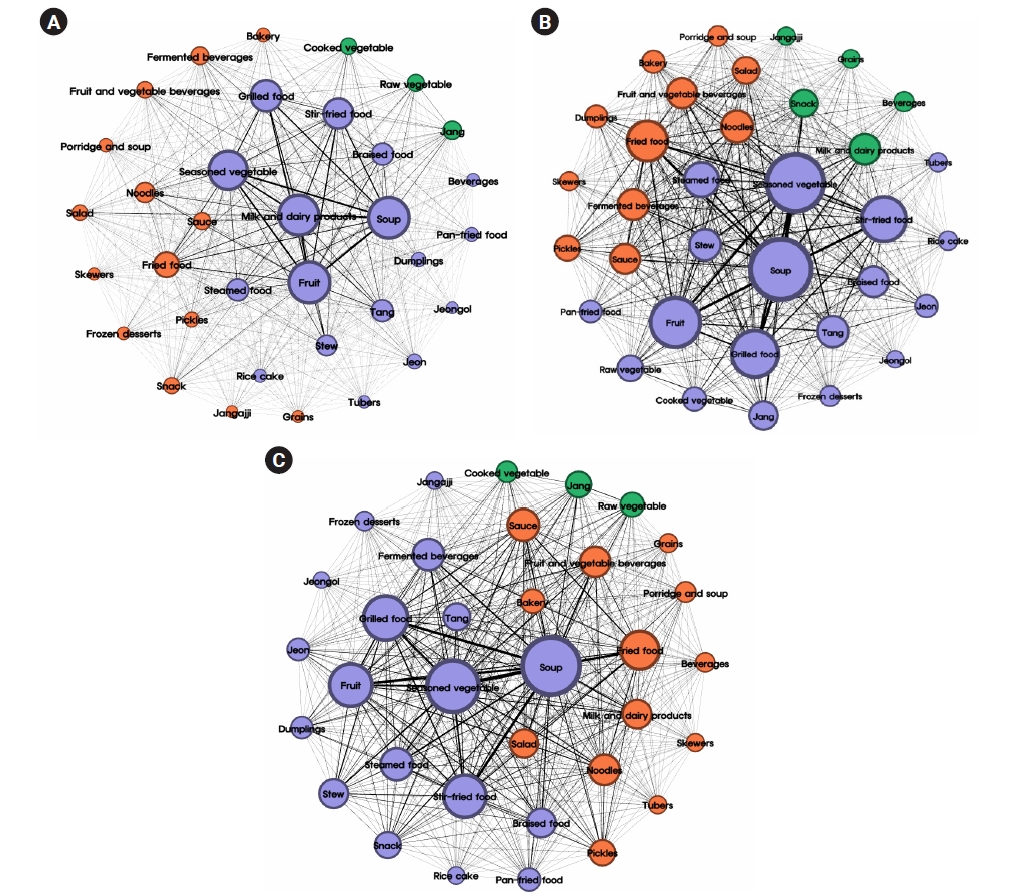
This study aimed to use big data from elementary, middle, and high school lunches to determine the primary food groups and menu items that contribute to lunch meals through text-mining and investigate the variations in food groups and menu composition patterns across different grade levels.
Methods
Between 2021 and 2023, a total of 7,892,456 lunch menus from 17 cities and provinces in South Korea were analyzed using big data from the National Education Information System (NEIS) system. After undergoing text preprocessing for text-mining, the collected menus were classified into 34 food groups based on primary ingredients and cooking methods, excluding the types of rice and kimchi. Subsequently, analyses of term frequency, term frequency-inverse document frequency (TF-IDF), centrality, and co-occurrence networks were performed on the food group and menu data.
Results
According to the TF-IDF, the most frequent food group across all grade levels was soup and seasoned vegetables, whereas milk was the most frequently provided menu. As the grade level increased, the frequency of grilled and fried food increased. In elementary schools, fruits exhibited the highest centrality, whereas soup had the highest centrality in middle and high schools. Co-occurrence frequency revealed that the soup-fruit combination was the most common in elementary schools, whereas soup and seasoned vegetables were most frequently paired in middle and high schools. The co-occurrence network of food groups and menus further indicated that menus regularly provided as standard meals and those frequently offered as special meals formed distinct communities.
Conclusion
This study investigated the food groups and menu provision patterns in school meals through text-mining techniques applied to large-scale school lunch. The findings may contribute in enhancing the quality of nutritional management, school foodservice, and menu composition of school meal programs.
- 1,514 View
- 50 Download

- [Korean]
- Impact of a public health center nutrition education program on patients with type 2 diabetes in a primary care-based chronic disease management project: a pilot intervention study
- Haerim Yang, Yoo Kyoung Park, Ji-hyun Lee, Hee-Sook Lim, Heejoon Baek, Hyejin Lee, Haeran Park, Pyunghwa Lee, Jooyoun Chung, Won Gyoung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(6):492-503. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00018
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
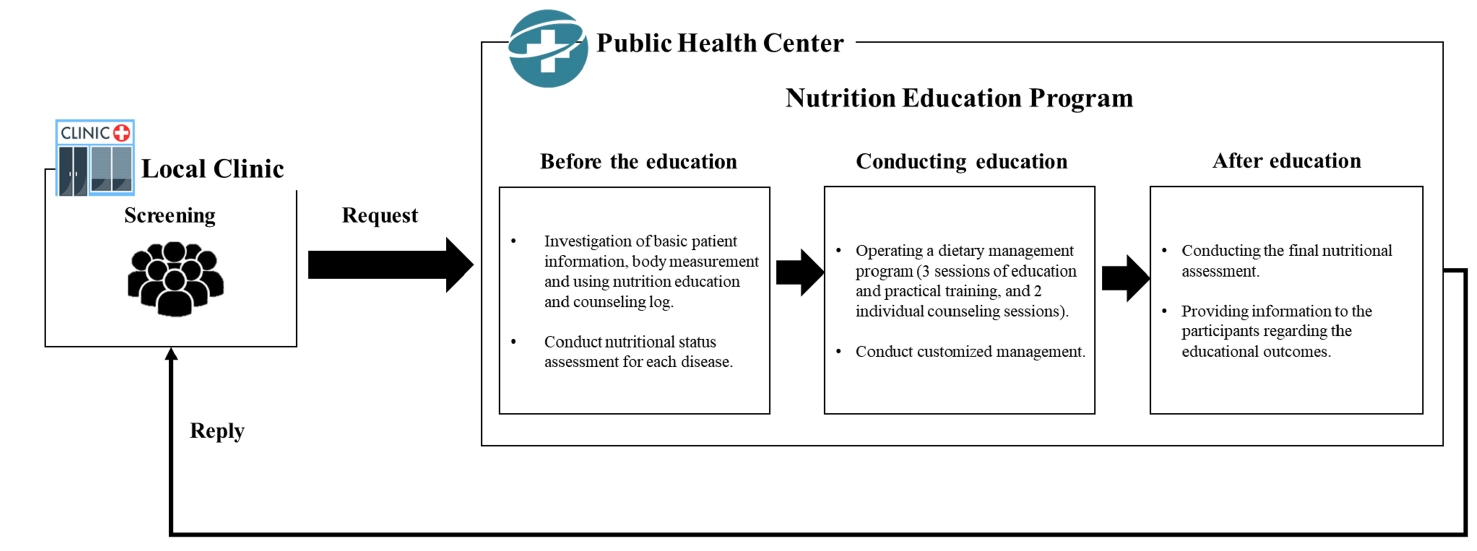
We investigated the impact of an advanced “Nutrition Education Program” on patients with Diabetes mellitus, type 2 from public health centers enrolled in a primary health care-based chronic disease management project. This 12-week dietary management program was developed by the Korea Health Promotion and Development Institute. We assessed if this program improved glycemic control and other health indicators through dietary and nutritional improvements.
Methods
Seventeen patients with Diabetes mellitus type 2 were enrolled in the “Nutrition Education Program.” These patients were referred to public health centers for lifestyle management based on physician assessments at local clinics that were participating in a pilot project on primary health care-based chronic disease management. The participants attended the program comprising face-to-face basic, in-depth, and practical training sessions at the health center during the third, fifth, and seventh weeks, respectively. Anthropometric measurements, body composition analysis, blood biochemical characteristics, nutritional knowledge, and self-efficacy evaluation were performed before and after the program. Data were analyzed using SPSS ver. 28.0.
Results
The mean age of the participants was 62 years, and most participants were female (14, 82.4%). No significant changes in patients’ anthropometric measurements or body composition were observed after the training. However, significant reductions were observed in the blood biochemical characteristics, including glycated hemoglobin, total cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein levels. Additionally, patients’ nutritional knowledge and self-efficacy scores increased significantly.
Conclusions
The “Nutrition Education Program” helped in improving glycemic control and other health indicators in patients with Diabetes mellitus type 2. Further research is required to objectively confirm the long-term and sustained effects of the program in a controlled study. Trial Registration Clinical Research Information Service Identifier: KCT0010010
- 1,825 View
- 74 Download

- [English]
- Effects of a nutrition education program on metabolic syndrome risk factors in middle-aged Korean adults: an intervention study
- Minji Kang, Young-Hee Park, Subeen Kim, Eunyoung Tak, Hyun Wook Baik, Hee Young Paik, Hyojee Joung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):265-277. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was conducted to evaluate the effects of a nutrition education program on metabolic syndrome in middle-aged Korean adults.
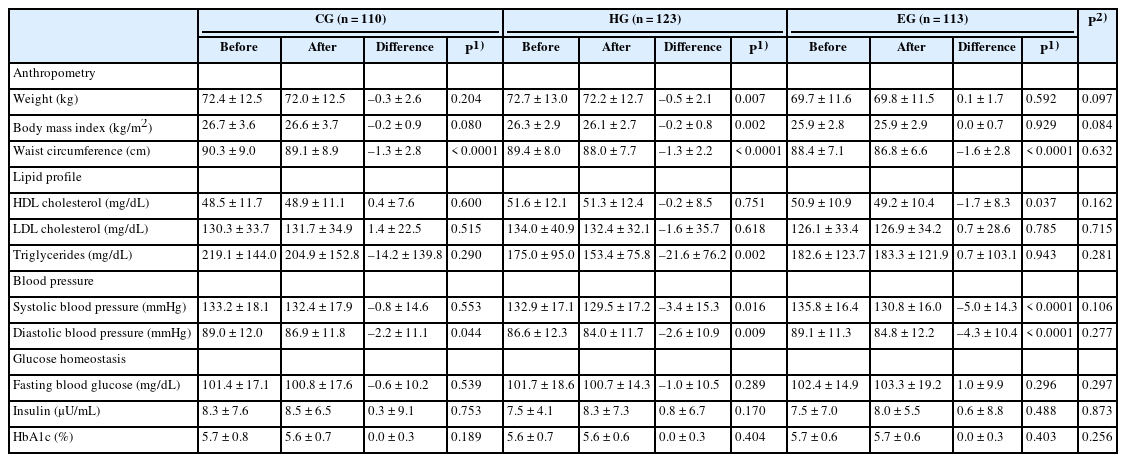
Methods
A total of 411 Korean adults 30–59 years of age were allocated randomly into three groups: the nutrition education group for promoting Han-sik consumption (HG), the nutrition education group for eating balanced diet (EG), and the control group (CG). The HG and EG received four face-to-face nutrition education sessions over 16 weeks to improve nutritional problems based on the individual’ usual diet. Effectiveness of the program was evaluated with the differences of self-reported dietary behaviors, dietary intakes, anthropometric measurements and biochemical indices between the baseline and the end of the nutrition education program. The changes within groups were analyzed using paired t-test and McNemar test and effectiveness among three groups was analyzed by repeated analysis of variance.
Results
After the nutrition education, the percentages of participants who achieved the recommended food group consumption in the Korean Food Guidance Systems significantly increased in HG (P = 0.022). Body weight (P = 0.007), body mass index (P = 0.002), and triglycerides (P = 0.002) significantly decreased in HG. Waist circumference and diastolic blood pressure decreased in all three groups (P < 0.05).
Conclusions
This study found that tailored nutrition education program for middle aged Korean adults showed beneficial effects on improving dietary behaviors and metabolic syndrome risk factors. Further studies are needed to assess the long-term effects of the nutrition education programs on metabolic syndrome risks.
- 3,532 View
- 80 Download

- [Korean]
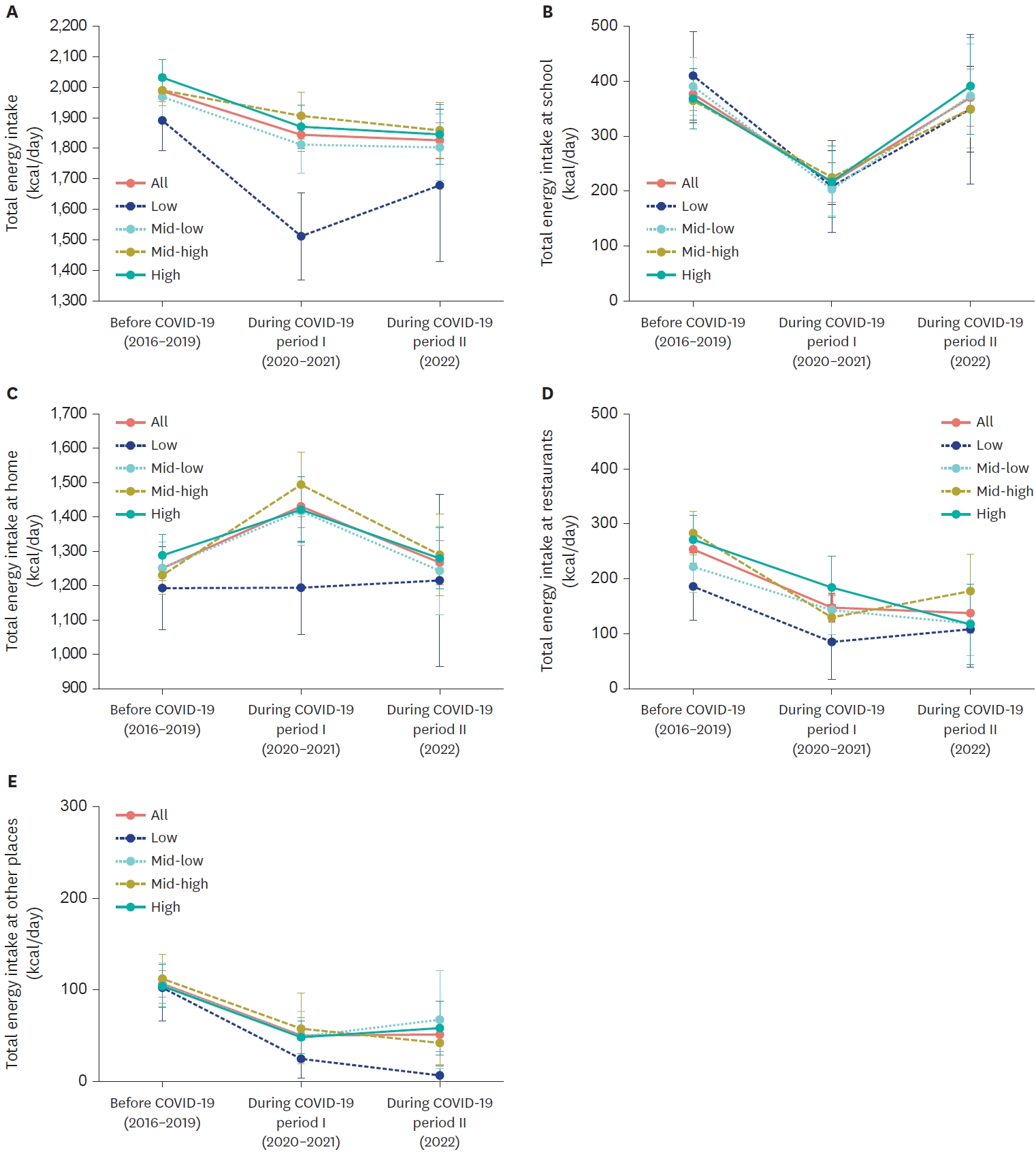
- Intake of energy and macronutrients according to household income among elementary, middle, and high school students before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: a cross-sectional study
- Chae-Eun Jeong, Heejin Lee, Jung Eun Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(3):234-252. Published online June 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.3.234
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the intake of energy and macronutrients among elementary, middle, and high school students according to household income before the COVID-19 pandemic (2016–2019), during the social distancing period (2020–2021), and after the social distancing measures were lifted (2022).
Methods
We included 5,217 students aged 5–18 from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) conducted between 2016 and 2022. Dietary intake was assessed using one-day 24-hour dietary recalls. We estimated the least squares means (LS-means) of intake according to household income for each period using a weighted linear regression model, adjusted for age and sex. Differences in LS-means between the periods were analyzed using the t-test.
Results
During the social distancing period, the LS-means of energy intake among students decreased significantly by 143.2 kcal/day compared to pre-pandemic levels (P < 0.001). Students from low-income households experienced a more pronounced decrease in energy intake (−379.1 kcal/day, P < 0.001) and macronutrient intake compared to those from other income groups. Energy intake at school significantly declined for all income groups during the social distancing period compared to before the pandemic. No significant changes in home energy intake were observed among low-income students, whereas there was an increase for students from higher-income groups. Before the pandemic, 8.5% of students from low-income households reported insufficient food due to economic difficulties; this figure rose to 21.3% during the pandemic.
Conclusions
During the pandemic, students from low-income families experienced significantly lower intake of energy and macronutrients compared to pre-pandemic levels. The most substantial reductions were noted among low-income students, largely due to the lack of compensation for decreased school-based intake with increased intake at home. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How Did the Dietary Behavior of Older Korean Adults Change During the COVID-19 Pandemic?
Yong-Seok Kwon, Dasol Kim, Hee-Sook Lim
Nutrients.2025; 17(12): 1973. CrossRef - Dietary Assessment of Older Korean Adults by Level of Plant Protein Intake
Yong-Seok Kwon, Ye-Jun Kim, Jeong-Hun Song, Yangsuk Kim
Nutrients.2025; 17(12): 1976. CrossRef - Analysis of Risk Factor Changes for Myopia in Korean Adolescents Before and After the COVID-19 Pandemic
Seeun Lee, So Ra Kim, Mijung Park
Medicina.2025; 61(10): 1798. CrossRef - Changes in Ultra-Processed Food Consumption among Adolescents before and after the COVID-19 Pandemic : Using Data from the 7th (2018~2019) and 8th (2020~2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hyun-Jin Hwang, Yoo Kyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2024; 33(6): 981. CrossRef
- How Did the Dietary Behavior of Older Korean Adults Change During the COVID-19 Pandemic?
- 2,457 View
- 104 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
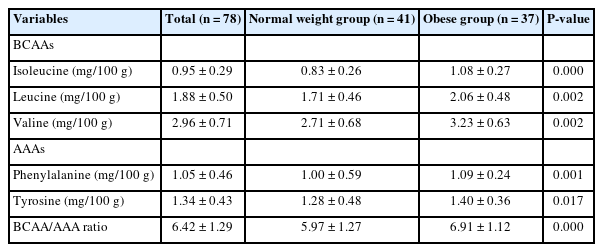
- Serum branch chain amino acids and aromatic amino acids ratio and metabolic risks in Koreans with normal-weight or obesity: a cross-sectional study
- Ji-Sook Park, Kainat Ahmed, Jung-Eun Yim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(3):212-221. Published online June 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.3.212
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Metabolic disease is strongly associated with future insulin resistance, and its prevalence is increasing worldwide. Thus, identifying early biomarkers of metabolic-related disease based on serum profiling is useful to control future metabolic disease. Our study aimed to assess the association of serum branched chain amino acids (BCAAs) and aromatic amino acids (AAAs) ratio and metabolic disease according to body mass index (BMI) status among Korean adults.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 78 adults aged 20–59 years in Korea. We compared serum amino acid (AA) levels between adults with normal-weight and adults with obesity and investigated biomarkers of metabolic disease. We examined serum AA levels, blood profile, and body composition. We also evaluated the association between serum AAs and metabolic-related disease.
Results
The height, weight, BMI, waist circumference, hip circumference, waist-hip-ratio, body fat mass, body fat percent, skeletal muscle mass, systolic blood pressure, and diastolic blood pressure were higher in the group with obesity compared to normal weight group. The group with obesity showed significantly higher levels of BCAA, AAA, and BCAA and AAA ratio. Further, BCAA and AAA ratio were significantly positively correlated with triglyceride, body weight, and skeletal muscle mass. The evaluation of metabolic disease risks revealed an association between the ratios of BCAAs and AAAs, hypertension, and metabolic syndrome.
Conclusions
Our study is showed the associations between BCAA and AAA ratio, obesity, and obesity-related diseases using various analytical approaches. The elevated BCAA and AAA ratio could be early biomarkers for predicting future metabolic diseases in Korean population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Role of Aromatic Amino Acids in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome through Patients’ Blood Metabolic Profiling: A Systematic Review of the Past Five Years
Apostolos Gkantzos, Stavros Kalogiannis, Olga Deda
Journal of Proteome Research.2025; 24(5): 2208. CrossRef - Current Data on the Role of Amino Acids in the Management of Obesity in Children and Adolescents
Diana Zamosteanu, Nina Filip, Laura Mihaela Trandafir, Elena Ţarcă, Mihaela Pertea, Gabriela Bordeianu, Jana Bernic, Anne Marie Heredea, Elena Cojocaru
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(15): 7129. CrossRef
- The Role of Aromatic Amino Acids in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome through Patients’ Blood Metabolic Profiling: A Systematic Review of the Past Five Years
- 1,730 View
- 23 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Association between dietary intake, body measurements, and urinary bone resorption markers in young adults with osteopenia and osteoporosis: a cross-sectional study
- Mi-Hyun Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(4):282-292. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.4.282
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Bone health in early adulthood, as individuals approach peak bone mass, plays a critical role in preventing osteoporosis later in life. This study aimed to investigate the associations between lifestyle and dietary factors, anthropometric measurements, and urinary bone resorption markers in young adults.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was conducted with 100 healthy Korean adults (50 men and 50 women) in their 20s and early 30s. Bone mineral density (BMD), anthropometric measurements, dietary intake (24-hour recall), and urinary bone resorption indicators (deoxypyridinoline and N-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen) were analyzed. Variables were compared between the osteopenia and osteoporosis groups (OSTEO group: 30% men and 60% women) and the healthy control group.
Results
Men in the OSTEO group were significantly taller than those in the control group (P < 0.05). Women in the OSTEO group had significantly lower body weight and body composition (muscle and body fat) than those in the normal group (P < 0.01). Men in the OSTEO group had a significantly higher intake of animal calcium (Ca) than those in the normal group (P < 0.05). Women in the OSTEO group had significantly higher dietary fiber, vitamin A, Ca, plant Ca, and potassium intake than did those in the normal group (P < 0.05). There were no significant differences in caffeinated beverage consumption, eating habits, or urinary bone resorption indicators between the OSTEO and control groups of either sex.
Conclusions
In our study of young South Korean adults, we observed low bone density levels, with particularly low BMD in taller men and underweight women. We found a higher nutrient intake in the OSTEO group, indicating the possibility of reverse causality, a phenomenon often found in cross-sectional studies. Therefore, there is a need to further elucidate dietary factors related to osteoporosis in young adults through prospective cohort studies involving a larger population.
- 926 View
- 17 Download

Review
- [English]
- Mercury exposure is associated with obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Jimin Jeon, Kyong Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(3):192-205. Published online June 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.3.192
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Previous studies have evaluated the association between mercury exposure and obesity but have yielded mixed conclusions. The aim of this study was to systematically review and summarize scientific evidence regarding the association between mercury exposure and obesity in the human population.
Methods
We conducted a systematic search of PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, and Science Direct for articles related to mercury exposure and obesity. Meta-analyses of the highest and lowest categories of mercury levels were evaluated using a random effects model. Begg’s test was used to detect publication bias.
Results
A total of 9 articles were included. The pooled random effects odds ratio (OR) for mercury exposure and obesity of all 9 studies was 1.66 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.16-2.38). This positive association was evident in adults (OR: 1.61, 95% CI: 1.02-2.54) and among studies with Asian populations (OR: 2.00, 95% CI: 1.53-2.59), but not among those with North America/African populations (OR: 0.90, 95% CI: 0.50-1.65).
Conclusions
The present meta-analysis identified a positive association between mercury exposure and obesity. These findings suggest that toxic environmental metals such as mercury may be an important risk factor for obesity along with dietary habits and lifestyles. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Re-thinking the link between exposure to mercury and blood pressure
Xue Feng Hu, Allison Loan, Hing Man Chan
Archives of Toxicology.2025; 99(2): 481. CrossRef - Associations of Metal Mixtures During Early Pregnancy With Midlife Obesity and Body Composition: A Prospective Study
Mingyu Zhang, Izzuddin M. Aris, Andres Cardenas, Sheryl L. Rifas‐Shiman, Pi‐I Debby Lin, Long H. Ngo, Emily Oken, Stephen P. Juraschek, Marie‐France Hivert
Obesity.2025; 33(10): 1984. CrossRef - Association Between Heavy Metals Exposure and Elevated High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein: Mediating Role of Body Mass Index
Seong-Uk Baek, Jin-Ha Yoon
Biomolecules.2025; 15(11): 1491. CrossRef - Association between heavy metal exposure and biomarkers for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Korean adolescents
Dong-Wook Lee, Jongmin Oh, Yu Min Lee, Hyun-Joo Bae, Youn-Hee Lim
Heliyon.2024; 10(19): e37840. CrossRef
- Re-thinking the link between exposure to mercury and blood pressure
- 2,318 View
- 65 Download
- 4 Crossref

Research Articles
- [English]
- Micronutrients and prevention of cervical pre-cancer in HPV vaccinated women: a cross-sectional study
- Chandrika J Piyathilake, Suguna Badiga, Nongnut Thao, Pauline E Jolly
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(1):61-73. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.1.61
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Prophylactic vaccines against high-risk human papillomaviruses (HR-HPVs) hold promise to prevent the development of higher grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN 2+) and cervical cancer (CC) that develop due to HR-HPV genotypes that are included in HPV vaccines, but women will continue to develop CIN 2+ and CC due to HR-HPV genotypes that are not included in the quadrivalent HPV vaccine (qHPV) and 9-valent HPV vaccine (9VHPV). Thus, the current vaccines are likely to decrease but not entirely prevent the development of CIN 2+ or CC. The purpose of the study was to determine the prevalence and determinants of CIN 2+ that develop due to HR-HPVs not included in vaccines.
Methods
Study population consisted of 1476 women tested for 37 HPVs and known to be negative for qHPVs (6/11/16/18, group A, n = 811) or 9VHPVs (6/11/16/18/31/33/45/52/58, group B, n = 331), but positive for other HR-HPVs. Regression models were used to determine the association between plasma concentrations of micronutrients, socio-demographic, lifestyle factors and risk of CIN 2+ due to HR-HPVs that are not included in vaccines.
Results
The prevalence of infections with HPV 31, 33, 35 and 58 that contributed to CIN 2+ differed by race. In group A, African American (AA) women and current smokers were more likely to have CIN 2 (OR = 1.76, P = 0.032 and 1.79, P = 0.016, respectively) while in both groups of A and B, those with higher vitamin B12 were less likely to have similar lesions (OR = 0.62, P = 0.036 and 0.45, P = 0.035, respectively).
Conclusions
We identified vitamin B12 status and smoking as independent modifiable factors and ethnicity as a factor that needs attention to reduce the risk of developing CIN 2+ in the post vaccination era. Continuation of tailored screening programs combined with non-vaccine-based approaches are needed to manage the residual risk of developing HPV-related CIN 2+ and CC in vaccinated women. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Relationship Between Metal Exposure and HPV Infection: Evidence from Explainable Machine Learning Methods
Huangyu Hu, Yue Wu, Jiaqi Liu, Min Zhao, Ping Xie
Biological Trace Element Research.2025; 203(4): 2206. CrossRef - The Impact of an Educational Program on Cervical Cancer Knowledge Among HIV-Positive Women in Bali, Indonesia
Desak Lestari, Ania Wellere, Ilene Brill, Ni Luh Sari, Pauline Jolly, Chandrika Piyathilake
International Journal of Women's Health.2024; Volume 16: 1677. CrossRef
- The Relationship Between Metal Exposure and HPV Infection: Evidence from Explainable Machine Learning Methods
- 1,444 View
- 15 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Comparison of the Nutrient Intake and Health Status of Elderly Koreans According to their BMI Status: Focus on the Underweight Elderly Population
- You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(5):422-434. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.5.422
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
With an increase in the population of the elderly in Korea, their nutritional status has become a cause for concern. This study was designed to compare the nutritional intake and health status of the Korean elderly according to their body mass index.
Methods
The subjects were 3,274 elderly people aged 65 and above who had participated in the 2016-2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. The subjects were divided into four groups: underweight, normal, overweight, and obese, based on their BMI. The general characteristics, daily energy, and nutrient intakes, nutrient intakes compared to the recommended nutrient intake, percentage of participants whose nutrient intake was lower than the estimated average requirement (EAR), index of nutrient quality, the mean adequacy ratio (MAR), intakes by food group, and health status of the four groups were compared.
Results
Underweight elderly people showed lower energy, lipids, dietary fiber, vitamin C, riboflavin, niacin, phosphorus, sodium, and potassium intake and MAR score (P < 0.001) compared to the normal or obese elderly. The mean protein, riboflavin, niacin, vitamin C, phosphorus, and iron intake of the underweight elderly was lower than the EAR (P < 0.05). Underweight elderly people also had a lower intake of vegetables and fats, oil and sweets food groups than the other groups (P < 0.001). The prevalence of diabetes and dyslipidemia was higher in the obese group, but the percentage of anemia was higher in the underweight group.
Conclusions
Underweight elderly people were vulnerable to undernutrition and were at a higher risk of anemia. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring the Association Between Older Adults’ Body Mass Index and Their Fall Experience, Chronic Diseases, and Exercise Frequency: Evidence from Korea
Daekeun Kwon, Su-Yeon Roh, Jeonga Kwon
Medicina.2025; 61(9): 1622. CrossRef - Effect of physical activity on free fatty acids, insulin resistance, and blood pressure in obese older women
Woo-Hyeon Son, Min-Seong Ha, Tae-Jin Park
Physical Activity and Nutrition.2024; 28(2): 1. CrossRef - Determinants of Length of Stay for Medical Inpatients Using Survival Analysis
Jaekyeong Kim, Haegak Chang, Seiyoung Ryu, Ilyoung Choi, Angela Eunyoung Kwon, Haeyong Ji
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2024; 21(11): 1424. CrossRef - The Relationship of Pork Meat Consumption with Nutrient Intakes, Diet Quality, and Biomarkers of Health Status in Korean Older Adults
Ah-Jin Jung, Anshul Sharma, Mei Chung, Taylor Wallace, Hae-Jeung Lee
Nutrients.2024; 16(23): 4188. CrossRef
- Exploring the Association Between Older Adults’ Body Mass Index and Their Fall Experience, Chronic Diseases, and Exercise Frequency: Evidence from Korea
- 2,738 View
- 49 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Investigation of Millennials' Perception of Vegan Trends and Future Needs
- Eun-Hye Song, Bok-Mi Jung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(5):373-386. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.5.373
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the perception of the vegan trend of millennials and their future needs.
Methods
This study was conducted online from June 21, 2021, to July 15, 2021, targeting 425 adult men and women born between 1980 and 2000. The contents of the survey were divided into four categories: general information, awareness of vegetables, awareness of vegan trends, and future needs for vegan trends.
Results
Most respondents recognized the importance of eating vegetables and perceived vegetarianism and veganism as a lifestyle. Regarding the perception of the vegan trend, the highest response rate was ‘The vegan trend is to be satisfied with my life regardless of other people’, while the lowest response rate was ‘The vegan trend is only a temporary fad’. The reasons for purchasing vegan products with high response rates were ‘interest in the earth and environment’, ‘protection of animal rights’, and ‘thinking about health’. The type of vegan product wanted in the future was delicious food, and convenience level was in the order of ‘completely cooked’, ‘half-cooked’, and ‘pre-processed’. Among the sustainable vegetarian types that millennials responded, ‘semi-vegetarian’, which can consume most animal products excluding red meat, showed the highest response rate.
Conclusions
The positive perceptions about vegetables are expected to increase. Efforts should be made to develop convenient meals using vegetables and provide reasonable prices to expand vegetable intake. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Towards a non-speciesist social life cycle assessment
Stefan Mann, Sebastian Richter, Melf-Hinrich Ehlers, Andreas Roesch, Melanie Douziech
The International Journal of Life Cycle Assessment.2025; 30(10): 2248. CrossRef - Quality properties of defatted rice bran extract powder and vegan cookies
A-Young Lee, Hyun-A An, Seung-Bin Han, Eun-Ju Cho, Hye-Jeong Kim, Dong-Jin Moon, Jeung-Hee Lee
Food Science and Preservation.2024; 31(6): 865. CrossRef - 코퍼스를 활용한 한국 사회 10년 비건 패션, 뷰티 변화 분석
소미 강, 하연 장, 주연 장
Journal of the Korean Society of Clothing and Textiles.2023; 47(4): 625. CrossRef
- Towards a non-speciesist social life cycle assessment
- 1,459 View
- 47 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Dietary Behaviors Associated with Health Perception of Korean Adolescents from Multicultural Families: based on data from the 2017 ~ 2019 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Surveys
- YueRong Hu, SuJin Song
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(3):192-204. Published online June 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.3.192
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the association between dietary behaviors and perceived health status among Korean adolescents from multicultural families.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 2,459 Korean adolescents from multicultural families (aged 13 ~ 18 years) who participated in the 2017 ~ 2019 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Surveys. Information on the sociodemographic variables, dietary behaviors, and lifestyle variables was selfreported using a web-based questionnaire. The dietary behaviors analyzed in this study were the breakfast and food intake frequencies, including fruit, vegetable, milk, fast food, carbonated drink, sweet drink, and high caffeine/energy drinks. The adolescents’ health perception was self-rated as healthy, average, or unhealthy. The dietary behaviors associated with health perception were examined using a multiple logistic regression after adjusting for the confounding variables.
Results
In this study population, 7.6% of adolescents perceived their health status as unhealthy, and 25.4% perceived it as average. The adolescents who were girls, middle school students, and in households with a low economic status showed significantly higher percentages of poor health perception (P-values < 0.001). Skipping breakfast was significantly associated with a negative health perception. Compared to the adolescents who consumed fruits every day, those who did not consume fruits during the previous week showed a higher odd ratio (OR) for a negative health perception [OR = 2.29, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.32–3.97]. The adolescents who frequently consumed carbonated drinks ( 5 times/week) perceived their health status as unhealthy relative to those who did not consume carbonated drinks (OR = 2.15, 95% CI = 1.25–3.71). Skipping breakfast was significantly associated with an increased OR for a negative health perception in girls but not in boys. Compared to adolescents with a normal weight, those with overweight/ obesity (OR = 1.75, 95% CI = 1.21–2.52) and underweight (OR = 2.19, 95% CI = 1.25–3.82) showed higher ORs for negative health perception. Positive associations of overweight/obesity and underweight with negative health perception were observed in boys but not in girls.
Conclusions
Dietary behaviors and weight status were associated with the health perception in Korean adolescents from multicultural families. These findings suggest that nutrition interventions on breakfast intake and healthy food choices for this population might effectively improve their weight and perceived health status. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The unequal weight of COVID-19 pandemic: national trends in body mass index among Korean adolescents by immigrant-origin and gender from 2013 to 2022
Nari Yoo, Yumin Hong, Yoonyoung Choi
International Journal of Adolescence and Youth.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- The unequal weight of COVID-19 pandemic: national trends in body mass index among Korean adolescents by immigrant-origin and gender from 2013 to 2022
- 984 View
- 19 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- A Study on the Dietary and Lifestyle Changes of Middle-Aged Women in the Gwangju Area in the COVID-19 Era
- Moon-Soon Kim, Bok-Mi Jung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(4):259-269. Published online August 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.4.259
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate the changes in the eating habits and lifestyle of middle-aged women in Gwangju during the COVID-19 pandemic. Methods: A total of 428 middle-aged women aged between 40 and 60 participated in a survey relating to general information, food and lifestyle, health functional food, and menopausal symptoms. The correlation between the variables was analyzed. Results: In the positive habits, the intake of nutritional supplements for immunity enhancement increased the most, followed by the use of media to learn healthy eating tips, and diets including healthy food. Negative habits increased in the order of frequency of taking delivery orders, levels of stress or anxiety, and time spent sitting or watching movies. In the case of recommended foods, the intake increased the most in the order of eggs, fruits, vegetables, milk/dairy products, and seaweed. Non-recommended foods increased in the order of meat, bread, rice, and noodles. The awareness of health functional foods was in the increasing order of interest, knowledge, consumption experience, and purchase amount. The type of health functional food intake was in the increasing order of probiotics, multivitamin and mineral supplements, vitamin C, collagen, and omega-3. Menopausal symptoms were in the increasing order of bone and joint pain, poor sleep quality, emotional ups and downs, loneliness, and feeling of emptiness. In the correlation of major variables, positive habits showed a significant positive correlation with recommended food intake and the recognition of health functional foods. Negative habits showed a significant positive correlation with non-recommended food intake and a significant positive correlation with menopausal symptoms. Recommended food intake showed a significant positive correlation with health functional food recognition and intake and menopausal symptoms. Conclusions: This study suggests that it is necessary to establish social measures to reduce the negative effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on middle-aged women and to ensure effective self-management through a healthy lifestyle since the pandemic has a long-term impact. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Barley-Based Cereals Enhance Metabolic Health and Satiety in Overweight Korean Adults: A Randomized Trial
Ingyeong Kang, Hyunsook Jang, Minchul Gim, Sang Eun Bae, Yu Jin Lee, Chai Sun Leem, Yoo Kyoung Park
Nutrients.2025; 17(17): 2801. CrossRef - Comparative study on the health and dietary habits of Korean male and female adults before and after the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic: utilizing data from the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019–2021)
Chaemin Kim, Eunjung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(1): 65. CrossRef - Quality Characteristics of Staple Breads Based on Baking Methods
Eun-Hee Doo
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(1): 77. CrossRef - Changes in Ultra-Processed Food Consumption among Adolescents before and after the COVID-19 Pandemic : Using Data from the 7th (2018~2019) and 8th (2020~2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hyun-Jin Hwang, Yoo Kyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2024; 33(6): 981. CrossRef - Dietary guidelines adherence and changes in eating habits among college students in the post-COVID-19 period: a cross-sectional study
Eunyoung Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(3): 220. CrossRef - Changes in dietary habits and chronic diseases before and after COVID-19 by regions using data from the 2018-2020 Korea Community Health Survey and Consumer Behavior Survey for Foods: a cross-sectional study
Surim Park, Eun-hee Jang, Seungmin Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(2): 124. CrossRef - 광주광역시 지역민의 영양교육 요구도 조사 분석
은평 양, 경윤 김, 승희 최, 금비 류, 옥경 김, 정미 윤
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(2): 100. CrossRef - Consumers’ perceptions of dietary supplements before and after the COVID-19 pandemic based on big data
Eunjung Lee, Hyo Sun Jung, Jin A Jang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(3): 330. CrossRef - Self-rated health according to change of lifestyle after COVID-19: Differences between age groups
Dan Bi Lee, Jung Hyun Ahn, Jin Young Nam
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2022; 39(2): 1. CrossRef - Factors Related to Changes of Daily Life during COVID-19
Kyungjin Min, Pilhan Yun, Sangshin Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2022; 47(4): 297. CrossRef - Dietary Behavior and Diet Quality in the Korean Adult Population by Income Level before and after the COVID-19 Pandemic: Using the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019-2020)
Hye-Min Na, Bok-Mi Jung
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2022; 33(3): 397. CrossRef
- Barley-Based Cereals Enhance Metabolic Health and Satiety in Overweight Korean Adults: A Randomized Trial
- 1,176 View
- 10 Download
- 11 Crossref

- [English]
- Vegetable and Nut Food Groups are Inversely Associated with Hearing Loss- a Cross-sectional Study from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Sunghee Lee, Jae Yeon Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(6):512-519. Published online December 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.6.512
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
A cross-sectional study was conducted to investigate the associations between food groups and hearing loss. Methods: Data of 1,312 individuals were used from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013. Hearing loss was determined with a pure tone average (PTA) of greater than 25 dB in either ear. The PTA was measured as the average hearing threshold at speech frequencies of 0.5, 1, 2, and 4 kHz. The dietary intake was examined with a food frequency questionnaire with 112 food items. The food items were classified into 25 food groups. A weighted logistic regression was used to investigate the association. Results: Individuals in the highest tertile of vegetables and nuts food groups were less likely to have hearing loss than those in the lowest tertile [Odds Ratio (OR) = 0.58 (95% Confidence interval (CI) 0.38-0.91), P = 0.019; OR = 0.59 (95% CI 0.39-0.90), P = 0.020, respectively], after adjusting for confounding variables of age, sex, body mass index, drinking, smoking, diabetes, hypertension, and physical activity. Conclusions: In this cross-sectional study, we observed that high intake of vegetables and nuts food groups revealed significant inverse associations with hearing loss, after adjusting for confounding variables among 1,312 participants.
- 737 View
- 2 Download

- [English]
- Biochemical Characteristics and Dietary Intake according to the Frequency of Milk Consumption in Korean Adolescents: Data from the 2010~2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Ji Hyun Kim, Sook-Bae Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(6):485-501. Published online December 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.6.485
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to examine the biochemical characteristics and dietary intake of adolescents aged 12 to 18 years according to the frequency of milk consumption. Methods: Data from the 2010~2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey was used for the study. The study examined adolescents’ (12~18 years) demographic characteristics (house income level, residence region, skipping or not-skipping of breakfast/lunch/dinner, eatingout frequency), anthropometric characteristics (height, weight, weight status), biochemical characteristics (fasting plasma glucose, blood urea nitrogen, creatine, triglycerides, cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, hemoglobin, hematocrit) and nutrient intakes through quantitative and qualitative evaluation using the Korean Dietary Reference Intakes (KDRI), index of nutrition quality (INQ), nutrition adequacy ratio (NAR) of 3 groups (< 1/week, 1~6/week, 1/day) according to the frequency of milk consumption. Results: There were significant differences in gender and income levels among the 3 groups. There were no differences in height, weight, and weight status among groups. There were differences in biochemical characteristics and nutrient intake. In boys, there were differences in the mean of BUN and HDL-cholesterol, in quantitative intakes of riboflavin, calcium, phosphorus, potassium by KDRI levels, in qualitative intakes of riboflavin, calcium, phosphorus by INQ and riboflavin, calcium, phosphorus by NAR among 3 groups. In girls, there were differences in the mean of blood urea nitrogen, creatine, HDL-cholesterol, in quantitative intakes of protein, riboflavin, calcium, phosphorus by KDRI levels, in qualitative intakes of riboflavin, calcium, phosphorus by INQ and riboflavin, calcium, phosphorus by NAR among the 3 groups. Conclusions: In Korean adolescents, boys had a higher frequency of milk consumption than girls, and higher the income level, higher the frequency of milk consumption. Consumption of milk appeared to have a positive association with triglycerides, HDL-cholesterol, and indices related to muscle mass. Regular consumption of milk is an important factor in enhancing the intake of riboflavin, calcium, and phosphorus, which adolescents lack. The results of the study indicate a need to prepare an environment and education program to increase milk consumption in adolescents at home and school. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Changes in Nutritional Status Through Low-Lactose Processed Milk Consumption in Korean Adults With Lactose Intolerance
Dong Hoon Jung, Gi Moon Nam, Chang Kyun Lee, Chul hong Kim, Hyun-San Lim, Ji Yeon Lee, Hee-Sook Lim
Clinical Nutrition Research.2025; 14(1): 30. CrossRef - Analysis of Dietary Behavior and Quality in Children and Adolescents with Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Using the Korean Nutrition Quotient Score
So Yoon Choi, Yoowon Kwon, Yoo Min Lee, In Hyuk Yoo, Tae Hyeong Kim, You Jin Choi, Su Jin Jeong
Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition.2025; 28(4): 256. CrossRef - Biochemical characteristics, nutrient intakes, and chronic disease risk according to the dietary fat energy ratio in middle-aged Korean: a cross-sectional study using data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Ga-Hyeon Jeong, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 528. CrossRef - Biochemical Characteristics and Dietary Intake according to Household Income Levels of Korean Adolescents: Using Data from the 6th (2013 ~ 2015) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yu-Kyeong Kwon, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(6): 467. CrossRef
- Changes in Nutritional Status Through Low-Lactose Processed Milk Consumption in Korean Adults With Lactose Intolerance
- 1,011 View
- 5 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Evaluation of Nutritional Status of Vitamins and Minerals According to Consumption of Dietary Supplements in Korean Adults and the Elderly: Report Based on 2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
- Ji-Myung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(4):329-339. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.4.329
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF
Objective
This study was undertaken to evaluate the intake of vitamins and minerals from dietary supplements (DSs) in Korean adults and elderly.
Methods
Data for this study was generated from the 2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). We analyzed 4,204 individuals aged 19 years and older (2,579 users and 1,625 non-users). The survey included 24-h recall questions on food and DS intakes, as well as questions on DS use over the past year. The nutrient DSs evaluated were calcium, phosphorus, iron, vitamin A, thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, and vitamin C. Total nutrient intakes were obtained by combining nutrient intakes of foods and DSs consumed by each subject.
Results
Most micronutrient intakes from food (except for thiamin) in adult users, and the four micronutrient intakes (iron, vitamin A, vitamin B2 and vitamin C) in elderly users, were significantly higher than values obtained in non-users. For total intake of nutrients and DSs, both adult and elderly users had a significantly higher intake than non-users. While proportions below Estimated Average Requirements for all micronutrients by adding respective DSs in users were significantly reduced in adults and elderly as compared to non-users, the proportions of above Tolerable Upper Intake Levels for calcium and vitamin A in adults, and vitamin A in elderly, were significantly increased. In the total subjects examined, consumption of DSs was associated with lower odds ratios of undernutrition of micronutrients, and with higher odds ratios of overnutrition of calcium, iron, and vitamin A, as compared to non-users of DSs.
Conclusions
Although DSs consumption by adults and the elderly improves the micronutrient status, it also increases the risk of excessive intake of certain vitamins and minerals.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship between self-care and health-related behaviors among Korean adults: a cross-sectional study
EunJung Lee, Jin A Jang, Ji-Myung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(2): 103. CrossRef - Folate intake in Korean adults: analysis of the 2016–2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey with newly established folate database
Eun-Ji Park, Inhwa Han, Kyoung Hye Yu, Sun Yung Ly
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(4): 418. CrossRef - Effect of Dietary Supplements on Vitamin and Mineral Intake Among Koreans: Data From the 2018-2020 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Moon Yeong Hwang, Jiyoun Hong
Food Supplements and Biomaterials for Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Estimated dietary vitamin D intake and major vitamin D food sources of Koreans: based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2016–2019
Ki Nam Kim, Jung-Sug Lee, Jee-Seon Shim, Mi Ock Yoon, Hyun Sook Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(3): 451. CrossRef - A Study on the Dietary Behavior of Korean Adults: Focus on Dietary Supplement Intake, Household Size, and COVID-19
Jinkyung Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(6): 468. CrossRef
- Relationship between self-care and health-related behaviors among Korean adults: a cross-sectional study
- 1,641 View
- 9 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Effect of Nutrition Counseling by Nutrition Care Process on Diet Therapy Practice and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
- Tae-Jeong Bae, Na-Eun Jeon, Soo-Kyong Choi, Jung-Sook Seo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(3):214-225. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.3.214
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the effects of nutrition counseling by the nutrition care process (NCP) on diet therapy practice and glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods
The survey was conducted on 49 patients whose hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) level ranged from 6.5% to below 10% among patients aged 30∼60s with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nutrition counseling by the NCP process was carried out twice: first nutrition counseling and follow up counseling. The questionnaires were composed of 54 questions in five fields (general characteristics, health-related behaviors, diet therapyrelated items, dietary life, diet therapy-related knowledge, diet therapy-related barriers). Nutrition intervention in nutrition counseling was performed based on the individualized diagnosis of NCP.
Results
All the subjects practiced self-monitoring of their blood glucose levels, regular exercise, and diet therapy after NCP-based nutrition counseling. Diet therapy-related knowledge and practice by the subjects were improved after nutrition counseling. While the intake of boiled white rice decreased, the intake of boiled brown rice and barley rice in the subjects increased significantly. After nutrition counseling, the weight and HbA1c of the subjects decreased.
Conclusions
These results suggest that personalized nutrition counseling by NCP process is effective for diet therapy compliance and glycemic control of type 2 diabetic patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutrition education programs necessary for social welfare facilities for persons with disabilities: a cross-sectional study
Jinkyung Kim, Min-Sun Jeon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(1): 1. CrossRef - Effect of Health educational intervention in the form of counseling on changes in anthropometric and biochemical parameters of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Dijana Stantić-Romić, Hajnalka Požar, Sanja Šumonja
Sestrinska rec.2023; 26(86): 17. CrossRef - The association between nutrition label utilization and disease management education among hypertension or diabetes diagnosed in Korea using 2018 Community Health Survey: a cross-sectional study
Miran Jin, Jayeun Kim, Kyuhyun Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(1): 38. CrossRef
- Nutrition education programs necessary for social welfare facilities for persons with disabilities: a cross-sectional study
- 1,258 View
- 52 Download
- 3 Crossref

Original Articles
- [English]
- Comparison of 24-hour Recalls with a Food Frequency Questionnaire in Assessing Coffee Consumption: The Health Examinees (HEXA) Study
- An Na Kim, Jiyoung Youn, Hyun Jeong Cho, Taiyue Jin, Sangah Shin, Jung Eun Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(1):48-60. Published online February 29, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.1.48
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Most cohort studies used food frequency questionnaires (FFQ) to evaluate coffee consumption as it assesses habitual dietary patterns, whereas some studies have used the 24-hour recalls (24HR) as it elicits in-depth description of foods and the amount eaten. The aim of this study was to compare FFQs and 24HR to assess the consumption of various types of coffee.
METHODS
We included 25,904 participants aged 40 years or older from the Health Examinees (HEXA) Study of the Korean Genome and Epidemiologic Study (KoGES). Each participant completed one FFQ and one-day (n=11,280) or two-day 24HR (n=14,624). We classified coffee types into: black coffee, coffee with sugar and cream, and coffee with sugar alone or cream alone. We compared the proportions of nondrinkers, black coffee, and coffee with sugar and cream through FFQ and 24HR.
RESULTS
Among those who completed one FFQ and one-day 24HR, 39.4% of “nondrinkers†on one-day 24HR reported that they did not drink coffee on their FFQs. Whereas among those who complete two-day 24HR, 71.2% of “nondrinkers†on two-day 24HR said that they did not drink coffee on their FFQs. Among those who completed one FFQ and oneday 24HR, 58.3% marked “black coffee†on one-day 24HR said that they drank black coffee on their FFQs. Among those who complete two-day 24HR, 58.8% marked “black coffee†on two-day 24HR said that they drank black coffee on their FFQs. The kappa coefficients and percent agreements were 0.4 and 59.6%, respectively, for the comparison of coffee intake between FFQ and one-day 24HR, and 0.6 and 72.8%, respectively, for the comparison of coffee intake between FFQ and two-day 24HR.
CONCLUSIONS
We found discrepancies between FFQs and 24HR in the types of coffee consumed. Such limitations should be considered when using the 24HR data to examine the effect of coffee consumption on disease development. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research Trends and Future Perspectives on Epigenetic Regulation of Food-derived Components for the Prevention of Chronic Diseases
Seon Kyeong Park, Jin-Taek Hwang
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2025; 54(4): 301. CrossRef - Association Between Instant Coffee Consumption and the Development of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Results From a Community-Based Prospective Cohort
Moon-Kyung Shin, Kyoung-Nam Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Genetic variation rs1121980 in the fat mass and obesity-associated gene (FTO) is associated with dietary intake in Koreans
Young Goh, Jeong-Hwa Choi
Food & Nutrition Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Coffee Consumption and the Risk of All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality in the Korean Population
Seong-Ah Kim, Li-Juan Tan, Sangah Shin
Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics.2021; 121(11): 2221. CrossRef
- Research Trends and Future Perspectives on Epigenetic Regulation of Food-derived Components for the Prevention of Chronic Diseases
- 1,746 View
- 46 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Effects of Low-carbohydrate and High-fat Diet Supplemented with Ketogenic Drink on Cognitive Function and Physical Performance in the Elderly at High Risk for Dementia
- Eun Ji Kim, Jung Sik Park, Won Sun Choi, Yoo Kyoung Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(6):525-534. Published online December 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.6.525
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Reduced glucose utilization in the main parts of the brain involved in memory is a major cause of Alzheimer's disease, in which ketone bodies are used as the only and effective alternative energy source of glucose. This study examined the effects of a low-carbohydrate and high-fat (LCHF) diet supplemented with a ketogenic nutrition drink on cognitive function and physical activity in the elderly at high risk for dementia.
METHODS
The participants of this study were 28 healthy elderly aged 60-91 years showing a high risk factor of dementia or whose Korean Mini-Mental State Examination (K-MMSE) score was less than 24 points. Over 3 weeks, the case group was given an LCHF diet with nutrition drinks consisting of a ketone/non-ketone ratio of 1.73:1, whereas the control group consumed well-balanced nutrition drinks while maintaining a normal diet. After 3 weeks, K-MMSE, body composition, urine ketone bodies, and physical ability were all evaluated.
RESULTS
Urine ketone bodies of all case group subjects were positive, and K-MMSE score was significantly elevated in the case group only (p=0.021). Weight and BMI were elevated in the control group only (p<0.05). Grip strength was elevated in all subjects (p<0.01), and measurements of gait speed and one leg balance were improved only in the case group (p<0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
We suggest that adherence to the LCHF diet supplemented with a ketogenic drink could possibly influence cognitive and physical function in the elderly with a high risk factor for dementia. Further, we confirmed the applicability of this dietary intervention in the elderly based on its lack of any side effects or changes in nutritional status. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- To Keto or Not to Keto? A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials Assessing the Effects of Ketogenic Therapy on Alzheimer Disease
Maria G Grammatikopoulou, Dimitrios G Goulis, Konstantinos Gkiouras, Xenophon Theodoridis, Kalliopi K Gkouskou, Athanasios Evangeliou, Efthimis Dardiotis, Dimitrios P Bogdanos
Advances in Nutrition.2020; 11(6): 1583. CrossRef
- To Keto or Not to Keto? A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials Assessing the Effects of Ketogenic Therapy on Alzheimer Disease
- 1,148 View
- 10 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Home Meal Replacement Use and Eating Habits of Adults in One-Person Households
- Mi Kyeong Choi, Eun Sun Park, Mi Hyun Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(6):476-484. Published online December 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.6.476
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The rise of one-person households may have consequences for food consumption patterns, and eating habits. This study investigated the home meal replacement (HMR) use and eating habits among adults in their 20s-30s living in one-person households.
METHODS
A total of 247 adults aged 26–39 years participated in this study. The subjects were divided into three group according to the household type; one-person households (n=80), two-person households (n=49), and multi-family (three and more members) households (n=118). Their use of HMRs (classified as ready-to-eat, ready-to-cook, and fresh convenience foods) and their eating habits were all compared.
RESULTS
The mean age of the subjects was 30.5 years, 47.8% were male, and there was no significant difference in age, gender, occupation, and monthly income according to the type of household. The intake frequency of total HMR and ready-to-eat foods was significantly higher in one-person households among the three groups. People in one-person households consumed more HMRs alone, and spent more money to buy HMRs. Undesirable dietary habit scores like unbalanced eating (p<0.05) and eating salty foods (p<0.05) were significantly higher in the one-person households. Among the total subjects, the unbalanced eating scores showed a significant positive correlation with the intake frequency of ready-toeat foods, while the unbalanced eating scores showed negative correlation with the preference of fresh convenience foods. The scores for eating salty foods showed a significant positive correlation with the intake frequency and preference of ready-to-eat foods and ready-to-cook foods, while there was negative correlation with the intake frequency and preference of fresh convenience foods.
CONCLUSIONS
Adults in their 20s–30s in one-person households consumed more ready-to-eat foods than those in multi-family households. In addition, people with one-person households had more unbalanced diets and ate more salty foods, and these undesirable eating habits showed a significant positive correlation with the use of ready-to-eat or ready-to-cook foods. These results should be addressed for producing healthier ready-to-eat/ready-to-cook foods and implementing nutrition education for making healthy food choices of one-person households, which are steadily increasing. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Understanding the charactersitics and types of single-person households based on food purchase frequencies in Korea: a cross-sectional study using the 2023 Consumer Behavior Survey for Foods
So-Yun Kim, Youngmin Nam, Jong-Youn Rha, Haerang Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(1): 27. CrossRef - Application of a living lab model to an evidence-based reduced-sodium healthy eating practice program in Korea: a pre-post study
Jung-Hyun Kim, Eugene Shim, Min Sook Kyung, Sooyoun Kwon, Hyoung su Park, Jae-Heon Kang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(1): 53. CrossRef - Dietary status and the relationship between dietary competencies, cooking skills, and nutrition quotient of middle-aged adults living alone in Korea
Sooyoun Kwon, Youngmi Lee, Yun-Jung Bae
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(2): 257. CrossRef - Maternal home meal replacement use and attitudes, and young children’s preferences by usage frequency in meals for young children: a cross-sectional study
Bo-Yeon Kim, Mi-Hyun Kim, Jee-Young Yeon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(2): 163. CrossRef - Comparative study on eating habits and health of single-person and multi-person households
Haerang Lee, Seon-Jip Kim, Minji Kang, Mi-So Shim
PLOS One.2025; 20(7): e0327763. CrossRef - Eating behaviors, home meal replacement consumption, and nutrition quotient: a comparative study of male shift and non-shift workers in Chungcheong, Korea
Yeon Jin Lee, Munkyong Pae
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(5): 758. CrossRef - 가정간편식 수산 제품 인식정도에 따른 가정간편식 수산 제품 이용실태 조사
정은 이, 복미 정
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2024; 40(4): 284. CrossRef - Diabetes Nutritional Management for Single-Person Households
Min Young Noh
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2024; 25(4): 236. CrossRef - Development of Functional Material by Using Bacillus
subtilis Harboring α-Amylase and Protease
Enzyme Activity
Jae-Hyuk Lee, Gi-Seong Moon
Current Topic in Lactic Acid Bacteria and Probiotics.2023; 9(2): 81. CrossRef - The frequency of convenience food consumption and attitude of sodium and sugar reduction among middle and high school students in Seoul: a descriptive study
Seoyeon Park, Yeonhee Shin, Seoyeon Lee, Heejung Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(4): 269. CrossRef - Problems Encountered in Analyzing the Market Size, Purchase, and Consumption of HMR in the Republic of Korea
Sung Ok Kwon, Injoo Choi, Yoojeong Joo, Jihyun Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(6): 480. CrossRef - Qualities of rice-based home meal replacement products upon
microwave cooking
Gi-Un Seong, Yu Mi Kim, Jun-Hyeon Cho, Ji-Yoon Lee, Sais-Beul Lee, Dongjin Shin, Dong-Soo Park, Kwang-Sup Youn, Ju-Won Kang
Korean Journal of Food Preservation.2022; 29(5): 715. CrossRef - Comparison of Dietary Behaviors and the Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Single- and Multi-Person Households among Korean Adults
Kyung Won Lee, Dayeon Shin
Healthcare.2021; 9(9): 1116. CrossRef - Relationship between Eating Behavior and Healthy Eating Competency of Single-Person and Multi-Person Households by Age Group
Seung-Hee Hong, Ji-Myung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 337. CrossRef - Analysis of Contamination of Total Aerobic Bacteria and Foodborne
Pathogens in Home Meal Replacement (HMR) and the Importance of Food Hygiene
Management
Hyun Jin Cho, Jeeyeon Lee
Resources Science Research.2021; 3(2): 63. CrossRef - Studies of Selection Attributes for Lunch Boxes (Dosirak) Using Conjoint Analysis among Single Men
A Reum Han, Sung Suk Chung, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2021; 50(8): 884. CrossRef - Healthy Eating Capability of One-person Households-The Effects of Eating Alone, Meal Types, and Dietary Lifestyles
Seonglim Lee, Ilsook Choi, Junghoon Kim
Family and Environment Research.2020; 58(4): 483. CrossRef
- Understanding the charactersitics and types of single-person households based on food purchase frequencies in Korea: a cross-sectional study using the 2023 Consumer Behavior Survey for Foods
- 1,400 View
- 13 Download
- 17 Crossref

- [English]
- Dietary and Lifestyle Factors Associated with Weight Status among Korean Adolescents from Multicultural Families: Using Data from the 2017–2018 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Surveys
- SuJin Song, Hyojune Song
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(6):465-475. Published online December 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.6.465
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study investigated dietary and lifestyle factors associated with the weight status among Korean adolescents in multicultural families.
METHODS
This cross-sectional study analyzed 1,751 multicultural families' adolescents who participated in the 2017–2018 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Surveys. Information on dietary and lifestyle factors was self-reported using a web-based questionnaire and this information included breakfast and foods consumption, perceived health status, alcohol drinking, smoking, physical activity, and weight control efforts. Body mass index (BMI) was calculated based on the self-reported height and body weight (kg/m²). Weight status was assessed according to the 2017 Korean National Growth Chart: underweight (weight-for-age <5(th) percentiles), overweight (85(th)≤ BMI-for-age <95(th) percentiles), and obese (BMI-for-age ≥95(th) percentiles). Multiple logistic regression analysis was performed to examine the dietary and lifestyle factors associated with weight status after adjustment for covariates.
RESULTS
Among Korean adolescents from multicultural families, the prevalence of overweight/obesity was 20.9%, whereas about 7% of adolescents were underweight. The weight status did not show differences according to gender, school level, area of residence, and household income. Compared to adolescents who did not have breakfast during the previous week, those who had breakfast 3–4 days/week and ≥5 days/week had a 42% (p=0.021) and a 37% (p=0.009) lower prevalence of overweight/obesity, respectively. The adolescents who frequently consumed carbonated soft drinks (≥5 times/week) showed an odds ratio (OR) of 1.69 (95% CI=1.01–2.83) for overweight/obesity relative to those adolescents who did not consume carbonated soft drinks. The OR of being underweight for adolescents who ate fast food ≥3 times/week was 1.97 (95% CI=1.04–3.71) compared to those adolescents who had not eaten fast food during the previous week.
CONCLUSIONS
Dietary and lifestyle factors were associated with overweight/obesity as well as underweight among Korean adolescents in multicultural families. Our findings could be used to design and provide nutrition interventions for this specific population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence of Malnutrition and Obesity Among Children and Adolescents From Immigrant Families Living in Korea
Seong-Woo Choi, So-Yeong Kim, Kyung-Ae Park
Journal of Korean Maternal and Child Health.2025; 29(1): 29. CrossRef - Fruit Consumption and Mental Health in Adolescents from Multicultural and Non-multicultural Families: Data from Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web Based Survey 2021
Soohyun Kim, Jeong-Hwa Choi, Young-Ran Heo
Human Ecology Research.2025; 63(2): 175. CrossRef - Identification of important features in overweight and obesity among Korean adolescents using machine learning
Serim Lee, JongSerl Chun
Children and Youth Services Review.2024; 161: 107644. CrossRef - Dietary Behaviors Associated with Health Perception of Korean Adolescents from Multicultural Families: based on data from the 2017 ~ 2019 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Surveys
YueRong Hu, SuJin Song
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(3): 192. CrossRef - Effects of heavy metal, vitamin, and curry consumption on metabolic syndrome during menopause: a Korean community-based cross-sectional study
Hai Duc Nguyen, Min-Sun Kim
Menopause.2021; 28(8): 949. CrossRef - Association between levels of thiamine intake, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases and depression in Korea: a national cross-sectional study
Hai Nguyen Duc, Hojin Oh, In Mo Yoon, Min-Sun Kim
Journal of Nutritional Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Antioxidant Vitamins, Curry Consumption, and Heavy Metal Levels on Metabolic Syndrome with Comorbidities: A Korean Community-Based Cross-Sectional Study
Hai Nguyen Duc, Hojin Oh, Min-Sun Kim
Antioxidants.2021; 10(5): 808. CrossRef - Study on the Dietary Behavior of Adolescents in Multicultural Families Using the Nutrition Quotient and Their Changes in the Nutrition Knowledge and the Dietary Attitudes after Nutrition Education
Yoo-Jin Jung, Sung Hee Min, Min June Lee
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2020; 30(3): 208. CrossRef
- Prevalence of Malnutrition and Obesity Among Children and Adolescents From Immigrant Families Living in Korea
- 1,398 View
- 5 Download
- 8 Crossref

- [English]
- Relationship between Dietary Behaviors and Life Stress of Middle School Students in Gyeonggi Area
- Kyung Ae Park, Myoung Sook Lee, Kyung Hee Song
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(5):384-394. Published online October 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.5.384
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The study was performed to examine the dietary behaviors and life stress of middle school students in the Gyeonggi area.
METHODS
A total of 580 middle school students (295males, 285 females) in the Gyeonggi area participated in the study between July and August in 2011. The study was a questionnaire-based survey that included dietary habits, dietary behaviors, and life stress.
RESULTS
For dietary habits, the score for drinking milk was higher in male students than in female students, whereas the score for eating fruits was higher in female students compared to male students. There were significant differences in foods eaten and preferred under stress between male and female students. Male students showed significantly less changes in the number of meals, amount of meal intake, number of snacks, snack intake, frequency of overeating, and appetite during stress than female students. Life stress score of students largely came from academic factors, and female students showed higher stress levels in personal and surrounding environment factors than male students. Life stress score was significantly lower in students with high and moderate levels of dietary habits than in students with a low level of dietary habits. Total score for dietary habits and scores for eating adequate amounts of foods for each meal, considering a combination of food groups at each meal and eating green and orange vegetables, were significantly negatively correlated with life stress score. Life stress score was significantly negatively correlated with meal regularity and positively with the level of overeating.
CONCLUSIONS
This study may provide basic information on dietary habits and life stress according to gender and the relationship between dietary behaviors and life stress of middle school students, and it suggests gender-based nutrition education programs to solve undesirable dietary habits and dietary behaviors in students with higher stress. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Study on the Eating Out Behavior and the Status of Meal Delivery and Take-Out Consumption according to the Food-related Lifestyles of Adolescents : Using the Consumption Behavior Survey for Food in 2020
Eun Jung Lee, Hyeon Min Yang, Yeong Ju Lee, Sun A Choi, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(4): 284. CrossRef - Life stress, dietary attitudes, and frequency of snack intake for college students in Seoul and Gyeonggi area: the difference between male and female students
Hyun Seung Oh, Yu bin Kim, Soyoung Park, Kyunghee Song
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(1): 91. CrossRef
- Study on the Eating Out Behavior and the Status of Meal Delivery and Take-Out Consumption according to the Food-related Lifestyles of Adolescents : Using the Consumption Behavior Survey for Food in 2020
- 1,046 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Comparison Analysis of Dietary Behavior and Nutrient Intakes of the Elderly according to Their Family Status: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013–2016
- Ji Hong Oh, Bok Mi Jung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(4):309-320. Published online August 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.4.309
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was undertaken to compare dietary life of the elderly living alone and in a family, and to compare differences based on gender, for the 2013-2016 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES).
METHODS
The subjects included 2,612 elderly people aged over 65 years who participated in the health survey, health examination and nutrition survey. Subjects on a diet therapy were excluded. This study analyzed the general characteristics, dietary habits, daily energy and nutrient intakes, CPF ratio, estimated average requirement (EAR), nutrient adequacy ratio (NAR) and mean adequacy ratio (MAR), index of nutrient quality (INQ), and food consumption of the elderly living alone and in a family. We also compared the differences based on gender.
RESULTS
Daily intake of food, water, dietary fiber, potassium, retinol, and riboflavin were low in the male elderly subjects living alone. The elderly living with family revealed higher NAR and MAR as compared to the elderly living alone. Although all MAR values were <1, the elderly living alone had lower values. Considering the intake of food, the consumption of seaweed, fish and shellfish, and oils (animal) was higher in elderly men living with families, whereas women living with families consumed more vegetables, fruits, seaweeds and seafood, as compared to their counterparts living alone. Furthermore, analyzing the foods consumed by the elderly people living alone, female subjects consumed more seaweed, milk and animal oil as compared to male subjects.
CONCLUSIONS
The results of this study indicate that the elderly living alone have poor nutrient intake as compared to the elderly living with families. Based on this research data, we recommend that it is necessary to improve the health and nutritional status of the elderly living alone. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Food insecurity and its associated characteristics of the elderly in Seoul: analysis of the data from the Seoul Food Survey 2023
Hyunjeong Park, Youngmin Nam, Linxi Huang, Youngmi Lee, Jihyun Yoon
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(1): 117. CrossRef - Profiling the socioeconomic characteristics, dietary intake, and health status of Korean older adults for nutrition plan customization: a comparison of principal component, factor, and cluster analyses
Kyungsook Woo, Kirang Kim
Epidemiology and Health.2024; 46: e2024043. CrossRef - Evaluation on the Nutrition Quotient Scores of Elderly People Living Alone in Korea
Gyoungok Gang, Min Lee, Eun-hui Choi, Hye-Lim Lee, Hyun-Young Lee, Hye-Ja Chang, Jung-Hwa Choi, Na-Young Yi, Kyung-Eun Lee, Min-Jae Chung, Tong-Kyung Kwak
Nutrients.2023; 15(17): 3750. CrossRef - Changes in nutritional status of Korean older adults during COVID-19 Pandemic by household income and demographic factors-using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey(2019-2020): a cross-sectional study
You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(4): 302. CrossRef - Comparison of the Nutrient Intake and Health Status of Elderly Koreans According to their BMI Status: Focus on the Underweight Elderly Population
You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(5): 422. CrossRef - Comparison of the health and nutritional status of Korean elderly considering the household income level, using the 2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jin Mo Khil
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(1): 39. CrossRef - Social participation, health‐related behavior, and depression of older adults living alone in Korea
Seojin Won, Hyemee Kim
Asian Social Work and Policy Review.2020; 14(1): 61. CrossRef - Evaluation of the dietary quality and nutritional status of elderly people using the Nutrition Quotient for Elderly (NQ-E) in Seoul
Sun-Wook Ham, Kyung-Hee Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(1): 68. CrossRef - Health and Nutrition Status of Elderly People with Multimorbidity: A Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2013~2015)
Na-Gyeong Oh, Jung-Sook Seo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(6): 502. CrossRef
- Food insecurity and its associated characteristics of the elderly in Seoul: analysis of the data from the Seoul Food Survey 2023
- 1,280 View
- 14 Download
- 9 Crossref

- [English]
- Dietary Life, Vitamin D Status and Blood Clinical Indices of University Laboratory Workers
- Jung Hyun Hwang, Hong Mie Lee, Jung Hee Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(3):245-256. Published online June 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.3.245
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Although the number of laboratory workers is constantly increasing every year, few studies have been conducted on the health and nutritional status of these research workers. This study determined the health status of laboratory workers by analyzing their anthropometric indices, dietary life, vitamin D status and blood clinical indices.
METHODS
The subjects consisted of 100 female laboratory workers. This study investigated their diet, anthropometric indices, vitamin D status and blood clinical indices. The subjects were divided into two groups according to their duration of working in a laboratory (<1 year,≥1 year).
RESULTS
The average age and body mass index (BMI) of subjects were 23.18 years and 21.51 kg/m2, respectively Those subjects with over 1 year employment (≥1 year) had a significantly higher waist-hip ratio than that of the subjects with the less than 1 year employment (<1 year). The mean serum vitamin D level of all the subjects was 10.04 ng/mL, which is close to a level of vitamin D deficiency. There was a significantly higher average intake of calories in the over 1 year employment group as compared to that of the less than 1 year employment group. The frequency of eating sweet snacks was significantly higher for the over 1 year employment group. The correlation analysis showed a significant positive correlation between the serum 25-(OH)-vitamin D level and the time of exposure to sunlight, while dietary intake of vitamin D did not show correlation with the serum 25-(OH)-vitamin D level. However, the serum 25-(OH)-vitamin D level was also negatively correlated with both the percentage of body fat and visceral fat.
CONCLUSIONS
Laboratory workers are a very high risk group in terms of their nutritional status of vitamin D. Therefore, they need greater time of exposure to sunlight as well as increasing their dietary consumption of vitamin D. In addition, it is important for laboratory worker to practice regular and balanced dietary habits in order to maintain a healthy life.
- 803 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Evaluation of the Nutrition Status and Metabolic Syndrome Prevalence of the Members according to the Number of Household Members based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2013–2014)
- Jin Young Lee, Soo Kyong Choi, Jung Sook Seo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(3):232-244. Published online June 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.3.232
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study evaluated the nutritional status and prevalence of metabolic syndrome of the people who participated in the KNHANES according to the number of household members. They were assessed by using information from the 2013~2014 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES).
METHODS
A total of 6,088 persons aged 19 years and over participated in 2013~2014 KNHANES, and they were classified into three groups according to the number of household members (single-person, two-person, three-person & over). The dietary behavior, nutritional status, health-related factors and the prevalence of metabolic syndrome of the subjects were investigated with using information from the survey questionnaires of KNHANES. The nutrient intake data of the subjects were obtained by the 24-hour recall method and this was analyzed for evaluating the nutrition adequacy ratio and the index of nutritional quality. The prevalence of metabolic syndrome among the subjects, and according to the study groups, was estimated using the blood and physical measurement data of the subjects.
RESULTS
As for EQ-5D index available for all the health states generated by the EQ-5D descriptive system, the single-person household member was the lowest among all the household types. The index of nutrition quality for protein, crude fiber, calcium, phosphorus, potassium, riboflavin and vitamin C in the single-person household was lower than that of the two-person or the three-person and over households (p<0.001). The mean adequacy ratio of single-person households was significantly decreased compared with that of the other types of households (p<0.001). The prevalence of metabolic syndrome was higher in the single-person households than that in the multiple-person households (p<0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
These results showed that dietary behaviors, nutrition status and health status might be influenced by the number of household members. The results from this study would be useful for improving Korean people's dietary life and health status by implementing evidence-based, specialized intervention for the members of diverse types of households. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary Behaviors and Health Status by Income Level in Single-Adult Households in Korea: An Analysis of Data From the 2016-2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Min-Hee Han, Bok-Mi Jung, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Clinical Nutrition Research.2025; 14(1): 55. CrossRef - Understanding the charactersitics and types of single-person households based on food purchase frequencies in Korea: a cross-sectional study using the 2023 Consumer Behavior Survey for Foods
So-Yun Kim, Youngmin Nam, Jong-Youn Rha, Haerang Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(1): 27. CrossRef - Beyond Individual Integration: Family Systems, Social Support Networks and Living Environment as Health Determinants Among Migrants in Germany
Franziska Reinhardt, Imad Maatouk
Journal of Migration and Health.2025; : 100368. CrossRef - Comparison of Food and Nutrient Intake according to the Income Level in Korean Adult Single-Person Households: Using Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016-2018)
Min-Hee Han, Bok-Mi Jung
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2024; 35(3): 445. CrossRef - Higher Animal-Based Protein Intake Levels Show a Greater Likelihood of Having Metabolic Syndrome in Single-Person Households Among Korean Adults
Yeongin Lee, Hyojee Joung
Nutrients.2024; 16(23): 4239. CrossRef - The association of the Korean Healthy Eating Index with chronic conditions in middle-aged single-person households
EunJung Lee, Ji-Myung Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(2): 316. CrossRef - Analysis of Agrifood Consumer Competency and Dietary Satisfaction according to Household Type Using the Consumer Behavior Survey for Food
Meera Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(4): 414. CrossRef - An analysis of customer needs for the operation of unmanned food stores on a university campus
Se-Eun Kim, Min-Seo Park, Hyun-Joo Bae
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(5): 587. CrossRef - Assessment of Nutrient Intake and Dietary Quality of Korean Adults in Metabolic Syndrome Patients According to Taking Medical Care: Based on the 2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Juhee Lee, Kyungsuk Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(4): 321. CrossRef - Relationships of Dietary Factors with Obesity, Hypertension, and Diabetes by Regional Type among Single-Person Households in Korea
Kyung Won Lee, Dayeon Shin
Nutrients.2021; 13(4): 1218. CrossRef - Living Environment Considerations on Obesity Prevention Behaviors and Self-Efficacy among Chinese Americans
Doreen Liou, Jessica A. Karasik
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(17): 9322. CrossRef - The Relationship between Meal Regularity and Oral Health and Metabolic Syndrome of Adults in Single Korean Households
Jin-Ah Jung, Hye-Won Cheon, On-Ju Ju
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2021; 21(3): 185. CrossRef - Association of Household Income Level with Vitamin and Mineral Intake
Haegyu Oh, Juyeon Kim, Yune Huh, Seung Hoon Kim, Sung-In Jang
Nutrients.2021; 14(1): 38. CrossRef - Nutritional status and metabolic syndrome risk according to the dietary pattern of adult single-person household, based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yu Been Keum, Qi Ming Yu, Jung-Sook Seo
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(1): 23. CrossRef - Home Meal Replacement Use and Eating Habits of Adults in One-Person Households
Mi-Kyeong Choi, Eun-Sun Park, Mi-Hyun Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(6): 476. CrossRef - Comparison of Dietary Behavior of Eating Alone in Single Households by Status of Workers and Age
Pil Kyoo Jo, Yu Jin Oh
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(5): 408. CrossRef
- Dietary Behaviors and Health Status by Income Level in Single-Adult Households in Korea: An Analysis of Data From the 2016-2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,174 View
- 8 Download
- 16 Crossref


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



