Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [English]
- Associations between diet quality and regional factors in Korea vary according to individuals’ characteristics: a cross-sectional study
- Hyunmi Han, Clara Yongjoo Park, Jeonghwa Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(4):274-285. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00157

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
Although diet quality is known to be associated with environment and individuals’ characteristics, these have not been studied together. We determined the association of diet quality with regional factors stratified by individuals’ sociodemographic characteristics.
Methods
This study used nationally representative survey data on regional factors (2010–2020) and the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data on individuals’ sociodemographic characteristics (2013–2018). Community-dwelling Koreans aged ≥ 20 were included (n = 26,853). Regions were categorized into metropolitan cities or provinces and subsequently according to regional factors (level of educational attainment, income per capita, food security status, physical activity facilities, time to the nearest large retailer, and internet use of the region). Individuals’ sociodemographic characteristics included age, education status, income, and number of household members. Diet quality was assessed using the Korean Healthy Eating Index (KHEI).
Results
In the entire population, education status of metropolitan cities was positively associated with the KHEI. Shorter time to retailers and higher internet use were positively associated with the KHEI in metropolitan residents with higher income levels but negatively associated with the KHEI in those with lower income status. Among provincial residents with a low education status or income, regional physical activity facilities were positively associated with the KHEI.
Conclusion
The association between diet quality and regional factors varied depending on the resident’s sociodemographic characteristics. Both regional and individual sociodemographic factors must be considered to address gaps in nutritional equity.
- 920 View
- 20 Download

- [English]
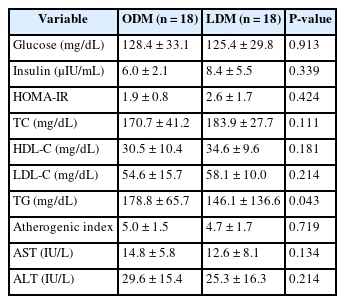
- Comparison of clinical characteristics and dietary intakes according to phenotypes of type 2 diabetes mellitus in South Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Mi-Jin Kim, Ji-Sook Park, Sung-Rae Cho, Daeung Yu, Jung-Eun Yim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):127-139. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00059
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Clinical nutrition treatment is the central part of diabetes management, such as prevention, treatment, and self-management of diabetes, and personalized clinical nutrition treatment, which enables improvement in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Our study aimed to contribute to the improvement of appropriate nutrition management in personalized treatment for obese and non-obese diabetes patients.
Methods
T2DM patients were recruited as participants, and 36 final participants were assigned to the lean diabetes mellitus group (LDM; body mass index [BMI] < 25 kg/m2) and the obese diabetes mellitus group (ODM; BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2). We assessed the dietary intakes, body composition, dietary habits, the Korean version of obesity-related quality of life, and biochemical indices.
Results
According to the phenotype’s comparison, the ODM group had a high prevalence of T2DM complications and hypertension, had a dietary habit of less than 10 minutes of mealtime duration and preferred fast food intake, and had a low obesity-related quality of life. However, the LDM group had a high choice of Korean dishes at the time of eating out and a high intake of vitamin C, and iodine because of the intake of vegetables and seaweeds.
Conclusion
We observed differences in diet, nutrient intake, and clinical characteristics according to the phenotype of T2DM patients. In particular, obese diabetes patients have an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, bad dietary habits, and low obesity-related quality of life. Therefore, personalized nutrition treatment is needed in consideration of the risk of cardiovascular disease and dietary habits for patients in the ODM group, as well as determining the energy requirements of Korean patients with T2DM.
- 1,363 View
- 31 Download

Original Article
- [English]
- The Characteristics of Infants' Temperament, Maternal Feeding Behavior and Feeding Practices in Picky Eaters
- Yoon Jung Kim, Sang Jin Chung, Young Shin Han, Yoonna Lee, Sang Il Lee, Ki Won Byun, Haymie Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2005;10(4):462-470. Published online August 31, 2005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to determine the characteristics of infants' temperaments, maternal feeding behaviors and feeding practices in picky eaters. Participants were 83 infants (aged 12 - 24 months) from "A" hospital (Seoul) and "B" public health center (Kyunggido). Mothers completed questionnaires that assessed their own feeding behavior, feeding practices, infants' temperament and infants' feeding behavior. Picky eaters' demographics were not significantly different from non-picky eaters after adjusting sex and age. The average of thiamin, niacin and vitamin E intakes of picky eaters were below 75% Korean RDA, whereas vitamin A intakes exceed 120% RDA in both groups. Activity level of infants' temperament and disinhibition of maternal feeding behavior in picky eaters were significantly higher than those in non-picky eater. All constructs of infants feeding behavior were significantly associated with certain constructs of infants' temperament, maternal feeding practice and maternal feeding behavior. The pickiness of infants feeding behavior was positively correlated with activity level of infants' temperament, pickiness and disinhibition of maternal feeding behavior and negatively correlated with adaptability of infants' temperament. Findings suggest that maternal feeding behavior and feeding practices as well as infants' temperament should be addressed in nutrition education for picky eaters.
- 228 View
- 1 Download


 KSCN
KSCN
 First
First Prev
Prev



