Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [English]
- Relationship between self-care and health-related behaviors among Korean adults: a cross-sectional study
- EunJung Lee, Jin A Jang, Ji-Myung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):103-113. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00255

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study investigated the relationship between self-care and health-related behaviors such as medication use, dietary supplementation, dietary habits, and physical activity among Koreans aged 20–60 years.
Methods
Data from a total of 300 participants (150 men and 150 women) living in Seoul and Gyeonggi provinces in Korea were analyzed to assess the relationship between health behaviors and dietary supplements (DSs) related to self-care. Based on self-care levels, the participants were classified into three groups: low (LS, n = 124), medium (MS, n = 78), and high (HS, n = 98).
Results
DSs (P < 0.001), physical activity (P < 0.001), recognizing the perceived health benefits of self-care (P < 0.001), self-care when sick (P = 0.039), and the reasons for self-care (P = 0.028) differed among the self-care groups. Daily diet frequency (P = 0.001), breakfast frequency (P = 0.026), regular exercise (P < 0.001), DSs use rate (P < 0.001), DSs use frequency (P = 0.013), and total dietary behavior score (P < 0.001) also differed significantly depending on the degree of self-care. The degree of self-care was significantly and positively correlated with DSs intake (r = 0.377, P < 0.001), physical activity (r = 0.433, P < 0.001), and total dietary behavior score (r = 0.185, P < 0.01).
Conclusion
The results demonstrated that the degree of self-care was related to DSs, physical activity, and total dietary behavior scores in Korean adults. Additionally, self-care capacity should be increased through health-related behaviors based on health education programs.
- 968 View
- 47 Download

- [English]
- Eating habits and dietary supplement utilization according to food-related lifestyle among Korean adults: a cross-sectional study
- EunJung Lee, Jin A Jang, Ji-Myung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):253-264. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
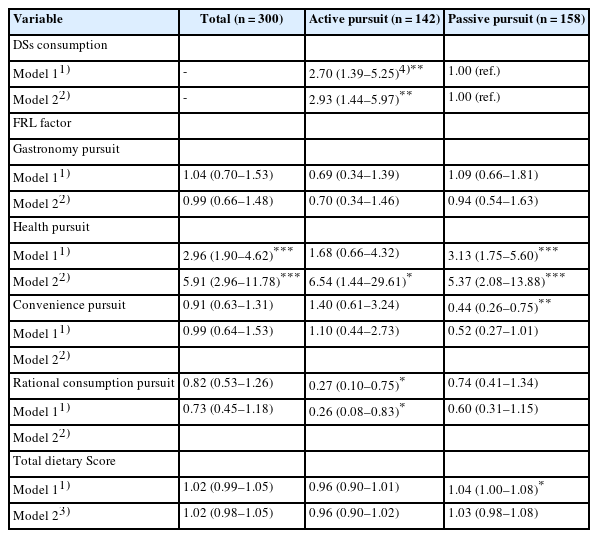
This study investigated the association between eating habits and the utilization of dietary supplements (DSs) according to food-related lifestyle (FRL) among Korean adults. Methods: This study included a total of 300 participants (150 men and 150 women) in their 20s to 60s living in Seoul and Gyeonggi Province. We identified two groups by factor and cluster analysis: an ‘active pursuit’ group and a ‘passive pursuit’ group. Differences in eating habits and DS utilization between the two groups were analyzed by chi-square test and t-test. Logistic regression analysis was used to analyze the effect of variables on DS consumption according to FRL. Results: There were significant differences between the two groups in terms of age, alcohol drinking frequency, total dietary score, change in DS consumption after coronavirus disease 2019, and current DS consumption (P < 0.05). The proportion who perceived many health benefits of DSs was higher in the ‘active pursuit’ group than in the ‘passive pursuit’ group (P = 0.003). The most commonly consumed type of DSs was multivitamins & minerals for the ‘active pursuit’ group, and omega-3 fatty acids for the ‘passive pursuit’ group. The ‘an active pursuit’ group consumed DSs 2.93 times more (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.44–5.97) compared to the ‘passive pursuit’ group, after adjusting for confounders. In the ‘active pursuit’ group, the health pursuit (odds ratio [OR] = 6.54, 95% CI: 1.44– 29.61) and rational consumption pursuit factors (OR = 0.26, 95% CI: 0.08–0.83) were associated with DS consumption, whereas only the health pursuit factor had a significant association (OR = 5.37, 95% CI: 2.08–13.88) within the ‘passive pursuit’ group. However, total dietary score and DSs consumption did not show a relationship. Conclusions: By understanding the consumption characteristics of DSs according to FRL, this can serve as basic data necessary for promoting health through the utilization of DSs and healthy behaviors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Discovering Vitamin-D-Deficiency-Associated Factors in Korean Adults Using KNHANES Data Based on an Integrated Analysis of Machine Learning and Statistical Techniques
Hongryul Ahn, Seungwon Kim, Jinmyung Jung, Chan Park
Nutrients.2025; 17(4): 618. CrossRef
- Discovering Vitamin-D-Deficiency-Associated Factors in Korean Adults Using KNHANES Data Based on an Integrated Analysis of Machine Learning and Statistical Techniques
- 2,510 View
- 85 Download
- 1 Crossref


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



