Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Article
- [Korean]
- Maternal home meal replacement use and attitudes, and young children’s preferences by usage frequency in meals for young children: a cross-sectional study
- Bo-Yeon Kim, Mi-Hyun Kim, Jee-Young Yeon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):163-172. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00066
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
With the increase in women’s workforce participation and changing family eating habits, home meal replacements (HMRs) have become more prevalent. However, research on how mothers incorporate HMR into meals of young children remains limited. This study examined mothers’ attitudes toward and use of HMR, as well as their association with young children’s HMR preferences.
Methods
A survey was conducted between June 1 and July 3, 2020, involving 337 mothers of 5-year-old children in Sejong, South Korea. The questionnaire assessed mothers’ perceptions of HMR, consumption patterns, and their children’s preferences for HMR.
Results
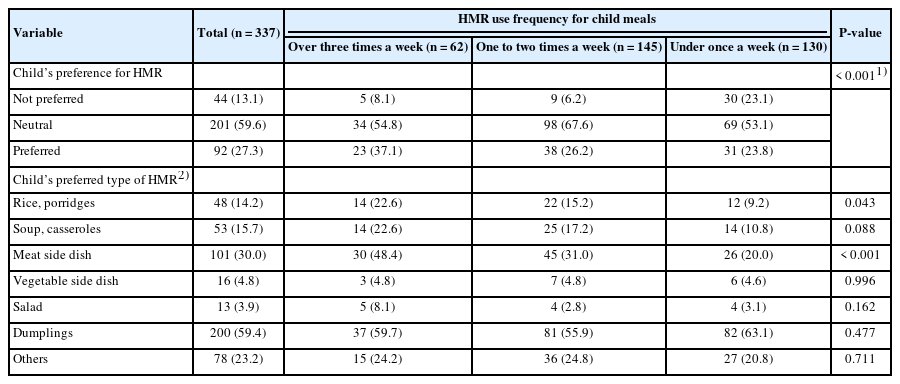
The average age of participating mothers was 38.3 years, with 93.2% living in nuclear families. Full-time homemakers constituted 40.1% of the respondents and showed lower HMR usage among them. HMR was primarily consumed as late-night snacks, side dishes, and dinners, with large discount stores (81.6%) being the primary purchase location. The high HMR consumption group exhibited more positive attitudes toward HMR (P < 0.001). HMR types varied in consumption frequency. Among ready-to-eat foods, kimbap (38.3%) was the most common, followed by meat side dishes (11.3%) and salads (11.0%). Among the heat-and-eat items, dumplings were the most frequently consumed. Simple cooking kits for Korean street food were used by 56.5% of mothers in the high-frequency HMR group, compared to 38.6% and 29.2% in the lower consumption groups (P < 0.01). Children’s preference for HMR was significantly associated with maternal HMR consumption frequency (P < 0.001). The most preferred items among children were rice porridge (P < 0.05) and meat side dishes (P < 0.001).
Conclusion
Higher maternal HMR consumption was associated with increased acceptance by children. Mothers who frequently used HMR exhibited more positive attitudes toward its palatability, convenience, nutritional value, and variety. While HMR offers diverse and tasty meal options, overreliance on processed foods warrants caution. Importantly, high HMR consumption during early childhood may influence long-term dietary behaviors, including a continued preference for HMRs.
- 840 View
- 24 Download


 KSCN
KSCN
 First
First Prev
Prev



