Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [Korean]
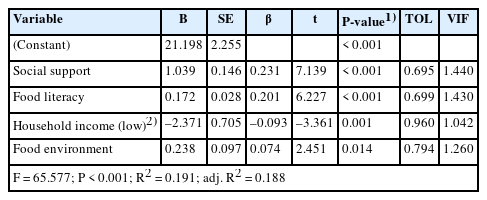
- Effects of primary caregivers’ food literacy, social support, food environment, and household income on the nutritional status of school-aged children: a cross-sectional study
- Seyeon Park, Ji-Yun Hwang, Sohyun Park, Hyun Joo Ryou, Jieun Oh
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(5):352-363. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00248

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The dietary habits of school-aged children play a critical role in their growth and development, and are strongly influenced by the home environment. Household income is closely associated with caregivers’ food literacy, social support, and food environment. This directly affects the nutritional status of children. This study aimed to provide evidence to inform policies and educational programs for improving dietary habits in children, and to establish a foundation for tailored support strategies for low-income families.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 846 primary caregivers of school-aged children from 17 regions across Korea, recruited through an online survey. Household income, caregivers’ food literacy, social support, and food environment were assessed. Nutritional status in children was measured using the Nutrition Quotient for Children (NQ-C). Statistical analyses included descriptive statistics, chi-square tests, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), analysis of covariance (ANCOVA), correlation analyses, and multiple linear regression.
Results
Caregivers from higher income households demonstrated significantly greater food literacy and social support (P < 0.001). Children from these households showed high balance scores and a large proportion of these children were in the “high” NQ-C grade. The NQ-C score in children was positively correlated with food literacy (r = 0.425), social support (r = 0.471), and the food environment (r = 0.235) (P < 0.001). Multiple regression analysis showed that food literacy (β = 0.256) and social support (β = 0.348) were significant predictors of nutritional status in children.
Conclusion
This study confirmed that the nutritional status in children is not only determined solely by household income but is also mediated by caregivers’ food literacy, social support, and food environment. These findings highlighted the limitations of providing only economic support. The findings underscore the need for multifaceted interventions such as strengthening parental nutrition education, expanding social support networks, and improving access to healthy foods.
- 280 View
- 13 Download

- [English]
- Nutrition quotient for preschoolers and key impacting factors in Korea: a cross-sectional study on food literacy, social support, and the food environment of primary caregivers
- Danbi Gwon, Ji-Yun Hwang, Jieun Oh
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):16-26. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00311
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study evaluated the nutrition quotient for preschoolers (NQ-P) and analyzed the impact of key factors, such as caregivers’ food literacy, social support, and food environment, on the eating habits of preschool children in Korea. This study also sought to provide foundational data for developing tailored nutrition education programs by identifying the nutrition education needs of caregivers.
Methods
This study was conducted among caregivers of preschool children (aged 0–6 years) using an online self-administered survey conducted from August 22 to August 28, 2023. A total of 1,116 survey responses were analyzed. This study assessed children’s NQ-P score, caregivers’ food literacy, social support, food environment, and nutritional education needs. Data were analyzed using SPSS 29.0 (IBM Co.).
Results
The average NQ-P score for preschool children was 52, showing a tendency for the balance score to decrease and the moderation score to increase with age. Children from rural and low-income areas exhibited significantly lower NQ-P scores. Caregivers’ food literacy was higher in urban and higher-income groups. Multiple regression analysis revealed that social support, food literacy, income, and food environment significantly affected children's NQ-P scores. The effectiveness of nutrition education varied based on the income level, with nutrition education on healthy eating being the most preferred topic for preschool children.
Conclusion
This study confirmed that caregivers’ food literacy and social support significantly affected preschool children’s nutritional status. This suggests a need for tailored nutritional education and dietary support policies, particularly for low-income and rural populations.
- 1,974 View
- 55 Download

- [English]
- Examination of explicit and implicit emotions and relationship with the intention to support breastfeeding in public: a descriptive study
- Katilin D. Overgaard, Lauren M. Dinour, Adrian L. Kerrihard, Yeon K. Bai
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(2):114-123. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.2.114
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Current social norms in the United States do not favor breastfeeding in public. This study examined associations between college students’ explicit and implicit emotions of breastfeeding in public and their intention to support public breastfeeding.
Methods
Twenty-two student participants viewed images of a breastfeeding woman with a fully-covered, fully-exposed, or partially-exposed breast in a public setting. After viewing each image, participants’ explicit emotions (self-reported) of the image were measured using a questionnaire and their implicit emotions (facial expression) were measured using FaceReader technology. We examined if a relationship exists between both emotions [toward images] and intention to support breastfeeding in public using correlation techniques. We determined the relative influence of two emotions on the intention to support breastfeeding in public using regression analyses.
Results
The nursing images depicting a fully-covered breast (r = 0.425, P = 0.049 vs. r = 0.271, P = 0.222) and fully-exposed breast (r = 0.437, P = 0.042 vs. r = 0.317, P = 0.150) had stronger associations with explicit emotions and intention to support breastfeeding in public compared to implicit emotions and intention. Breastfeeding knowledge was associated with a positive explicit emotion for images with partial- (β = 0.60, P = 0.003) and full-breast exposure (β = 0.65, P = 0.002).
Conclusions
Explicit emotions appear to drive stated intentions to support public breastfeeding. Further research is needed to understand the disconnect between explicit and implicit emotions, the factors that influence these emotions, and whether stated intentions lead to consistent behavior.
- 590 View
- 11 Download

- [Korean]
- Dietary Status of Preterm Infants and the Need for Community Care
- Ji Su Jeon, Won Hee Seo, Eun mi Whang, Bu Kyung Kim, Eui Kyung Choi, Jang Hoon Lee, Jeong Hee Shin, Young Shin Han, Sang-Jin Chung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(4):273-285. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.4.273
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study compared the nutritional intakes of early and late preterm infants in a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) and at home. The dietary problems and the need for community care services for premature infants were further investigated.
Methods
This is a cross-sectional and descriptive study on 125 preterm infants and their parents (Early preterm n = 70, Late preterm n = 55). The data were collected by surveying the parents of preterm infants and from hospital medical records.
Results
No significant differences were obtained between the early and late preterm infant groups when considering the proportion of feeding types in the NICU and at home. Early preterm infants were fed with a greater amount of additional calories at home and had more hours of tube feeding (P = 0.022). Most preterm infants had feeding problems. However, there was no significant difference between early and late preterm infants in the mental pain of parents, sleeping, feeding, and weaning problems at home. Many parents of preterm babies had no external support, and more than half the parents required community care to take care of their preterm babies.
Conclusions
Regardless of the gestational age, most preterm infants have several problems with dietary intake. Our study indicates the need to establish community care services for preterm infants.
- 606 View
- 10 Download

- [Korean]
- Nutritional Status of Intensive Care Unit Patients According to the Referral to the Nutrition Support Team and Compliance with the Recommendations
- Yunjin Sohn, Taisun Hyun
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(2):121-131. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.2.121
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to examine the effectiveness of the intervention of the nutrition support team (NST) on the nutritional status of critically ill patients.
Methods
The medical records of 176 adult patients who were admitted to the intensive care unit and received enteral or parenteral nutrition for more than 7 days were retrospectively analyzed. The patients were classified into the NST and non-NST groups according to whether they were referred to the NST or not. The NST group was further classified into the compliance and non-compliance groups depending on their compliance with the NST recommendations.
Results
The NST referral rate was 56.8%, and the rate of compliance with the NST recommendations was 47.0%. Significantly higher energy and protein were provided to the NST and the compliance groups than to the non-NST and the non-compliance groups. The proportion of patients who reached the target calories after the initiation of enteral nutrition was significantly higher in the NST and the compliance groups than in the non-NST and the non-compliance groups. The serum albumin and hemoglobin levels significantly decreased in every group, but the changes were significantly lower in the compliance group. The nutritional status at discharge from the intensive care unit compared to the status at admission was significantly worse in the NST, non-NST, and non-compliance groups. However, the status was maintained in the compliance group. The length of stay in the intensive care unit was significantly shorter in the compliance group.
Conclusions
Compliance with the NST recommendations was found to provide more calories and protein and prevent the deterioration of the nutritional status of critically ill patients. Therefore, effective communication between medical staff and the NST from the early stages of admission to the intensive care unit is needed to improve referrals to the NST and compliance with the recommendations. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Nutritional Status on Pressure Ulcers and Death among Critically Ill Patients
Miyeon Kim, Soyoung Yu, Hye-Ja Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2024; 49(4): 305. CrossRef
- Impact of Nutritional Status on Pressure Ulcers and Death among Critically Ill Patients
- 1,130 View
- 34 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Articles
- [English]
- Analysis of Nutrition Teachers' Awareness of Necessity for an Operating School Meal Support Center in Chungnam
- Jonghwa Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(6):506-515. Published online December 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.6.506
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
We investigated the operation needs of school meal support centers (SMSC) in Chungnam-do based on analysis of nutrition teachers' perception of them.
METHODS
The Chungnam government established the first SMSC in 2012. Thirteen SMSCs are currently being operated in Chungnam-do. To analyze the results quantitatively, we investigated nutrition teachers opinions regarding the necessity for SMSCs as a dependent variable and derived the independent variables based on the causal relationships with dependent variables using the ordered logit model. Those independent variables included region, school type, number of students, attitude regarding free meal policy, satisfaction with school meal policy, and preference for local food.
RESULTS
Briefly, teachers in the region in which the SMSC was located more strongly supported the SMSC. In addition, teachers in public schools with a smaller number of students believed that having a SMSC is more beneficial, and that other variables also affected the necessity for SMSCs. Moreover, nutrition teachers preferred local foods rather than organic foods because of the unstable supply of organic foods.
CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of this study, it was recommended that the local government implement the policy consistently. Moreover, it was recommended that the government operate the SMSC more efficiently, enhance the roles of the SMSC as the local organization responsible for student nutritional planing and expand the coverage of agricultural products.
- 675 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- The Relationship between Stress, Social Support and Healthy Diet Score among Chinese University Students in Korea
- Sunghee Lee, Zhen Feng, Youngmee Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(4):273-280. Published online August 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.4.273
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The study aimed to examine whether healthy diet score was associated with stress and social support among 472 Chinese college students in Korea.
METHODS
The study participants were 472 (187 male, 285 female) Chinese college students in Gyeong-gi area. From April 2013 to Oct 2013, participants were asked to fill out questionnaires on healthy diet score (20 questions), stress (20 questions), and social support (20 questions). Each question was scored by a 5-point Likert scale (total scores of each questionnaire were ranged from 20 to 100). Questions on healthy diet were sub-categorized as 'Healthy food eating (HFE)', 'Healthy eating habits (HEH)', and 'Avoidance of unhealthy food (AUF)'. Reliability test was conducted with Cronbach's alphalpha (alpha=0.79).
RESULTS
Healthy diet score was higher in participants who stayed longer in Korea, who spoke Korean language fluently, and who assessed his or her own health status as very good. Adjusted means of healthy diet scores were estimated after adjusting for age, gender, body mass index, duration of staying, and Korean language fluency. According to tertile categories, participants with low tertile stress but high tertile social support showed the highest score of healthy diet (72.59+/-1.45), whereas participants with high tertile of stress but low tertile of social support had the lowest score of healthy diet (59.22+/-1.54). As for the three sub-categories of healthy diet score, the score of HFE increased as the score of social support increased.
CONCLUSIONS
Our findings suggested that social support system is beneficial to alleviate stress and to improve healthy diet score.
- 687 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- School Dietitians' Satisfaction with and Needs for School Meal Service Support Centers
- Hyeyeong Cho, Sooyoun Kwon, Youngmi Lee, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2012;17(2):194-204. Published online April 30, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.2.194
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to investigate school dietitians' satisfaction with and needs for School Meal Service Support Centers. A web-based on-line survey was conducted with 1,102 nutrition teachers or school dietitians using four School Meal Service Support Centers during the summer of 2011. The data from 578 respondents (52.5%), consisting of 165 (44.4%), 334 (53.4%), 41 (67.2%), and 38 (86.4%) dietitians using Seoul, Gyeonggi, Suncheon and Gyeongju centers, respectively, were analyzed. The main reason for using the centers was subsidies from local governments. The dietitians using the metropolitan centers, which were Seoul and Gyeonggi centers, tended to buy agricultural products through the centers only, and those using local centers, which were Suncehon and Gyeongju centers, bought those products from the private suppliers as well as from the centers. The dietitians' overall level of satisfaction with the centers was not high showing 3.3 out of 5 points; it was significantly associated with the operating system and services of the centers such as system efficiency, delivery accuracy, communication, and information provision rather than the agricultural products provided by the centers. The dietitians preferred joint operation of the centers by local governments and producers' groups. They wanted School Meal Service Support Centers to be evaluated every year. It was suggested that efforts should be made to improve the operation system and service of School Meal Service Support Centers for improving dietitians' satisfaction with the centers. In addition, an evaluation system for School Meal Service Support Centers should be implemented soon based on school dietitians' needs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Surveys to Determine the Real Prices of Ingredients used in School Foodservice
Seo-Hyun Lee, Min A Lee, Jae-Yoon Ryoo, Sanghyo Kim, Soo-Youn Kim, Hojin Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(3): 188. CrossRef - Recognition of Environmentally-friendly Agricultural Products for School Foodservice of Nutrition Teachers and Parents in 2018 at Seongnam in Gyeonggi province
Jisoo Kwon, Wookyoun Cho
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(4): 290. CrossRef - An Analysis of Importance-Performance on School Meal Support and Local Food Supply Policy
Choong-Seop An, Won-Tae Kim, Ho Kim
Korean Journal of Organic Agricultue.2018; 26(4): 585. CrossRef - Analysis of Nutrition Teachers' Awareness of Necessity for an Operating School Meal Support Center in Chungnam
Jonghwa Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(6): 506. CrossRef - A Study on the Satisfaction for Food Service with School Food Service Center of Elementary and Middle School Parents in Chungnam
Sung-Bum Yang
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(3): 404. CrossRef - Status of Purchasing Food Materials and Satisfaction with Service Quality of Group-buying Companies in Foodservice at Child-care Centers
Yoonjae Yeoh
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2015; 25(1): 193. CrossRef
- Analysis of Surveys to Determine the Real Prices of Ingredients used in School Foodservice
- 888 View
- 1 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [English]
- Assessment of the Support Program of Foodservice Management for Community Child Centers in Jeollanam-do, Korea
- Sooyoun Kwon, Youngmi Lee, Soyoung Kim, Jinyoung Kim, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2012;17(1):91-100. Published online February 29, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.1.91
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of the foodservice management support program focusing on menu management in community child centers. The support program provided reference menus, staff training, and field consulting to 10 community child centers in the Jeollanam-do province for one month, August in 2010. One month menus were developed, based on children's preference for menu items, foodservice personnel's preference for food materials, and availability of local specialty foods, and offered as reference menus. In addition, staff training and field consulting focusing on menu management were conducted before and during the pilot period, respectively. To evaluate the support program, menus, foodservice personnel's knowledge level and perceived performance in foodservice management, and children's level of satisfaction for foodservice were analyzed before and after the support program. As a result of analysis of 222 and 210 menus of before and after the support program, respectively, the number of dishes per meal increased from five to six on average, and the proportion of meals including five food groups, which were grain, meat, vegetable, fruit, and milk and dairy product, rose from 2% to 24%. Foodservice personnel's knowledge level regarding foodservice management increased significantly (p = 0.007), however, their perceived performance in foodservice management did not show any significant changes. Children were more satisfied with 'food' (p = 0.001), 'sanitation' (p = 0.001), and 'environment' (p < 0.008) of foodservice in community child centers after the support program. In conclusion, the foodservice management support program focusing on menu management in this study was effective for improving menu quality of and children's satisfaction with foodservice in community child centers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Investigation of the Management of Foodservice Facilities inCommunity Child Centers in Daegu and Gyeongbuk Area
Suk-Hyeon Park, Hyeon-A Jung
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2017; 27(4): 459. CrossRef - Food Service Status at Community Child Care Centers in Busan
Jeong-Sook Lee
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2014; 20(1): 50. CrossRef
- Investigation of the Management of Foodservice Facilities inCommunity Child Centers in Daegu and Gyeongbuk Area
- 955 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Child-Care Facility and Kindergarten's Demands on Foodservice Support by Center for Child-Care Foodservice Management (CCFSM) in Seoul and Gyeonggi-do
- Soo Youn Kim, Il Sun Yang, Bo Sook Yi, Seung Hee Baek, Seo Young Shin, Hae Young Lee, Moon Kyung Park, Young Shin Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(6):730-739. Published online December 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.6.730
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to analyze the differences between child-care facilities and kindergartens towards the need for foodservice support by Center for Child-Care Foodservice Management (CCFSM). For this study, questionnaires were sent out from August of 2008 to April of 2009 to directors of 1,478 child care facilities and 299 kindergartens in Seoul and Gyeonggi-do via postal service. A total of 267 questionnaires were usable with 203 (13.7%) of child-care facilities and 64 (21.4%) of kindergartens. Statistical data were analyzed by SPSS 15.0 for descriptive analysis and t-test. For political and administrative support, government funding for foodservice was the highest need and hiring nutritionists was significantly different by type of facility (p < 0.01). Both child-care facilities (4.29) and kindergartens (4.41) demanded the balanced menu from CCFSM. There were significant differences of "information about food material sanitation management" (p < 0.05), "hygiene safety management method according to working process" (p < 0.05), "hygiene safety management method of foodservice facilities and equipment" (p < 0.05). In education and training contents from center, "types and methods to manage foodservice facilities and equipment" for directors, "dietary education by age" for teachers, and "the rules of personal sanitation and working process" and "gas, electricity and fire prevention" for culinary workers had the highest mean score of requirements.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Foodservice Status and Perception regarding Foodservice Management in Kindergartens attached to Elementary Schools in Seoul
Ranmi Jung, Gun-Hee Kim, Jieun Oh, Sunny Ham, Seungmin Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(6): 492. CrossRef - Analysis of Job Importance and Job Performance in Dietitians by Kindergarten Establishment Type
Seonyeong Baek, Yulee Shin, Gunhee Kim, Jieun Oh, Seungmin Lee, Sunny Ham
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2020; 30(4): 274. CrossRef - Assessment of the Effectiveness and Perception of Education by Center for Child-Care Foodservice Management: Focus on Parents of Child-Care and Kindergarten in Seoul
Se-Young Ju, Wan-Soo Hong
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2018; 34(4): 404. CrossRef - A Comparison of Hygiene and Safety Management Execution depending on the Characteristics of Children's Food Service Facilities
Jin-Young Lee
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(4): 573. CrossRef - The Assessment of Food Safety Practices and the Effect of Visiting Education on Food Safety Improvement in Children's Foodservice Facilities
Jae-Eun Paik, Hyun-A Lee, Hyun-Joo Bae
Korean journal of food and cookery science.2015; 31(6): 764. CrossRef - Center for Children's Foodservice Management (CCFSM) Employees' Perception of Difficulties in Performing Tasks
Eun Hye Park, Young Eun Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2015; 44(4): 619. CrossRef - Task Satisfaction, Job Satisfaction, Organizational Commitment, and Turnover Intension of Center for Children's Foodservice Management Employees
Eun Hye Park, Young Eun Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2015; 44(12): 1881. CrossRef - Food Service Status at Community Child Care Centers in Busan
Jeong-Sook Lee
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2014; 20(1): 50. CrossRef - The Effect of a Periodic Visiting Education Program on Food Safety Knowledge of Cooks in Children's Foodservice Facilities
Jinah Kim, Youngmee Lee
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2014; 20(1): 36. CrossRef - Analysis of Relative Importance of Key Performance Indicators for Center for Child-Care Foodservice Management through Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP)
Yun-Hui Jeong, In-Sook Chae, Il-Sun Yang, Hye-Young Kim, Hae-Young Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(2): 154. CrossRef - Evaluation of Sanitation Management Practices and Microbiological Quality of Foods in Kindergarten Foodservice Settings
Joo-Eun Lee, Kyung-Sook Choi, Young-Jae Kang, Tong-Kung Kwak
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2012; 28(5): 515. CrossRef - Assessment of Kindergarten Principals and Teachers' Performance Degree of Foodservice Hygiene Management and Foodservice Employees' Hygiene Knowledge
Joo-Eun Lee, Kyung-Sook Choi, Tong-Kung Kwak
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2012; 18(4): 308. CrossRef
- Foodservice Status and Perception regarding Foodservice Management in Kindergartens attached to Elementary Schools in Seoul
- 1,061 View
- 4 Download
- 12 Crossref

- [English]
- Government-Funded Meal Support Program for Low-Income Children through Convenience Stores : Current Status and Nutritional Quality of Available Meal Items in Seoul
- Haelim Choi, Sooyoun Kwon, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(2):253-264. Published online April 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.2.253
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The objectives of this study were to investigate the current status of the Korean government-funded meal support program for low-income children through convenience stores and to evaluate the nutritional quality of the meal items available under the program. The POS data of three convenient stores where children had used their electronic meal cards most often in Seoul during January 2010 and the kinds and amounts of ingredients of the meals items available to the children were obtained from the headquarter of the convenient stores. A total of 5,081 transactions by 693 children included in the POS data was analyzed. In addition, nutritional contents of meal items, which were meal boxes (11 kinds), kimbab (13 kinds), rice balls (27 kinds), inari sushi (1 kind), and sandwiches (26 kinds), were analyzed with Can Pro 3.0. The results showed that children had purchased flavored-milk products most often. Children tended to purchase meal items together with drinks (60.9% of transactions), but some purchased drinks (27.6%) or meal items only (11.5%). Except for meal boxes, none of the meal items satisfied 1/3 of Estimated Energy Requirements of the 9-11 year-old boys per day. The average energy contents of different kinds of meal boxes, kimbabs, rice balls, and sandwiches were 619, 357, 200, and 380 kcal, respectively, and the energy content of a package of Inari sushi was 457 kcal. Vitamin C amount was found to be deficient in all the meal items, compared to 1/3 of Recommended Intake of the 9-11 year-old boys per day. The results of this study could be useful to develop nutritionally appropriate meal items for the convenient stores participating in the government-funded meal support program for children from low-income families.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Intake Status and Satisfaction of Home-delivered Meal Boxes for Children from Low-income Families in Seongnam-city, Gyeonggi-do
SooYoun Kwon, OkSun Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2023; 33(2): 149. CrossRef - A Qualitative Study on the Dietary Experience with the Children’s Meal Card : Focused on College Students Living in Busan
Soo Jin Lee, Ho Kyung Ryu
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2022; 33(2): 205. CrossRef - Evaluation of Nutritional Quality of Convenience Store Meal Boxes according to Store Company and Meal Price
Changgyu Cho, Youngmin Nam, Hye-Jong Yoo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(2): 105. CrossRef - Analysis of the Dietary Life of Adolescents by Household Types in Korea using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Soo Jin Lee, Ho Kyung Ryu
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2021; 32(2): 285. CrossRef - Analysis of the Affiliate-stores Distribution and Users of an Electronic-card for Children’s Meal Service in Busan
Soo Jin Lee, Ji Yoon Lee, Jung Eun Kang, Ho Kyung Ryu
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2021; 32(1): 29. CrossRef - Study on Middle and High School Students' Use of Convenience Foods at Convenience Stores in Incheon
Seul-Ki Lee, Mi-Kyeong Choi, Mi-Hyun Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(2): 137. CrossRef - A Survey of Satisfaction with Quality attributes of Meal Services for Low-income Children in Wonju
Hae Sook Oh
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2014; 25(2): 233. CrossRef - A comparison study of hygiene status in meals for poorly-fed children through microbiological analysis
Ok-Kyeong Yu, Hyun-Suk Kim, Moon-Sun Byun, Mina Kim, Youn-Soo Cha
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2014; 47(3): 214. CrossRef - The Current Status of Foodservice Management in the Restaurants Participating in the Government-funded Children's Model Program in Korea during Summer Vacation
Jinyoung Kim, Sooyoun Kwon, Youngmi Lee, Haelim Choi, Jihyun Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2012; 17(2): 182. CrossRef
- Analysis of Intake Status and Satisfaction of Home-delivered Meal Boxes for Children from Low-income Families in Seongnam-city, Gyeonggi-do
- 1,109 View
- 1 Download
- 9 Crossref

- [English]
- Current Status of Meal Box Service Management for Children from Low-income Families During Summer Vacation
- Borham Yoon, Jihyun Yoon, Jae Eun Shim, Sooyoun Kwon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14(2):206-215. Published online April 30, 2009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to investigate the current status of foodservice management in organizations delivering meal boxes for low-income children during summer vacation. A survey was conducted with persons in charge of meal box production and service of these organizations via mail. Out of 114 questionnaires distributed nationwide, 100 were analyzed (87.8% analysis rate). Over half (53%) of the organizations delivered meal boxes consisting of rice and side dishes while the rest delivered side dishes only. About 81% of the organizations received KRW 3,000 per meal from their local governments and the rest received KRW 3,500. Only 28% of organizations had employed a dietitian. Over one-third (38%) of the respondents were unaware of the official nutritional standard of the foodservice program for low-income children during vacation. Most of the organizations (94%) had menu planned in advance. The average percentage of food cost was 84.1%. Over 40% of the organizations did not keep food samples for sanitation test (43%) and did not take any measures for keeping food temperature during delivery (45%). The organizations delivering rice and side dishes were more likely to be located in cities rather than rural areas and received higher reimbursement rate. The organizations receiving reimbursement of KRW 3,500 or hiring a dietitian were more likely to use standardized recipes, keep food samples for sanitation test, or take measures for keeping food temperature during delivery compared to the counterparts. Respondents reported that increasing reimbursement rate was the most necessary for improving the quality of meal box. This study results showed that the meal box delivery service for low-income children was not properly managed during the vacation, with regards to menu planning and food production. It is recommended that reimbursement rate for meal boxes should be adjusted depending on meal box types and local conditions.
- 306 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- The Outcome of Nutrition Support of Surgery Patients with Hypermetabolic Severity by Total Parenteral Nutrition and Enteral Nutrition and Biochemical Data
- Miyong Rha, Eunmi Kim, Young Y Cho, Jeong Meen Seo, Haymie Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2006;11(2):289-297. Published online April 30, 2006
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study evaluated the nutrition intake and changes in laboratory data of surgery patients with hypermetabolic severity on nutrition support. From January 2002 to September 2002, 66 hospitalized surgery patients who had received enteral nutrition (EN, n=19) and total parenteral nutrition (TPN, n=47) for more than 7 days were prospectively and retrospectively recruited. The laboratory data was examined pre-operatively, and on the post-operative 1, 3, 7 day and at the time of discharge. The characteristics of the patients were examined for the hypermetabolic severity, The hypermetabolic scores were determined by high fever (> 38 degrees C), rapid breathing (> 30 breaths/min), rapid pulse rate (> 100 beats/min), leukocytosis (WBC>12,000/microliter), leukocytopenia (WBC<3,000/microliter), status of infection, inflammatory bowel disease, surgery and trauma. The scores for the hypermetabolic status were divided into three groups (mild 0-10, moderate 11-40, severe>41). According to the results of the study, 38.3% (n=23), 45.4% (n=30) and 19.6% (n=13) were in the mild, moderate, and severe groups, respectively. There was a decrease in the serum albumin level and weight loss according to the hypermetabolic severity. However, the white blood cells (WBC), fasting blood sugar (FBS), c-reactive protein (CRP), total bilirubin, GOT, and GPT increased. The nutritional intake was TPN (32.5 kcal/kg, protein 1.2 g/kg, fat 0.25 g/kg), EN (28.1 kcal/kg, protein 1.0 g/kg, fat 1.01 g/kg). The serum albumin, hemoglobin and cholesterol were higher in the EN group than in the TPN group. But the FBS, total bilirubin, GOT and GPT were higher in the TPN group than the EN group. In conclusion, there was a negative correlation between the changes in the laboratory data and the hypermetabolic severity. There was an increase in the number of metabolic complications in the TPN group.
- 228 View
- 2 Download

- [English]
- Effects of the APACHE III Score, Hypermetabolic Score on the Nutrition Status and Clinical Outcome of the Patients Administered with Total Parenteral Nutrition and Enteral Nutrition
- Miyong Rha, Eunmi Kim, Young Y Cho, Jeong Meen Seo, Haymie Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2006;11(1):124-132. Published online February 28, 2006
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The aim of this study is to evaluate the clinical outcome. Between January 1, 2002 to September 30, 2002, we prospectively and retrospectively recruited 111 hospitalized patients who received Enteral Nutrition (ENgroup n = 52) and Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPNgroup n = 59) for more than seven days. The factors of clinical outcomes are costs, incidences of in-fection, lengths of hospital stay, and changes in weight. The characteristics of patients were investigated, which included nutritional status, disease severity (APACHE III score) and hypermetabolic severity (hypermetabolic score). Hypermeta-bolic scores were determined by high fever (>38 degrees C), rapid breathing (>30 breaths/min), rapid pulse rate (>100 beats/min), leukocytosis (WBC > 12000 mm3), leukocytopenia (WBC < 3000 mm3), status of infection, inflammatory bowel disease, surgery and trauma. There was a positive correlation between hypermetabolic score and length of hospital stay (ICU), medical cost, weight loss, antibiotics adjusted by age while APACHE III score did not show correlation to clinical outcome. Medical cost was higher by 18.2% in the TPN group than the EN group. In conclusion, there was a strong negative correlation between the clinical outcome (cost, incidence of infection, hospital stay) and hypermetabolic score. Higher metabolic stress caused more malnutrition and complications. For nutritional management of patients with malnutrition, multiple factors, including nutritional assessment, and evaluation of hypermetabolic severity are needed to provide nutritional support for critically ill patients.
- 261 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Importance, Support and Application for Contract Foodservice Management Company's Infra-System in the Viewpoint of Headquarters and Branch Office
- Il Sun Yang, Moon Kyung Park, Kyung Soo Han, In Sook Chae, So Hyun Park, Hae Young Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2004;9(2):233-240. Published online April 30, 2004
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was design to grope the suggestions leading synergic effects by bridging the gap between headquarters and branch office, and so to identify the infra-system of contract foodservice management company (CFMC) necessary for operating any kind of branch office including school, hospital and business and industry (B&I). Among 8 categories consisted of infra-system in CFMC, 'C8. Evaluation & analysis for branch office's operation' was the most important category in the headquarter's viewpoint, while 'C3. Sanitation management system' was the most important category in branch office's viewpoint. In support and application, 'C3. Sanitation management system' was the highest category in both headquarters and branch offices including school, hospital and B&I. As a result of analysis on gap between main and branch office in importance, support and application in 8 categories, the efforts of communication and community of perception for infrastructure were needed, because 'C4. Education & training for human resource management (HRM) system' and 'C8. Evaluation & analysis for branch office's operation' in importance, 'C2. Menu management system', 'C4. Education & training for HRM system', 'C6. Facility & utility support system' and 'C8. Evaluation & analysis for branch office's operation' in support had a gap. Correlation analysis to grasp the relation between importance of infra-system and headquarters' support or branch office's application showed that headquarters's importance and support were correlated positively in 'C3. Sanitation management system', 'C6. Facility & utility support system', 'C7. Customer satisfaction management system' and 'C8. Evaluation & analysis for branch office's operation' and branch office's importance and application were correlated positively in 'C1. Procurement & food processing system', 'C5. Management Information system', 'C7. Customer satisfaction management system' and 'C8. Evaluation & analysis for branch office's operation'. Lastly, 'C6. Facility & utility support system' in the branch office of school and hospital and 'C2. Menu management system' in the branch office of B&I were high in importance, low in support and application, therefore intensive support for these categories was needed. In conclusion, continuous check and improvement for categories, which were identified as an urgent problems to be solved in this study, among infra-structure qualifying for CFMC,would enable contract foodservice industry that has grown quantitatively till now to grow qualitatively.
- 251 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- The Effect of Individualized Nutritional Education on Adults having two or more Symptoms of Chronic Degenerative Disease
- Jin Sook Yoon, Young Hye Jeong, Jung A Park, Hyun Mee Oh
- Korean J Community Nutr 2002;7(6):794-802. Published online December 31, 2002
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was intended to evaluate the overall effects of nutritional education on adults having two or more symptoms of chronic degenerative disease. A nine week nutritional education program was provided for 65 adults with chronic diseases. We assessed the changes in dietary knowledge, eating behavior and socio-psychological factors. When we evaluated the nutrient intakes of the subjects, their energy intake was 79.4% of the Korean Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDA). Their dietary intake of other nutrients was also below the RDA level except for Vitamin C. Their knowledge of dietary therapy was slightly improved after the implementing of nutritional education. The dietary behavior of 'night snacks before sleep' was significantly improved. While the overall fear due to disease was significantly increased, self-efficacy was not improved. Self-efficacy for eating "three regular meals" and "choosing fruit, vegetable and grain" were significantly decreased. Family support for "buying food which is good for my health" was also significantly increased, whereas "advises me to eat appropriate foods for health" was decreased. Biochemical analysis indicated that blood levels of triglyceride, cholesterol and blood pressure improved after nutrition education. Therefore, we concluded that nutritional education program for people with chronic degenerative diseases could change the diet therapy knowledge, dietary behavior, and the fear due to disease, support from family and behavior intention toward the direction to improve the chronic disease condition. However, it did not improve self-efficacy. Our study also indicated that nutritional education strategies to improve self-efficacy should be an important aspect in a long term education plan for patients to establish desirable eating habits.
- 267 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- The Effects of Stress and Social Support on Obesity in Junior High School Students Living in Small Cities
- Young Ok Lim, Young Nam Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2002;7(5):705-714. Published online October 31, 2002
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to examine the relative importance of everyday life stress, obesity stress, and social support on the BMIs of junior high school students. Subjects in this study consisted of 229 adolescents from two junior high schools in Iksan-city and Hamyul-eup. For data analyses, the frequencies, percentages, means, t-tests, Chi-squares, one-way ANOVAs, Pearson's correlation coefficients and regressions were conducted using SPSS WIN program. The mean BMI of the subjects was 20.18, and the ratio of students' BMIs less than 20 was 56.8%, that of students' BMIs greater than or equal to 25 was 8.3%. There were no statistical differences in BMIs by grade and sex. Statistically significant differences in the obesity of the junior high school students were detected according to demographic characteristics such as economic levels, areas of residence, TV watching time, and fathers' physiques. There were significant differences in everyday life stresses, obesity stresses, and social support by sex, but not by grade. Girls showed higher stress levels than boys, specially in family-related life stresses, social relationships, and self-related stresses. Also girls showed higher stress level related to obesity than boys. Girls got more support from their mothers, siblings and friends than boys. With respect to the type of social support, girls perceived more financial, informational, emotional, and judgemental support than boys. These results suggest that girls became more stressed, although on the other hand, they received more social support than boys. The higher the economic level, the longer the TV watching time, and the higher the stresses from everyday life and obesity, the higher the BMIs of the junior high school students were. In conclusion, everyday life stress and obesity stress were the important factors in relation to the junior high school students' obesity.
- 270 View
- 3 Download

- [English]
- A Study on the Sociopsychological Factors Influencing the Dietary Compliance of Diabetics Using Questionnaire
- Dong Yean Park, Sun Jung Choe, Hae Ryun Park, Hong Seok Ahn
- Korean J Community Nutr 2000;5(1):36-49. Published online March 31, 2000
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of the study was to find the sociopsychological factors predicting the intention of compliance with the dietary regimen in diabetes with a questionnaire. Data were collected from 282 adult noninsulin-dependent diabetics in Seoul, Kyoggida, and Kyongsangbukdo in Korea. Stepwise multiple regression analysis was conducted with predictor variables from theories of the Health Belief Model, Social Cognitive Model, The Theory of Reasoned Action, and Social Support. The behavioral intention of compliance with the prescribed diet was the independent variable. Subjects norm self-efficacy knowledge about diet therapy, outcome expectation, relationship with medical team, threat of deterioration of disease, and social support were the independent variables, The mean score of behavior intention was high ie 35.3 out to 42. Subjective norm and self-efficacy were the significant variables to predict the intention of dietary compliance. These variables comprised 39% of the common variance. To increase dietary compliance by influence of the referents and improve self-efficacy significant referents must be included and concrete and practical methods to follow the dietary regimen must be provided in nutrition education.
- 241 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Evaluation and Categorization of Commercially Prepared Enteral Nutrition Formulas
- Dong yeon Kim, Hee Jae Suh
- Korean J Community Nutr 1998;3(5):729-738. Published online November 30, 1998
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In order to investigate the types of enteral nutrition formulas currently used in hospitals and evaluate and categorize the commercially prepared enteral nutrition formulas formulas available in the domestic market, we asked dietitians working in 6 hospitals in Seoul to complete the questionnaire and obtained compositional characteristics of 12 commercially prepared enteral nutrition formulas. The average proportion of patients receiving the commercially prepared enteral nutrition formulas(60.6%) was greater than that of patients receiving the in-hospital preparations(31.9%). In the group of patients receiving the in-hospital prepared formulas, the enteral feeding was mainly administered orally, whereas, in the group of patients receiving the commercially prepared formulas, tube feeding was the primary route of formula administration. In both groups, however, a greater proportion of patients received the formulas as total replacements of their meals and for the purpose of dietary supplementation. On the basis of major criteria for evaluation of the commercially prepared enteral nutrition formulas, the 6 products out of the 9 nutritionally complete products formulated for the purpose of dietary supplementation were grouped into the same category(standard protein, caloric density of 1kcal/ml, and tube/oral), so they were considered therapeutically comparable. However, the remaining 3 products were different in protein content(high protein) or route of administration(tube only). Of the 3 nutritonally complete products formulated specifically for the purpose of dietary therapy, 2 products were formulated for patients with renal disease, and the one product was formulated for diabetic patients. Therefore, the data in this study showed that the commercially prepared enteral nutriton formulas became an important part of the enteral nutrition for hospitalized patients in Korea, but the domestic market has not yet generated a wide variety of the formulas, not providing many choices for clinicians to manage the diets for their patients. The results of this study would be helpful for clinicians in choosing appropriate products for their patients, for manufactures in developing new products, and for regulatory authorities to establish the regulation for the broad group fo heterogeneous products that are marketed and will be developed as medical foods. In addition, the process of maintaining the categories for evaluation of the commercially prepared enteral nutrition formulas should be dynamic because new products may not reasonably fit any of the existing categories.
- 328 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- A Study of the Obesity Index and Psychosocial Factors Influencing Obesity among Adolescent Girls
- Kyung Won Kim, Young Ah Kim, Jung Hee Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 1997;2(4):496-504. Published online October 31, 1997
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to investigate the dietary intake, obesity index and psychosocial factors influencing obesity among 200 high school girls in Seoul. The Social Cognitive Theory provided the Conceptual basis for this study. A cross-sectional survey was conducted to examine factors related to obesity, including self-efficacy for controlling overeating, social support for eating behavior, perception of body image and weight control, nutrition knowledge, and attitudes toward obesity. The data were analyzed using t-test and multiple logistic regression. The results of this study are as follows : 1) The mean age of the girls was 16.4 years, and the rate of overweight and obesity(measured by obesity index) was 27.0%. 2) The mean energy intake of subjects was 1832.3+/-384.0kcal. The energy derived from carbohydrates, proteins and fats was 62.7%, 13.8%, and 23.5%, respectively. There was no significant difference between the obese and the comparison group in energy intake. 3) The result of multivariate analysis indicated that obesity had a significant relation to the perception of ideal body image, social support for eating behavior, and self-efficacy for controlling overeating(p<0.01). As subjects preferred thinner body images(OR=0.39) and received less social support(OR=0.93), the odds of being classified as obese increased. The odds of being obese were also associated with self-efficacy, however, the relation was not strong(OR=1.04). 4) Specific social support was related to obesity among adolescent girls. As subjects received more support from family member, the odds of being obese decreased. The emotional support as well as family member's positive nutrition behavior plays a significant role. In addition, instrumental support from friends was associated with obesity. With repect to self-efficacy, the odds of being obese were increased as subjects felt less confident in controlling overeating when tempting food was placed in front of them or after an argument. In contrast, the obese group felt more confident in controlling overeating for the rest of the specific situations examined. These findings suggest that educational interventions for weight control should incorporate strategies to help participants realize their degree of obesity, to reduce the discrepancy between current and ideal body image, to elicit and maintain social support from friends and family, and to increase the self-efficacy for changing eating behaviors.
- 295 View
- 4 Download


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



