Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [English]
- The impact of flash continuous glucose monitoring and nutrition coaching on dietary self-efficacy and weight management in university students in Korea: a pre-post intervention study
- Soojin Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(3):183-196. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00073
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the impact of a 4-week multicomponent intervention combining flash continuous glucose monitoring (flash-CGM), group nutrition education, and personalized nutrition coaching on dietary self-efficacy (DSE) and weight management in healthy university students.
Methods
A total of 27 university students participated in a pre-post intervention study. The intervention included a single 4-hour group-based nutrition education session, flash-CGM usage (FreeStyle Libre; Abbott Diabetes Care), and weekly one-on-one nutrition coaching. Participants wore the CGM device for 28 days (replaced after 14 days), and were guided in using the FoodLens app (DoingLab) for dietary tracking and a mobile app-linked digital scale for weight monitoring. Outcomes measured before and after the intervention included DSE, body mass index (BMI), nutrition quotient (NQ) and glycemic indicators. Statistical analyses included Wilcoxon signed-rank and Mann-Whitney U-tests with significance set at P < 0.05.
Results
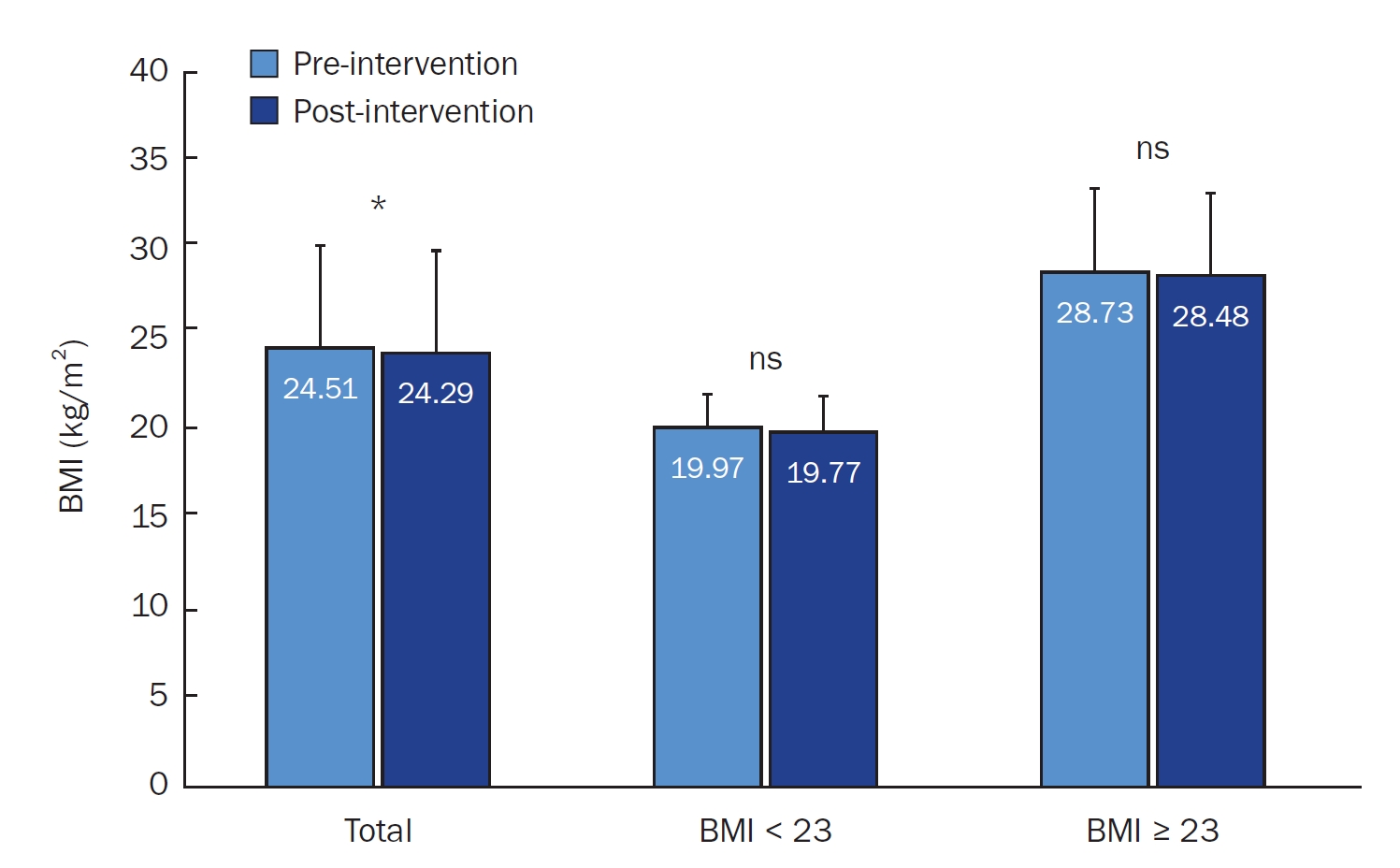
There was a significant increase in DSE (P < 0.05), particularly in managing eating behavior under stress and fatigue. A modest but significant decrease in BMI was observed in the overall group (P < 0.05), though changes were not significant in the BMI ≥ 23 kg/m2 subgroup. Glycemic indicators showed minimal changes. The overall NQ score improved slightly, with significant increases in fruit intake (P < 0.01) and nutrition label checks (P < 0.05). High satisfaction levels (4.52 ± 0.65 on a 5‑point scale) were reported for device usability and coaching services.
Conclusion
The multicomponent intervention improved DSE, NQ scores, and supported modest weight reduction among university students. The combined effect of CGM, nutrition education, and coaching appears promising; however, further studies are needed to isolate the effects of each component and evaluate long-term outcomes. Trial Registration: Clinical Research Information Service Identifier: KCT0010255.
- 1,329 View
- 24 Download

- [Korean]
- Development and Validation of a Questionnaire on the Feasibility of a Mobile Dietary Self-Monitoring Application
- Heejin Lee, Jeong Sun Ahn, Jung Eun Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(2):146-157. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.2.146
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to develop and assess the content validity and internal consistency of a questionnaire on the feasibility of mobile dietary self-monitoring applications.
Methods
We developed a feasibility questionnaire to assess the overall usage, convenience, usefulness, and satisfaction of mobile dietary applications. The initial draft of the questionnaire contained 17 items with yes/no, multiple-choice, and open-ended questions and 52 items on 5-point Likert scales. To validate the content, ten experts evaluated the relevance of the items for each subscale using a 5-point scale. We calculated the item-level content validity index (I-CVI) and scale-level content validity index (S-CVI). A total of 102 adults answered the questionnaires which reflected the experts' reviews. We conducted an exploratory factor analysis to determine the underlying structure of responses and categorized convenience, usefulness, and satisfaction. We also calculated Cronbach's alpha coefficient to examine the internal consistency of items in each subscale.
Results
The S-CVI score of the items was 0.86, and we removed items with an I-CVI score of < 0.80. We combined, revised, or separated some remaining items and added one item as per the experts' comments. As a result, we included 16 items about overall usage and 42 sub-questions. Based on the responses of the 102 adults, we performed exploratory factor analysis using the principal axis method. We retained items with a factor loading of > 0.40, resulting in a final set of 35 questions (convenience: 15, usefulness: 12, satisfaction: 8 items). The Cronbach's alpha values of the three scales were 0.93, 0.91, and 0.91 for 1) usefulness, 2) convenience, and 3) satisfaction, respectively.
Conclusions
We developed a feasibility questionnaire for mobile dietary self-monitoring applications and examined its content validity and internal consistency. Our questionnaire has the potential to measure the feasibility of mobile dietary self-monitoring applications.
- 1,213 View
- 27 Download

Original Articles
- [English]
- The Perception of Laymen and Experts Toward Mobile Applications for Self-monitoring of Diet Based on in-depth Interviews and Focus Group Interviews
- Jeong Sun Ahn, Sihan Song, Sang Eun Moon, Sejin Kim, Jung Eun Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(3):202-215. Published online June 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.3.202
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
We conducted a qualitative study to explore the feasibility of mobile applications for self-monitoring of diet.
METHODS
We conducted in-depth and focus group interviews with eight laymen who had used mobile dietary applications and eight experts. Interviews were audio-recorded and analyzed using an open coding method.
RESULTS
The qualitative data of our study revealed two key themes: (1) perceptions, opinions and attitudes towards mobile applications of self-monitoring of diet and (2) future directions to improve mobile applications.
CONCLUSIONS
Our qualitative study suggested the potential use of mobile applications as a food-tracking and dietary monitoring tool and the need for improved mobile applications for self-monitoring of diet. The results of our study may provide insights into how to technically improve mobile applications for self-monitoring of diet, how to utilize dietary data generated through mobile applications, and how to improve individual's health though mobile applications. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- NBH (Nutritious Balanced and Healthy) – An AI Enhanced Fitness Analyzer
Indhumathi Nagarajan, ABITHA V, AKSHAYA P, DHANSARA S, DHARANGINEE K R
SSRN Electronic Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Diet-Related Mobile Apps to Promote Healthy Eating and Proper Nutrition: A Content Analysis and Quality Assessment
Jihye Choi, Chongwook Chung, Hyekyung Woo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(7): 3496. CrossRef - Application and evaluation of mobile nutrition management service for breast cancer patients
Ji Hee Choi, Seon-Joo Park, Hee Kwon, Hae-Jeung Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(1): 83. CrossRef
- NBH (Nutritious Balanced and Healthy) – An AI Enhanced Fitness Analyzer
- 1,025 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Current Status of Parents' Monitoring of and Level of Trust in School Lunch Programs
- Boyoung Hur, Injoo Choi, Meeyoung Kim, Jinwook Kwon, Jiyoung Lee, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(5):401-412. Published online October 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.5.401
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to investigate the current status of parents' monitoring of school lunch programs and to examine the relationship of parents' school lunch monitoring with their level of trust in school lunch programs.
METHODS
During November 2016, a web survey was conducted with 1,283 parents who had participated in monitoring of school lunch programs. A total of 621 parents completed the questionnaires (48.4% response rate) and the responses from 442 parents were analyzed (34.5% analysis rate) for elementary (n=196) and middle/high school parents (n=246), respectively.
RESULTS
Both the elementary and middle/high school parents most wanted to participate in monitoring 1~2 times per month, which was less frequent than their current practice. They showed the highest experience rate in ‘food sanitation’ area in both the prior training and actual practice of school lunch monitoring. They most responded ‘increasing trust in school lunch programs’ as a merit and ‘lack of parents participating in monitoring’ as a problem of school lunch monitoring. The average levels of trust did not differ between elementary and middle/high school parents. Multiple regression analyses showed that elementary school parents' level of satisfaction in the monitored school lunch programs was positively associated with the parents' level of trust in general school lunch programs. Monitoring frequency and parents' age, in addition to level of satisfaction in the monitored school lunch program, were associated with level of trust in general school lunch programs among middle/high school parents.
CONCLUSIONS
There was room for change in parents' school lunch monitoring programs to meet parents' needs better. Well-managed school lunch monitoring programs contributing to parents' satisfaction with school lunch programs could increase parents' level of trust in school lunch programs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- 제한적인 등교 상황에서 중고등학생의 신체적·정신적 건강 및 식생활 행태 변화:
민지 손, 은주 윤
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(3): 213. CrossRef - Analysis of the CCP Performance and Barriers of School Foodservice Employees in the Incheon Area
Ji Eun Lee, Jung Hwa Choi
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2020; 31(3): 411. CrossRef - Development of Model for 「The Survey on School Foodservice Program」
Hae-Young Lee, Bo-Sook Yi, Jina Cha, Sun-Ok Ham, Moon-Kyung Park, Mi-Nam Lee, Hye-Young Kim, Haeng-Hwa Kang, Jin-Wook Kwon, Yun-Hui Jeong
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(1): 60. CrossRef
- 제한적인 등교 상황에서 중고등학생의 신체적·정신적 건강 및 식생활 행태 변화:
- 920 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Developing Food Safety Education Program for Employees at School Foodservice Implementing HACCP
- Hye Yeon Lee, Hyun Joo Bae
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(1):84-92. Published online February 29, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.1.84
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was performed to develop a food safety education program for school foodservice employees and evaluate its effectiveness.
METHODS
Food safety education programs were made into two levels; one for new employees in school foodservice and another for employees in charge of Critical Control Point (CCP) monitoring. The programs were for 40-minute-long lecture using PowerPoint. The effectiveness of these programs were assessed based on eleven evaluation items by school foodservice dieticians (n=30) and the Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) specialist (n=13). All statistical analyses are conducted by SPSS package program (ver 20.0).
RESULTS
According to the results of evaluating the food safety education program by dietitian and HACCP specialist, the overall satisfaction score was 4.14, evaluated by 5 point scale. There were no significant difference in results of evaluation between dieticians and HACCP specialists. The score of 'it is helpful to work' and 'pictures, images and charts are pertinent to study' were higher than others while the score of 'education contents is pleasant and interesting' and 'screen is pleasant and interesting' were the lowest among all evaluation items.
CONCLUSIONS
To increase the school foodservice quality, employees should be offered regular food safety education and training through effective education media including prerequisite program and HACCP manual for school foodservice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- 일부 학교급식 위생관리 컨설팅을 통한 개선사항 도출 연구
해림 조, 서진 김, 중범 김, 수연 김
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2025; 41(3): 151. CrossRef - Analysis of the implementation of legislation mandatory requirements in organizing meals in schools of the Sverdlovsk region
Tatiana Mazhaeva, Valentina Kozubskaya, Elena Potapkina
Food Industry.2025; 10(2): 67. CrossRef - A study on the diet and nutrition management status and educational needs in elderly care facilities in Korea: focus group interviews with staff from children’s and social welfare meal management support centers and elderly care facilities
Seo Young Choi, Hyun joo Ryou, Jieun Oh
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(4): 286. CrossRef - Assessment of Effectiveness of Inspections and Preventive Measures
in Organizing School Meals
Valentina I. Kozubskaya, Tatyana V. Mazhaeva, Elena P. Potapkina, Vladimir B. Gurvich
ЗДОРОВЬЕ НАСЕЛЕНИЯ И СРЕДА ОБИТАНИЯ - ЗНиСО / PUBLIC HEALTH AND LIFE ENVIRONMENT.2025; : 57. CrossRef - Perception on HACCP System of School Foodservices Dietitians in Chungbuk
Ji Hyeoun Im, Miao Miao Li, Young Eun Lee
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2019; 35(1): 57. CrossRef - Perception of Use of Environment-friendly Agricultural Products during School Foodservice of Mothers of Elementary School Students in Gyeonggi
Young-Un An, Myung-Hee Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi, Mi-Hyun Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(3): 234. CrossRef
- 일부 학교급식 위생관리 컨설팅을 통한 개선사항 도출 연구
- 1,076 View
- 2 Download
- 6 Crossref

Randomized Controlled Trial
- [English]
- Weight Control Program through the Fortification of Food Consumption Monitoring on Obese Female College Students: Using Smart-Phone with Real Time Communication Application
- Young Suk Kim, Jae Kyung Shin, In Sun Hong, Seon Hee Kim, Un Jae Chang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(6):697-705. Published online December 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.6.697
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was conducted to investigate the effects of real time communication digital photography method using Kakao Talk application in smart-phone for the fortification of food consumption monitoring and weight reduction. Thirty-four female college students were randomly assigned to the camera-phone (CP) group or smart-phone (SP) group. Each group participated in the weight control program for 8 weeks. The mean energy intake of CP group during program was 1353.5 kcal and the SP group consumed 1289.2 kcal. The total energy intake of both groups was significantly decreased during the program. The CP group lost 1.9 kg of body weight and 1.9% of body fat and the SP group lost 4.3 kg of body weight and 3.0% of body fat. The body weight was significantly decreased in the SP group compared to the CP group. The triglyceride and total cholesterol, and LDL-cholesterol level of SP group were significantly decreased during the program. However, there were no significant changes in CP group during the program. Also there were no significant changes in lipid profile between two groups. In this study, it is considered that real time communication digital photography method using Kakao Talk application in smart-phone might influence weight control through a trained consumption monitoring. Therefore, smart-phone can lead individuals to rely more heavily on easy-to-monitor visual cues.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Leveraging Multimodal Supports using Mobile Phones for Obesity Management in Elementary-School Children: Program Providers' Perspective from a Qualitative Study
Mi-Young Park, Jae Eun Shim, Kirang Kim, Ji-Yun Hwang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(3): 238. CrossRef - Development of tailored nutrition information messages based on the transtheoretical model for smartphone application of an obesity prevention and management program for elementary-school students
Ji Eun Lee, Da Eun Lee, Kirang Kim, Jae Eun Shim, Eunju Sung, Jae-Heon Kang, Ji-Yun Hwang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2017; 11(3): 247. CrossRef - Effect of Food Consumption Monitoring Using a Smartphone on Weight Changes in Obese Women
Young-Suk Kim, Jeong-Ja On, Yang-Hee Hong, In-Sun Hong, Un-Jae Chang
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2014; 20(2): 123. CrossRef
- Leveraging Multimodal Supports using Mobile Phones for Obesity Management in Elementary-School Children: Program Providers' Perspective from a Qualitative Study
- 856 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

Original Article
- [English]
- The Effect of the Consumption Monitoring Inaccuracy by Vision on Kimbab Intake and Satiety Rate
- Un Jae Chang, Eun Young Jung, Hyung Joo Suh, Jin Man Kim, In Sun Hong
- Korean J Community Nutr 2008;13(2):237-243. Published online April 30, 2008
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - It was examined whether altering vision would influence food intake through consumption monitoring and whether this would be reflected in consumption estimate and satiety. The experiment was designed in two visibility levels: 1) an accurate visual cue (bowl covered with wrap) vs 2) a biased visual cue (bowl covered with foil). Thirty three female college students participated in this study. The subjects ate Kimbab in the lab once a week for 2 weeks. They were served 24 pieces of Kimbab in a bowl covered either with wrap or foil. The results showed that the actual Kimbab intake from the bowl covered with foil was significantly lower than the test using wrap (13.4 +/- 3.3 pieces vs 15.0 +/- 3.8 pieces, p < 0.05). And there were no significant differences from the cognitive Kimbab intake between the tests with foil and wrap. However, the satiety rate of Kimbab in a bowl covered with foil was significantly higher than that with wrap at 1 hour and 2 hour after the Kimbab eaten (p < 0.05). Less consumed cases were recognized by subjects due to the inaccuracy during the consumption monitoring process. This result revealed that vision influences not only eating behavior but also subjective feelings of satiety after meal. In conclusion, the consumption monitoring by visual cues can play an important role in food intake and satiety rate.
- 245 View
- 1 Download


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



