Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Note
- [English]
- Pilot evaluation of a cooking-based nutrition education program to promote vegetable intake among children in Seoul, South Korea: a single-group pre–post study
- Sil-Ah Kim, Su-Jin Lee, Min-Ah Kim, Ji-Eun Oh, Sohyun Park, Hyun-Joo Ryou, Ji-Yun Hwang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(4):249-260. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00220
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
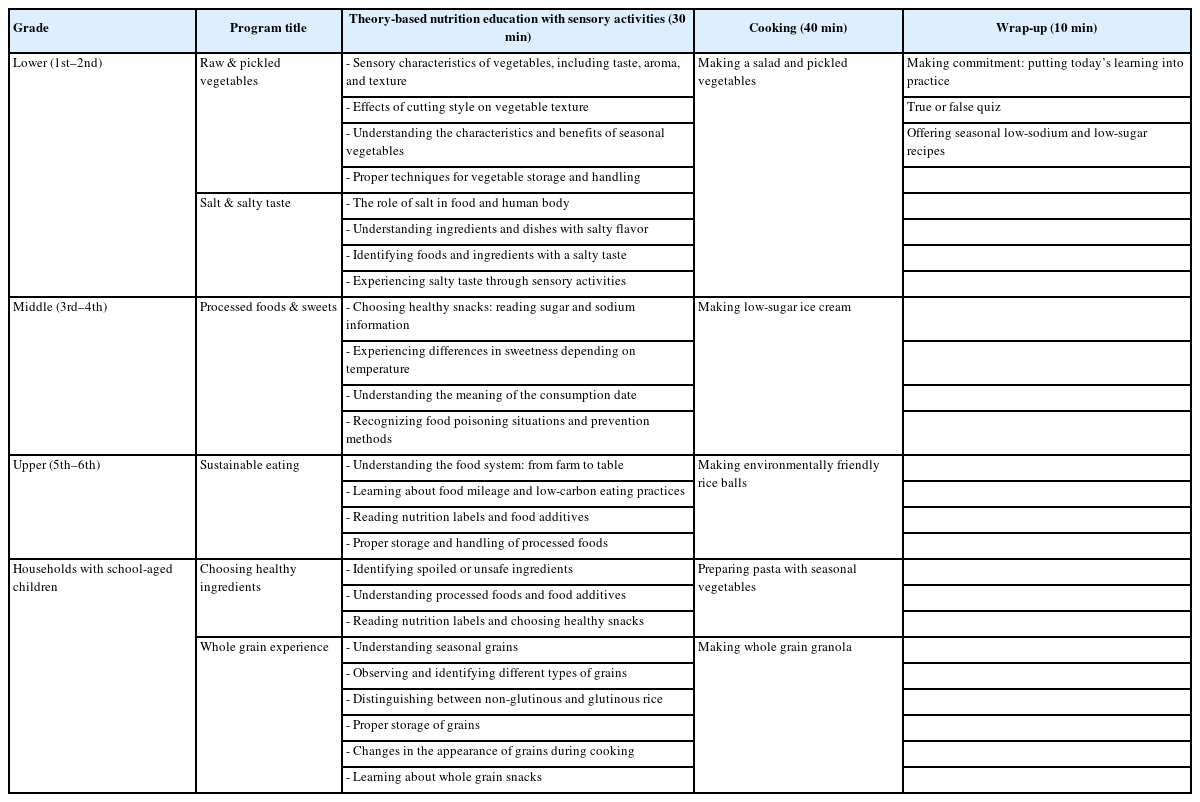
Food neophobia in children is often associated with limited exposure and familiarity to some foods. Cooking-based nutrition education (CBNE), which promotes acceptance through direct experience, may support the development of healthy eating habits. This study aimed to develop and implement a standardized CBNE program for school-aged children in Seoul, South Korea, and to evaluate its effectiveness by assessing changes in raw vegetable intake. Raw vegetable intake is an early indicator of the effectiveness of nutrition education on diverse topics in promoting healthy eating habits.
Methods
A single-group pre–post study was conducted with 37 children aged 6–11 years who participated in a 2-day CBNE program in October 2023. The participants completed pre- and post-education questionnaires and raw vegetable intake assessments. Four low-preference vegetables (bell pepper, carrot, cucumber, and tomato) were selected and served raw (25 g each) before and after the program. Intake changes were analyzed using paired t-tests, and Pearson’s correlation and hierarchical regression analyses were performed to identify predictors.
Results
Total raw vegetable intake significantly increased post-education (P = 0.008), particularly for carrots (P = 0.023). By subgroup, raw vegetable intake significantly increased in girls, upper-grade students, and those who consumed four or more vegetable side dishes per meal. Hierarchical regression analysis revealed that while vegetable preference was initially significant, vegetable-related experiences (β = 0.395, P = 0.026) and diversity of vegetable side dishes per meal (β = 0.403, P = 0.032) were stronger predictors in the final model (adj R2 = 0.333).
Conclusion
The CBNE program may enhance vegetable intake in children. Although preference remained the strongest individual factor, vegetable experience and the diversity of vegetable side dishes per meal had a greater combined effect. These findings underscore the importance of repeated and diverse exposure, not only by supporting previous studies that link such exposure to increased intake but also by suggesting that environmental support may be essential for sustaining healthy eating habits.
- 470 View
- 23 Download

Research Articles
- [Korean]
- Behavioral intention toward planetary health diet among adult users of government worksite cafeterias in Seoul, South Korea: a mixed-methods study based on the theory of planned behavior and focus groups interviews
- Ji-Won Kang, Su-Jin Lee, Sil-Ah Kim, Ji-Yun Hwang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(3):224-236. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00108
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
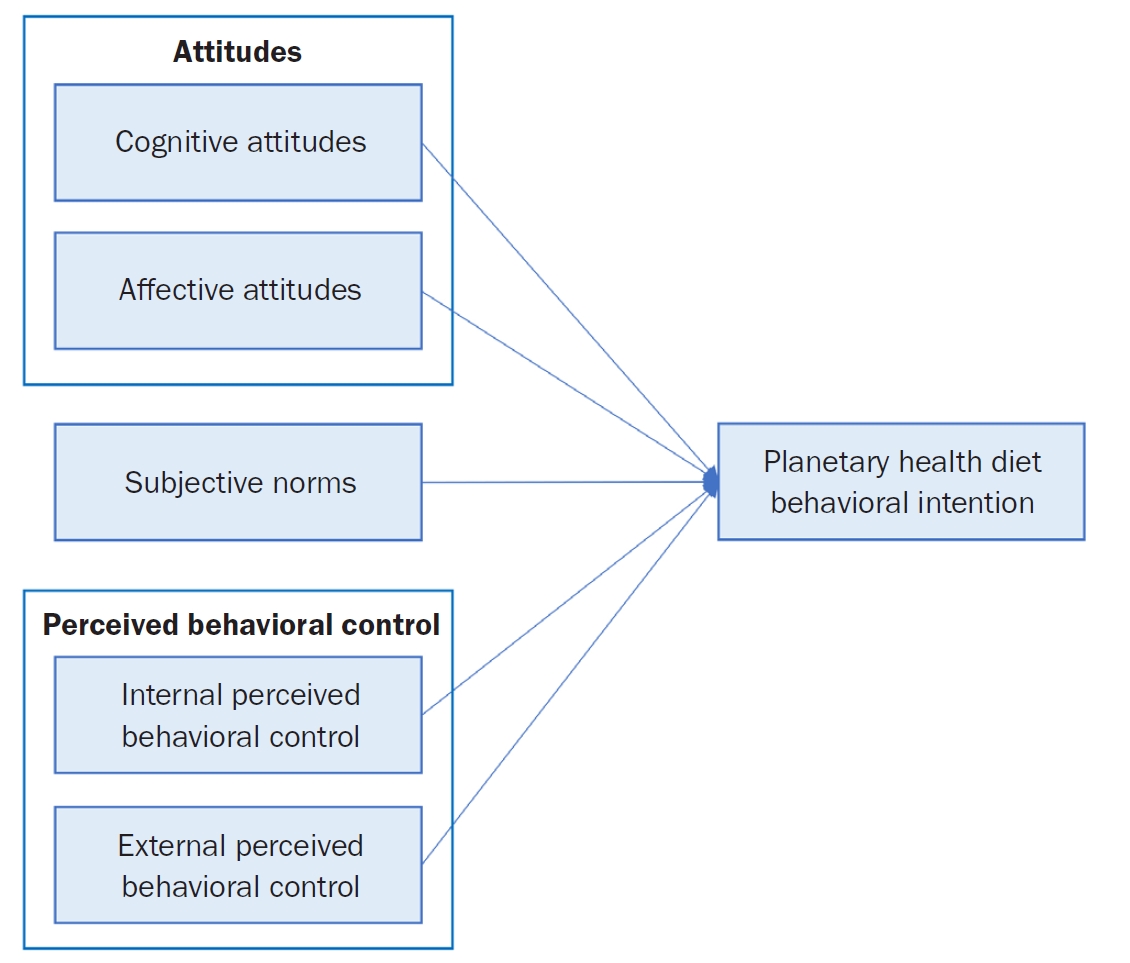
To reduce urban carbon emissions, in this study, we aimed to suggest strategies for disseminating the planetary health diet (PHD) guidelines to adult cafeterias in a government worksite in Seoul based on the theory of planned behavior (TPB) and focus group interviews (FGI).
Methods
A total of 132 adults who worked at a government worksite in Seoul and used its cafeteria were included for a TPB-based survey. Factor analyses and multiple regression were used to investigate the relationships between attitude (cognitive•affective), subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control (PBC, internal•external) and the behavioral intention to adopt the PHD. To identify the contextual factors related to PHD dissemination, 14 participants underwent in-depth interviews.
Results
Affective attitudes and PBC (internal•external) constructs of the TPB were significantly related with the intention to adopt PHD: external PBC (β = 0.324, P < 0.001), internal PBC (β = 0.269, P < 0.01), and affective attitudes (β = 0.226, P < 0.05). The FGI results highlighted the insufficiency of simply providing healthy meals to encourage the adoption of PHDs, but that menu development and natural acceptance strategies are needed to increase palatability. In addition, the need for strategies to promote PHDs at an organizational level was identified, as it is directly influenced by the company of partners with whom one dines. Furthermore, users' perceptions of how “Meals for the Planet” are delivered and suggestions for its improvement were also interpreted.
Conclusion
Our results suggest that users' beliefs, convictions, and emotions are important while promoting or educating individuals about sustainable PHDs. Our findings are expected to help local governments or private group cafeterias that wish to introduce PHDs in the future, given the growing importance of environmentally conscious eating. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Planetary Health Diet Adherence in Korean Adults: Association with the Korean Healthy Eating Index
Su-Jin Lee, Ji-Yun Hwang
Nutrients.2025; 17(19): 3060. CrossRef
- Planetary Health Diet Adherence in Korean Adults: Association with the Korean Healthy Eating Index
- 676 View
- 47 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Application of a living lab model to an evidence-based reduced-sodium healthy eating practice program in Korea: a pre-post study
- Jung-Hyun Kim, Eugene Shim, Min Sook Kyung, Sooyoun Kwon, Hyoung Su Park, Jae-Heon Kang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):53-63. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00346
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
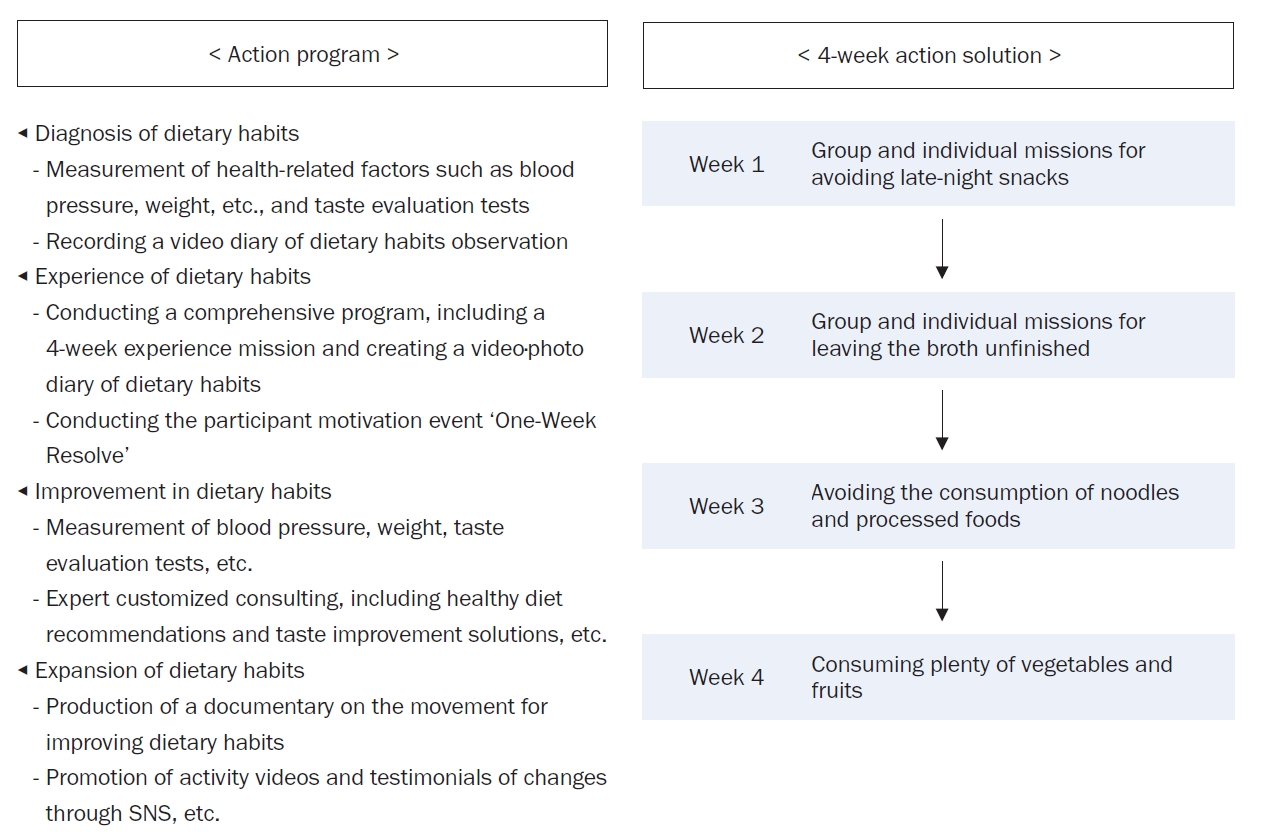
To apply a healthy dietary program with reduced sodium intake, developed using data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), focusing on the sodium intake level and eating patterns.
Methods
The program was implemented using a living lab model, an open innovation ecosystem for user-centered problem-solving. Analysis of the KNHANES data revealed that older age groups had a low energy intake but a high sodium intake, particularly among those who frequently dined out. The program was designed to improve sodium-reduction literacy and enhance practical competency. Over four weeks, 40 participants tracked their dietary intake and worked with a clinical nutritionist through a process of diagnosis, experience, improvement, and expansion. A self-administered survey was conducted before and after the program to assess effectiveness.
Results
Participants were four teenagers (10%), 26 in their twenties (65%), and 10 aged ≥ 30 years (25%), with eight males (20%) and 32 females (80%). Post-program analysis showed significant improvements in sodium-related nutrition knowledge (P < 0.01), with increased agreement on adopting low-sodium intake practices (e.g., interest in sodium content, choosing lower-sodium foods). Nutrient intake analysis showed a decrease in energy, carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins (P < 0.001), with sodium intake decreasing from 3,382.37 mg/d to 2,119.05 mg/d (P < 0.001).
Conclusion
The community-based, living lab model for the sodium-reduction program effectively improved participant sodium-reduction literacy and practical competency, suggesting that step-by-step, autonomous learning, can reduce sodium intake and promote healthier eating habits.
- 1,287 View
- 45 Download

- [Korean]
- Development and application of a dietary program to reduce sugar intake using a living lab approach in Korea: an intervention study
- Jung-Hyun Kim, Min Sook Kyung, Seul Ki Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(6):504-513. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00318
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to develop and apply a dietary program to reduce sugar intake among community residents using a Living Lab approach.
Methods
We developed and applied a community-based dietary program to reduce sugar intake. Participants were recruited from community organizations, including a children’s food service management center, elementary to high schools, a university, a family center, a community health center, and an elderly welfare center. The dietary program was conducted in two phases; start and next levels. The start level included a pre-assessment of dietary behaviors and participation in educational platforms, whereas the next level included activities using educational platforms, tailored mission and feedback, and pre- and post-surveys. Extension educators at each community organization implemented the dietary program following organization-specific guidelines. Changes in participants’ nutrition knowledge, dietary behaviors and perceptions, self-efficacy, intention to reduce sugar intake, and participants’ program satisfaction were analyzed using paired t-tests.
Results
In total, 1,238 and 339 individuals participated in the start and next level, respectively. Participants reported significantly lower scores on dietary behavior items regarding drinking more juice or soft drinks after program participation (P = 0.009) and craving sweet foods (P = 0.046). They reported a higher intention to take interest in sugar content in food (P = 0.009) and lower-sugar recipes (P = 0.019), eat less food with high sugar content (P = 0.020), and drink water or sparkling water instead of soft drinks (P = 0.042). Nutrition knowledge did not significantly change after program participation. Program satisfaction significantly increased from the start level to the next level (P<0.050).
Conclusion
This study showed the potential of using a Living Lab approach to implement community-wide dietary interventions. Further research is required to evaluate the effectiveness of the Living Lab approach in various community settings.
- 1,261 View
- 53 Download

- [Korean]
- Food purchase patterns, food policy recognition, and food environment satisfaction among adults in Jeju, Korea, according to food security: a cross-sectional study
- Sumin Kim, Youjeong Jang, Hyunji Ham, Hanbin Ko, Insuk Chai, Kyungho Ha
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(5):406-417. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00012
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
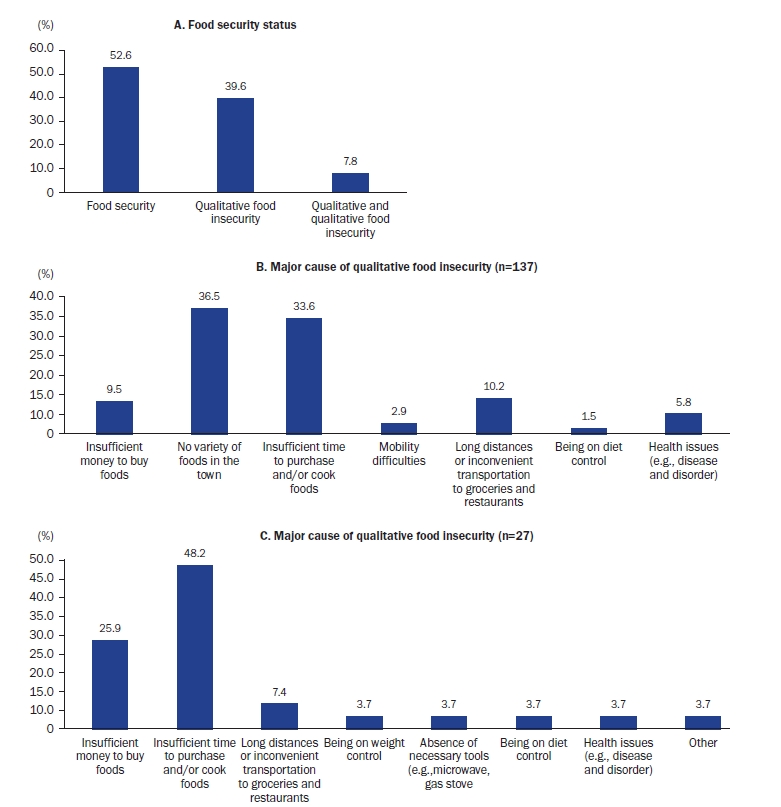
Recently, food insecurity has been a major public health issue along with the food crisis caused by COVID-19, climate change, and the polarization of food supply due to socioeconomic disparities. Food insecurity is known to be related to the food choices and environment of the consumer. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the food security statuses of adults in Jeju and investigate their food purchase patterns, food policy recognition, and food environment satisfaction.
Methods
Based on data from the 2022 Jeju Food Survey, 346 adults aged ≥19 years in Jeju were classified into food security and insecurity groups (quantitatively and qualitatively) using the questionnaire. Food purchase patterns, including purchasing frequency, items, and reasons, were surveyed for local and eco-friendly foods. The recognition and necessity of several food policies and satisfaction with diet and food environment (availability, accessibility, affordability, accommodation, and acceptability) were measured using the Likert scale.
Results
Among the total participants, 47.4% were in the food insecurity group. The frequency of purchasing local and eco-friendly foods did not significantly differ by food security status. The insecurity group exhibited a higher recognition rate of basic rights to food (36.0%) than the security group (24.7%, P = 0.023). The recognition and necessity of specific food policies did not significantly differ by food security status, except for the policy of promoting food communities, for which the food security group exhibited higher recognition than the food insecurity group did (P = 0.004). The food insecurity group exhibited significantly lower scores regarding satisfaction toward diet and food environment factors (P < 0.05 for all).
Conclusions
Overall, the food security group reported higher satisfaction with their diet and food environment than the food insecurity group. Further in-depth studies to investigate the determinants of food insecurity and effective promotional strategies for food policies are needed.
- 1,445 View
- 48 Download

- [Korean]
- Relationship between Eating Behavior and Healthy Eating Competency of Single-Person and Multi-Person Households by Age Group
- Seung-Hee Hong, Ji-Myung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(5):337-349. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.5.337
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to analyse the relationship between eating behaviour and healthy dietary competency of single and multi-person households, to improve healthy eating behavior.
Methods
This study was conducted on 6,355 adult household members who participated in the Food Consumption Behavior Survey 2020. The subjects were divided into age groups comprising young people in their 20s and 30s, middle-aged people in their 40s and 50s, and the elderly in their 60s and above. The eating behavior and healthy dietary competency of single-person and multi-person households were then analyzed.
Results
The average age of the members in the single-person households was found to be higher. Single-person households were also found to have a lower marriage rate and lower monthly household income than multi-person households across the age groups of young, middle-aged, and elderly people (P < 0.05). Among each of the age groups, single-person households had significantly higher rates of skipping breakfast and eating breakfast, lunch, and dinner alone than multi-person households (P < 0.05). Young single-person households had lower average scores on healthy dietary competency than multi-person households (P = 0.032). When adjusted for age, gender, marriage, education, occupation, and household income, single-person households had a higher risk of delivery/take-out, eating out, or skipping meals compared to multi-person households (P < 0.05). In multi-person households, the risk of skipping meals, eating alone, eating out, or delivery/take-out decreased as healthy dietary competency improved (P< 0.05). On the other hand, in single-person households, as healthy dietary competency increased, the risk of delivery/take-out or eating alone decreased (P< 0.05).
Conclusions
The results of this study suggest that healthy dietary competency and eating practices can be improved by providing customized dietary education by age group for single and multi-person households. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Dietary Habits, Physical Activity, and Perceived Health Status on Health‐Related Quality of Life by Household Characteristics of Patients With Chronic Diseases: The Korea Community Health Survey (KCHS)
Soyean Kang, Hae Sagong, Juyoung Lee
Public Health Nursing.2025; 42(3): 1182. CrossRef - Understanding the charactersitics and types of single-person households based on food purchase frequencies in Korea: a cross-sectional study using the 2023 Consumer Behavior Survey for Foods
So-Yun Kim, Youngmin Nam, Jong-Youn Rha, Haerang Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(1): 27. CrossRef - Dietary status and the relationship between dietary competencies, cooking skills, and nutrition quotient of middle-aged adults living alone in Korea
Sooyoun Kwon, Youngmi Lee, Yun-Jung Bae
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(2): 257. CrossRef - A study on regional differences in dietary behaviors and satisfaction in Korea focusing on urban and rural comparisons: a cross-sectional study
Jong-Youn Rha, Sohyun Kim, Hae-Rang Lee, Juhyeon Kil
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(2): 140. CrossRef - Antioxidant and Nutrition Facts Analysis of Konjac Jelly Stick Containing Pinus koraiensis Leaf Powder
Eunbin Park, Soo-In Ryu, Kyung Tae Jang, Jean Kyung Paik
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2025; 54(5): 402. CrossRef - Comparative study on eating habits and health of single-person and multi-person households
Haerang Lee, Seon-Jip Kim, Minji Kang, Mi-So Shim
PLOS One.2025; 20(7): e0327763. CrossRef - The impact of flash continuous glucose monitoring and nutrition coaching on dietary self-efficacy and weight management in university students in Korea: a pre-post intervention study
Soojin Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(3): 183. CrossRef - Single-Person Households: Insights from a Household Survey of Fruit and Vegetable Purchases
Andres Silva, Maripaz Rivera, Samuel Durán-Agüero, Maria Isabel Sactic
Nutrients.2024; 16(17): 2851. CrossRef - Association of delivered food consumption with dietary behaviors and obesity among young adults in Jeju
Minjung Ko, Kyungho Ha
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(3): 336. CrossRef - Comparison of Food and Nutrient Intake according to the Income Level in Korean Adult Single-Person Households: Using Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016-2018)
Min-Hee Han, Bok-Mi Jung
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2024; 35(3): 445. CrossRef - Hazardous alcohol use is associated with food insecurity in adults living alone: Findings from a nationwide study in Korea
Seong-Uk Baek, Yu-Min Lee, Jin-Ha Yoon, Jong-Uk Won
Social Science & Medicine.2024; 362: 117468. CrossRef - Malnutrition risk, nutritional knowledge, and dietary intake in chronic kidney disease patients on hemodialysis: comparison according to coexisting diabetes
HyunJung Yoo, Sang Cheol Lee, Hye-Kyeong Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(5): 481. CrossRef - A pilot investigation of a combined food literacy and exercise program for college students: a one-group pre-post intervention study
Minjeong Jeong, Jinhyun Kim, Dahye Han, Eunjin Jang, Kyoungho Choi, Sohyun Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 455. CrossRef - Associations of cooking practices and healthy eating habits among young Korean adults in their 20s
So-Young Kim, Ji Yu Choi
International Journal of Gastronomy and Food Science.2023; 31: 100644. CrossRef - 밀키트 이용 고객의 식생활 양식과 밀키트 선택속성이 밀키트 제품의 만족도에 미치는 영향 분석
세은 김, 현주 배
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(3): 187. CrossRef - The relationship between the prevalence of anemia and dietary intake among adults according to household types based on data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hye Won Kim, Ji-Myung Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(5): 510. CrossRef - Improving the nutrition quotient and dietary self-efficacy through personalized goal setting and smartphone-based nutrition counseling among adults in their 20s and 30s
Dahyeon Kim, Dawon Park, Young-Hee Han, Taisun Hyun
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(4): 419. CrossRef - Comparison of Eating Habits and Behaviors of Young Single-Person Households based on Food-Related Lifestyle
Dokyung Kim, Sim-Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2023; 23(3): 117. CrossRef - Perception to the dietary guidelines for Koreans among Korean adults based on sociodemographic characteristics and lifestyle
Yejin Yoon, Soo Hyun Kim, Hyojee Joung, Seoeun Ahn
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(6): 742. CrossRef - Association between Healthy Eating Index and Mental Health in Middle-Aged Adults Based on Household Size in Korea
Ji-Myung Kim, EunJung Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(8): 4692. CrossRef
- Impact of Dietary Habits, Physical Activity, and Perceived Health Status on Health‐Related Quality of Life by Household Characteristics of Patients With Chronic Diseases: The Korea Community Health Survey (KCHS)
- 1,428 View
- 74 Download
- 20 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Can Dining Alone Lead to Healthier Menu Item Decisions than Dining with Others? The Roles of Consumption Orientation and Menu Nutrition Information
- EunSol Her, Carl Behnke, Barbara Almanza
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(3):155-166. Published online June 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.3.155
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Driven by a growth of single-person households and individualized lifestyles, solo dining in restaurants is an increasingly recognizable trend. However, a research gap exists in the comparison of solo and group diners’ menu-decision making processes. Based on the self-control dilemma and the temporal construal theory as a theoretical framework, this study compared the ordering intentions of solo vs. group diners with healthy vs. indulgent (less healthy) entrées. The mediating role of consumption orientation and the moderating role of amount of menu nutrition information were further explored to understand the mechanism and a boundary condition.
Methods
A scenario-based online survey was developed using a 2 (dining social context: solo vs. with others) × 3 (amount of menu nutrition information: no nutrition information vs. calories vs. calories/fat/sodium), between-subjects, experimental design. Consumers’ level of nutrition involvement was controlled. A nationwide survey data (n = 224) were collected from a crowdsourcing platform in the U.S. Data were analyzed using multivariate analysis of covariance, independent t-test, univariate analysis of covariance, and moderated mediation analyses.
Results
Findings reveal that solo (vs. group) diners have less (vs. more) intentions to order indulgent menu items due to a more utilitarian (vs. more hedonic) consumption orientation in restaurant dining. Findings also show that solo (vs. group) diners have more (vs. less) intentions to order healthy menu items when the restaurant menu presented nutrition information including calories, fat, and sodium.
Conclusions
The findings contribute to the literature of foodservice management, healthy eating, and consumer behavior by revealing a mechanism and an external stimuli of solo vs. group diners’ healthy menu-decision making process in restaurants. Furthermore, the findings provide restauranteurs and health professionals with insights into the positive and negative impacts of menu nutrition labelling on consumers’ menu-decisions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Eating contexts encourage sustainable food choices: The mediating role of the symbolic meanings of foods
Chujun Wang, Xiaoang Wan
Appetite.2025; 207: 107896. CrossRef - A systematic review of solo dining research
Huiling Huang, Scarlett Sijia Feng, IpKin Anthony Wong
International Journal of Hospitality Management.2025; 130: 104226. CrossRef
- Eating contexts encourage sustainable food choices: The mediating role of the symbolic meanings of foods
- 1,057 View
- 9 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- The Changes in Obesity Prevalence and Dietary Habits in Korean Adults by Residential Area during the Last 10 Years – Based on the 4th (2007-2009) and the 7th (2016-2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data
- Da-Mee Kim, Kyung-Hee Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(1):37-47. Published online February 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.1.37
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to discover the changes in obesity prevalence and dietary habits in Korean adults residing in various residential areas during the last 10 years. Methods: Data on Korean adults aged 19 years and above was obtained from the 4th (2007-2009) and the 7th (2016-2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. The subjects were classified into metropolitan 4th : n=5,977, 7th : n=6,651), urban (4th : n=4,511, 7th : n=5,512) and rural (4th : n=3,566, 7th : n=2,570) based on their residence. The general characteristics, nutrient intake, intake amount, food groups, and healthy dietary factors were analyzed. The association between residential areas and obesity prevalence were analyzed by multiple logistic regression. Results: In urban and rural areas, the obesity rate increased in the 7th survey compared to the 4th survey, excluding the metropolitan area. The carbohydrate intake decreased, and lipid intake increased in the 7th survey compared to the 4th survey. Over the same period, the intake of cereals and vegetables decreased, and the intake of meat and processed foods increased. Rural residents had a higher intake of cereals and vegetables, and a lower intake of milk and processed foods than those in metropolitan areas and urban residents. The proportion of subjects who practiced a healthy diet increased in the 7th survey compared to the 4th survey. In the 4th survey, there was no relationship seen between the prevalence of obesity and the subject’s residential area, but in the 7th survey, the odds ratio of obesity was higher in rural areas than in the metropolitan areas, confirming the regional gap (OR: 1.16, 95% CI=1.00-1.36, p=0.044). Conclusions: This study showed that the obesity prevalence increased in rural residents compared to metropolitan residents, indicating a gap between the regions. The nutrient intake and intake of food groups changed in the 10 years under consideration, and there were differences seen between regions. Therefore, it is necessary to formulate a policy that will reduce obesity prevalence and health inequalities between regions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between chemotherapy and the risk of developing breast cancer-related lymphedema: a nationwide retrospective cohort study
Sung Hoon Jeong, Seong Min Chun, Hyunji Lee, Miji Kim, Mira Choi, Ja-Ho Leigh
Supportive Care in Cancer.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of Pancreatic Cancer After Acute Pancreatitis: A Retrospective Analysis of the Korean National Sample Cohort
Sung Hoon Jeong, Kyungduk Hurh, Eun-Cheol Park, Ja-ho Leigh, Seung Hoon Kim, Sung-In Jang
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of ultra-processed food with diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in elderly populations (urban and rural): a cross-sectional study
Seung Jae Lee, Mi Sook Cho
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(1): 51. CrossRef - Association of heavy metal complex exposure and neurobehavioral function of children
Minkeun Kim, Chulyong Park, Joon Sakong, Shinhee Ye, So young Son, Kiook Baek
Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Anti-Obesity Activity of Ethanol Extract of Veronica peregrina L.
Su Min Kim, Cheol Park, Yung Hyun Choi, Hye Jin Hwang
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(4): 350. CrossRef - Effect of Type of Nutrition Labeling on the Healthfulness Evaluation and Purchase Intentions of Home Meal Replacements (HMR) in South Korea
Mee-Young Joe
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(5): 387. CrossRef - Blood Biochemical Characteristics, Dietary Intake, and Risk Factors Related to Poor HbA1c Control in Elderly Korean Diabetes Patients: Comparison between the 4th(2007-2009) and the 7th(2016-2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
Sung-Won Oh, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(5): 406. CrossRef - Interactions between red and processed meat consumption and APOA5 gene variants associated with the incidence of metabolic syndrome in Korean adults
Woo Jeong Choi, Dayeon Shin
Genes & Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Dietary Quality with Subjective Health-Related Perception and Chronic Diseases According to Age Segmentation of Korean Elderly
Sojeong Lee, Seungmin Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 363. CrossRef - Regional Disparity in Adult Obesity Prevalence, and Its Determinants
Bongjeong Kim
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2021; 46(4): 410. CrossRef - Obese Frailty and Combined Exercise
Hae Sung Lee, Jong-Hee Kim
Exercise Science.2021; 30(4): 419. CrossRef
- Association between chemotherapy and the risk of developing breast cancer-related lymphedema: a nationwide retrospective cohort study
- 668 View
- 5 Download
- 11 Crossref

Original Articles
- [English]
- Relation between the Total Diet Quality based on Korean Healthy Eating Index and the Incidence of Metabolic Syndrome Constituents and Metabolic Syndrome among a Prospective Cohort of Korean Adults
- Saerom Shin, Seungmin Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(1):61-70. Published online February 29, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.1.61
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - OBJECTIVES
This study examined the association of the total diet quality with the incidence risk of metabolic syndrome constituents and metabolic syndrome among Korean adults.
METHODS
Based on a community-based cohort of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES) from 2001 to 2014, data from a total of 5,549 subjects (2,805 men & 2,744 women) aged 40~69 years at the baseline with a total follow-up period of 38,166 person-years were analyzed. The criteria of the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel was employed to define metabolic syndrome. The total diet quality was estimated using the Korean Healthy Eating Index (KHEI). Hazard ratios (HR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) for risk of metabolic syndrome constituents and metabolic syndrome in relation to KHEI quintile groups was calculated by multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression model.
RESULTS
After adjusting for age, energy intake, income, education, physical activity, smoking, and drinking, the incidence of abdominal obesity and high blood pressure was significantly lower, by approximately 29.7% (P < 0.01) and 25.2% (P < 0.01), respectively, in the fifth KHEI quintile compared to the first quintile in men. A significant decreasing trend of the metabolic syndrome incidence was observed across the improving levels of KHEI (HRq5vs.q1: 0.775, 95% CIq5vs.q1: 0.619~0.971, P for trend < 0.01). In women, the incidence of abdominal obesity and metabolic syndrome was significantly lower, by approximately 29.8% (P < 0.01) and 22.5% (P < 0.05), respectively, in the fifth KHEI quintile compared to the first quintile adjusting for multiple covariates. On the other hand, the linear trend of metabolic syndrome risk across the KHEI levels did not reach the significance level.
CONCLUSIONS
A better diet quality can prevent future metabolic syndrome and its certain risk factors among Korean men and women. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The mediating effect of the Korean Healthy Eating Index on the relationship between lifestyle patterns and metabolic syndrome in middle-aged Koreans: data from the 2019–2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Sori On, Woori Na, Cheongmin Sohn
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(1): 96. CrossRef - FTO rs9939609 polymorphism is associated with dietary quality in Korean females
Minjeong Kim, Jeong-Hwa Choi
European Journal of Nutrition.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Gender-specific association of diet with the risk of loss of muscle mass in Korean baby boomers: a prospective population-based cohort analysis
Eun-Hee Jang, Seungmin Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(4): 635. CrossRef - Association between Korean Healthy Eating Index and abdominal obesity in Korean adults: the mediating effect of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein
Jina Yoon, Dayeon Shin
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(1): 88. CrossRef - Association between Dietary Quality and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Korean Adults: A Nationwide, Population-Based Study Using the Korean Healthy Eating Index (2013–2021)
Seong-Uk Baek, Taeyeon Kim, Yu-Min Lee, Jong-Uk Won, Jin-Ha Yoon
Nutrients.2024; 16(10): 1516. CrossRef - TAS2R38 bitterness receptor genetic variation is associated with diet quality in Koreans
Hae Young Kim, Jeong-Hwa Choi
Appetite.2024; 200: 107561. CrossRef - Contents of Pantothenic Acid in Frequently Consumed Korean Vegetables and Fruits
Jihwan Kim, Jina Lee, Yoonjeong Kim, Eunji Park, Jinju Park, Youngmin Choi, Younghwa Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2024; 53(8): 816. CrossRef - Association of Social Jetlag with the Dietary Quality Among Korean Workers: Findings from a Nationwide Survey
Seong-Uk Baek, Jin-Ha Yoon
Nutrients.2024; 16(23): 4091. CrossRef - Association between green tea consumption and metabolic syndrome among Korean adults: results from the Health Examinees study
Hyeonjin Cho, Sunwoo Han, Jiwon Jeong, Hyein Jung, Sangah Shin
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(1): 70. CrossRef - Obesity-Status-Linked Affecting Factors of Dyslipidemia in Korean Young-Adult Men: Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019–2021)
Min Kwon, Jinheum Kim, Eunjeong Cha
Healthcare.2023; 11(14): 2015. CrossRef - The association of the Korean Healthy Eating Index with chronic conditions in middle-aged single-person households
EunJung Lee, Ji-Myung Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(2): 316. CrossRef - Association between the Korean Healthy Eating Index and Serum Vitamin D Level in Korean Adults: 2013–2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
So-Yoon Choi, Yu-Jin Kwon, Ji-Won Lee
Korean Journal of Family Practice.2023; 13(4): 218. CrossRef - Benefits of adherence to the Korea Healthy Eating Index on the risk factors and incidence of the metabolic syndrome: analysis of the 7th (2016–2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Sun A Choi, Sung Suk Chung, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(1): 120. CrossRef - Prediction of metabolic and pre-metabolic syndromes using machine learning models with anthropometric, lifestyle, and biochemical factors from a middle-aged population in Korea
Junho Kim, Sujeong Mun, Siwoo Lee, Kyoungsik Jeong, Younghwa Baek
BMC Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of the Nutrition Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Carrots and Parsnips
Yeon-Jin Park, So-Yeon Han, Jae-Joon Lee
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2022; 33(1): 83. CrossRef - Analysis of Fruit Consumption and the Korean Healthy Eating Index of Adults Using the 2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Sun A Choi, Sung Suk Chung, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2021; 50(10): 1124. CrossRef - Association of Dietary Quality with Subjective Health-Related Perception and Chronic Diseases According to Age Segmentation of Korean Elderly
Sojeong Lee, Seungmin Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 363. CrossRef - Association between frailty and dietary quality in community-dwelling elderly: data from the 6th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2014–2015)
Woori Na, Hyeji Kim, Cheongmin Sohn
Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Nutrition.2021; 68(3): 268. CrossRef - Changes in Prevalence of Body Mass Index and Metabolic Syndrome during COVID-19 Lockdown Period
Ji Young Kwon, Sang-Wook Song, Ha-Na Kim, Sung Gu Kang
Korean Journal of Family Practice.2021; 11(4): 304. CrossRef
- The mediating effect of the Korean Healthy Eating Index on the relationship between lifestyle patterns and metabolic syndrome in middle-aged Koreans: data from the 2019–2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,117 View
- 41 Download
- 19 Crossref

- [English]
- Development and Application of an Education Program for Healthy Dietary Life for Elementary School Aftercare Class Children
- Jung Hyun Kim, Min Sook Kyung, In Young Park, Young Sim Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(6):497-511. Published online December 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.6.497
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - OBJECTIVES
This study aimed to develop a school-centered healthy eating environment for children in elementary care classrooms and prevent incorrect eating habits and obesity through the development and application of standardized healthy eating habit-forming educational materials.
METHODS
Ten schools in eight districts of Gyeonggi-do and 400 students from 19 care classes were selected. Based on the developed educational materials, the program was applied to students once in two weeks. ‘Notices for Parents’ forms were also sent to the students' home to educate their parents. Pre and post-surveys were conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of the education. The pre-education, education, and aftercare were conducted from September 28 to September 31, 2016, from October 3 to November 30, 2016, and from December 5 to December 9, 2016, respectively.
RESULTS
The healthy eating program for elementary care classes was designed to develop a school-centered healthy eating environment and provide standardized educational material for healthy eating habits. Twelve educational topics were developed: 〈Eat Evenly〉, 〈Eat Breakfast〉, 〈Eat vegetables and Fruits〉, 〈Clean Body, Strong Body〉, 〈Healthy and Tasty Snacks〉, 〈Keep Healthy Weight〉, 〈Food that enters our body〉, 〈What is safe food?〉, 〈Food selection and Storage〉, 〈Our land, Our grain〉, 〈Enjoy Traditional Food〉, and 〈Food manners〉. Moreover, the materials were produced in four forms: for students, for after school caring teachers, for external specialists, and for parents. The effectiveness evaluation was conducted to confirm the application of the program. The average eating habits score was 3.3 ± 0.6, with no significant difference between before and after application. The score of overall satisfaction of the education was 3.9 ± 0.9. The most satisfying content was ‘Did you get to know how to eat evenly?’. Significant increases were observed in two contents for parents regarding their children's knowledge changes after the education: ‘Five nutrients needed for growing children’ and ‘Knowing sugar foods and sugar-containing foods’. On the other hand, their educational satisfaction was 3.6 ± 0.6, which was lower than the children's satisfaction. This might be because their education was conducted only through the ‘Notices for Parents’ form.
CONCLUSIONS
In the long term, the healthy eating habit-formation education for lower elementary school children is expected to be beneficial. To prevent obesity and establish healthy eating habits of children, it is important to develop healthy eating education programs centered on elementary school aftercare classes, including the development of educational materials and an application system through connection with the home and community. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Interactive Live and Online Cooking Program for Children in Vulnerable Families—An Exploratory Study
Jiyoung Park, Sein Hwang, Seolhyang Baek, Gill A. Ten Hoor
Healthcare.2022; 10(12): 2389. CrossRef
- An Interactive Live and Online Cooking Program for Children in Vulnerable Families—An Exploratory Study
- 910 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- A Study on the Development of the Goals and Contents System of Healthy Dietary Education Program for After-School Care in Lower Grade in Elementary School
- Jung Hyun Kim, Myoung Hee Lee, Okjin Park, Kyung Sook Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(1):24-37. Published online February 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.1.24
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - OBJECTIVES
The study purpose is to develop a content system for a healthy dietary education program for after-school care in lower grade in elementary school.
METHODS
The contents of healthy dietary education in the 2015 revised curriculum and textbooks and the major education programs related to dietary life that are currently used in elementary school education were analyzed. Focus group interviews were held with field experts related to lower grade in elementary care class. Accordingly, the structuring of the education area and the detailed education contents were systematized.
RESULTS
From the analysis results, the contents of curriculum, textbook, and administrative department were classified as hygiene safety, health, and culture. The goal of the educational content system was divided into three areas: nutritional dietary life, food hygiene and health, and food culture. The subjects consisted of dietary balance, healthy body weight, digestion and absorption, food hygiene, Korean agricultural products, traditional food, and table manners. The curriculum was composed of 12 content elements.
CONCLUSIONS
In order to ensure that after-school care students can grow into healthy, growth-oriented and creative talents, the role of the caring guide is important, and associated guidelines are needed in the future. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Application of an Education Program for Healthy Dietary Life for Elementary School Aftercare Class Children
Jung-Hyun Kim, Min Sook Kyung, In-Young Park, Young Sim Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(6): 497. CrossRef
- Development and Application of an Education Program for Healthy Dietary Life for Elementary School Aftercare Class Children
- 743 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Current Status and Suggested Future Directions of Nutrition Intervention using Healthy School Tuck Shops: the Teenage Perspective
- Suhyun Oh, Kirang Kim, Ji Yun Hwang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(3):226-233. Published online June 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.3.226
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to investigate the current status and to suggest future directions for health management of teenagers who use healthy school tuck shops to improve teenagers' eating habits while reducing and preventing obesity.
METHODS
A total of 29 students (16 middle school students and 13 high school students) took part in the interview for this study, and the interview was conducted for each school's focus group by using qualitative research methodology.
RESULTS
The current status of using healthy school tuck shops and suggested future directions were divided into two categories. Personal barriers such as discrepancies between personal perceptions and behaviors and lack of food choice suitable to individual tastes can be solved by rebuilding the operating system to provide intuitive promotion of behavior and customized products through improvements in existing products and new product development. A lack of consistent management from low utilization convenience and difficulty in maintaining a constant purchase price can be handled by establishing a solution to restricted physical access for products, as well as seeking profit by improving distribution costs via continuous cooperation between the school and community.
CONCLUSIONS
Continuous funding and a system that reflects the needs and preferences of healthy school tuck shop users should be applied for sustainable operation of healthy school tuck shops to improve teenagers' eating habits. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Eating Out Status according to Skipping and Type of Breakfast among Male High School Students in Incheon
Eun-Jin Choi, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(2): 102. CrossRef
- Eating Out Status according to Skipping and Type of Breakfast among Male High School Students in Incheon
- 758 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Associations between Exposure to Unhealthy Food Outlets Within Residential District and Obesity: Using Data from 2013 Census on Establishments and 2013-2014 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Yoonjung Kim, Sung Nim Han
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(5):463-476. Published online October 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.5.463
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - OBJECTIVES
Environmental, social and personal factors influence eating patterns. This study aimed to investigate the relationship between unhealthy food outlets within a residential area and obesity using nationally representative Korean survey data and data from the Census on Establishments.
METHODS
Data on the food intakes and socioeconomic variables of a total of 9,978 adults aged ≥ 19 years were obtained from the 2013-2014 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Geographic locations of restaurants were obtained from the 2013 Census on Establishments in Korea. Administrative area was categorized into tertiles of count of unhealthy food outlets based on the distribution of number of unhealthy food outlets among all urban (Dong) and rural (Eup or Myun) administrative districts in Korea. Multilevel logistic regressions model were used to assess the association between the number of unhealthy food outlets and obesity.
RESULTS
People living in the district with the highest count of unhealthy food outlets had higher intakes of fat (45.8 vs. 44.4 g/day), sodium (4,142.6 vs. 3,949.8 mg/day), and vitamin A (753.7 vs. 631.6 µgRE/day) compared to those living in the district with the lowest count of unhealthy food outlets. A higher count of unhealthy food outlets was positively associated with frequent consumption of instant noodles, pizza, hamburgers and sandwiches, sweets and sour pork or pork cutlets, fried chicken, snacks, and cookies. Higher exposure to unhealthy food outlets was associated with increased odds of obesity (1st vs. 3rd tertile; OR 1.689; 95% CI 1.098-2.599).
CONCLUSIONS
A high count of unhealthy food outlets within a residential area is positively associated with the prevalence of obesity in Korea. The results suggest that food environmental factors affects the health outcomes and interventions aiming to restrict the availability of unhealthy food outlets in local neighborhoods may be a useful obesity prevention strategy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Obesity-Related Factors in Adult Women with Early Menarche
Hunha Cho, Jeong-Won Han
Healthcare.2023; 11(4): 557. CrossRef - Associations between adolescent dietary habits, obesity and food environment around schools in Seoul
Hyun-Jae Woo, Hong Lim Lee, Hae-Young Kim
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2022; 39(5): 55. CrossRef - Relationship between the Intake of Children's Favorite Foods and Policy based on Special Act on Safety Control of Children's Dietary Life
Taejung Woo, Jihye Yoo, Kyung-Hea Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(2): 106. CrossRef
- Obesity-Related Factors in Adult Women with Early Menarche
- 979 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- The Relationships among Quality of Life and Stress, Health-related Habits and Food Intake in Korean Healthy Adults Based on 2013 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Su Bin Lee, Hyun Jin Choi, Mi Joung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(6):411-422. Published online December 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.6.411
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - OBJECTIVES
This study investigated the socioeconomic factors that affect quality of life (QL) in healthy adults and to study the relationship between QL and health-related habits and food intake.
METHODS
Subjects consisted of 1,154 healthy adults without any known disease, aged 19 to 65 years from the 2013 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data. We used SPSS statistical program version 20.0 for data analysis.
RESULTS
The average age and QL score of the study population were 36.7 years and 0.99 points, respectively. Males had a significantly higher QL score than the females (p < 0.001), and employed subjects and those employed in permanent positions had significantly higher scores as compared respectively with unemployed subjects and those employed in temporary positions (p < 0.001, p < 0.05). The group that responded "almost every day" to the "frequency of binge drinking" and "frequency of disruption of daily life due to drinking" had significantly lower QL scores as compared to other groups (p < 0.05). Further, the scores were significantly higher for individuals who practiced "intense physical activities" and "walking" (p < 0.001). The groups that responded that they were "very stressed" showed significantly lower QL scores in comparison to the other groups (p < 0.05). There were no significant differences in QL scores according to anthropometric or biochemical indices. When subjects were divided into two groups based on average QL scores, the frequency of intake of "barbecued beef" was significantly higher while the frequency of intake of "fried eggs or rolled omelet," and "soy milk" was significantly lower in the high QL group.
CONCLUSIONS
Based on these findings, it is evident that in healthy adults without any known underlying illnesses, psychological factors such as economic activity, occupational environment, and stress are considered to have a greater impact on their QL than are nutrient intake, blood biochemical indices, and anthropometric status. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Study on the relationship between dietary habits and the quality of life of some high school students in Seoul based on the nutrition quotient for adolescents (NQ-A)
Ho-Jung Kim, Jung-Sug Lee, Yookyung Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(3): 320. CrossRef - DOES HEALTH LITERACY AND LIFE SATISFACTION PROMOTE HEALTHY EATING AMONG MARRIED WOMEN IN TURKEY?
Mahmut Kılıç, Nurgül Nehir Yılmaz
Eskişehir Türk Dünyası Uygulama ve Araştırma Merkezi Halk Sağlığı Dergisi.2024; 9(3): 323. CrossRef - The Connection between Hand Washing and Brushing Teeth
Ra-Ae Bak, Sun-Jung Shin, Hee-Jung Park, Jin-Young Jung, Hwa-Young Lee, Nam-Hee Kim
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2023; 23(2): 132. CrossRef
- Study on the relationship between dietary habits and the quality of life of some high school students in Seoul based on the nutrition quotient for adolescents (NQ-A)
- 818 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- The Relationship between Stress, Social Support and Healthy Diet Score among Chinese University Students in Korea
- Sunghee Lee, Zhen Feng, Youngmee Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(4):273-280. Published online August 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.4.273
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - OBJECTIVES
The study aimed to examine whether healthy diet score was associated with stress and social support among 472 Chinese college students in Korea.
METHODS
The study participants were 472 (187 male, 285 female) Chinese college students in Gyeong-gi area. From April 2013 to Oct 2013, participants were asked to fill out questionnaires on healthy diet score (20 questions), stress (20 questions), and social support (20 questions). Each question was scored by a 5-point Likert scale (total scores of each questionnaire were ranged from 20 to 100). Questions on healthy diet were sub-categorized as 'Healthy food eating (HFE)', 'Healthy eating habits (HEH)', and 'Avoidance of unhealthy food (AUF)'. Reliability test was conducted with Cronbach's alphalpha (alpha=0.79).
RESULTS
Healthy diet score was higher in participants who stayed longer in Korea, who spoke Korean language fluently, and who assessed his or her own health status as very good. Adjusted means of healthy diet scores were estimated after adjusting for age, gender, body mass index, duration of staying, and Korean language fluency. According to tertile categories, participants with low tertile stress but high tertile social support showed the highest score of healthy diet (72.59+/-1.45), whereas participants with high tertile of stress but low tertile of social support had the lowest score of healthy diet (59.22+/-1.54). As for the three sub-categories of healthy diet score, the score of HFE increased as the score of social support increased.
CONCLUSIONS
Our findings suggested that social support system is beneficial to alleviate stress and to improve healthy diet score.
- 590 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Investigation on Influencing Environmental Factors on Health Status of Korean Septuagenarians Dwelling in Longevity Region in Jeonla Province
- Chung Shil Kwak, Miyong Yon, Mee Sook Lee, Se In Oh, Sang Chul Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(2):142-162. Published online April 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.2.142
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - OBJECTIVES
To evaluate the critical environmental factors on healthy-aging of Korean people, we investigated the significant factors influencing health status of septuagenarians living in rural area of Jeonla province, known to be one of the representative longevity regions in Korea.
METHODS
We divided subjects into healthy group (36M/25F) or poor-health group (26M/73F) based on self-reported health status, body mass index, a number of prescription, and blood test data. General characteristics, physical measurements, lifestyle, dietary behavior and nutrient intake, physical health and mental health data were statistically compared between the two groups.
RESULTS
Average age was not different between healthy group and poor-health group in men and women, respectively. In men, significantly favorable factors to health were observed to be higher education, regular exercise, higher grip strength and walking function, body mass index (> or = 18.5 kg/m2), moderate frequency of drinking and eating-out, non-smoking, normal red blood cell (RBC) count, higher serum dehydroepiandrosterone-sulfate (DHEAS) level, good digestive function and appetite, normal hearing function, regular meals, adequate vegetable and fruit intake, diverse food intake, adequate energy and nutrients (protein, vitamin B1, B6, C and E, folate, niacin, P, Zn and K) intake, higher mini-nutrient status assessment (MNA) score and low level of depression. On the other hand, in women, those were literacy, living arrangement, moderate frequency of drinking, healthy teeth, higher grip strength and walking function, bone mineral density, normal RBC and white blood cell (WBC) count, higher DHEAS concentration, higher MNA score, normal cognition and memory function, having snack and adequate fruit intake.
CONCLUSIONS
These results could be useful to plan effective strategies to increase health-life expectancy of Korean old people living in rural areas. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Validation of the Yonsei Lifestyle Profile-Satisfaction (YLP-S) Using the Rasch Measurement Model
Kang-Hyun Park, Ickpyo Hong, Ji-Hyuk Park
INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative analysis of dietary behavior and nutrient intake of elderly in urban and rural areas for development of “Village Lunch Table” program: Based on 2014 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
Youngmi Lee, Yourim Choi, Hae Ryun Park, Kyung Hee Song, Kyung Eun Lee, Chang Hee Yoo, Young Suk Lim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(2): 171. CrossRef - A Study on the Body Composition, Physical Activity Level, Basal Metabolic Rate, and Daily Energy Expenditure of Elderly in Busan
Hwa-Jae Lim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(2): 178. CrossRef - The Comparative Analysis of Health Risk Factor according to HbA1c Level of Elderly Women Dwelling in Jeonla Province - Blood Health Status, Food Habit and Nutrient Intake -
Se In Oh, Chung Shil Kwak, Mee Sook Lee
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(3): 392. CrossRef - Changes in the Nutrition Status of Elderly Females in Health Promotion Programs of Health Centers in Chungbuk Province
Myoung-Sook Kim
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2015; 26(2): 225. CrossRef - A Study on the Blood Health Status and Nutrient Intake in Elderly Women Dwelling in Longevity Region in Jeonla Province according to Family Arrangement
Se In Oh, Chung Shil Kwak, Miyong Yon, Mee Sook Lee
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2014; 27(5): 940. CrossRef
- Development and Validation of the Yonsei Lifestyle Profile-Satisfaction (YLP-S) Using the Rasch Measurement Model
- 721 View
- 1 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [English]
- Consumers' Purchasing Intentions of Organic Foods in relation to the Perceived Health Concerns, Healthy Eating Practices and Attitudes, and Food Choice Motives
- Myeong Hwa Cha, Yoo Kyeong Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14(3):286-294. Published online June 30, 2009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigated the correlations of five constructs - health concerns, healthy eating practices and attitudes, food choice motives, attitudes toward organic foods - in the formation of behavioral to the purchasing intentions of organic foods. An instrument encompassing health perception, attitudes, habits and personal traits was developed through the comprehensive reviews of the literature and the assured validity and internal reliability of the contents. The questionnaire was administered to the students of three universities at Daegu, Kyungpook province. A total of 288 questionnaires were collected for a response rate of 96.0%. The correlations of five constructs and purchasing intention were tested simultaneously using structural equation modeling. Healthy eating practices and attitudes toward organic foods were found to be the determinants which directly influence the intention to purchase organic foods. Health concerns didn't show direct relation to the purchasing intention of organic foods. The hypothesized path from the health concerns to the purchasing intentions was not supported. The results indicated that food choice motives and healthy eating attitudes should be managed to achieve higher behavioral intention to purchase organic foods.
- 202 View
- 2 Download

- [English]
- Development of Nutrition Education Materials for Healthy Aging
- Yun Ahn, Kyung A Kim, Hyunjoo Kang, Kyungwon Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2006;11(6):740-749. Published online December 31, 2006
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The objective of this study was to develop nutrition education materials for older adults, 'nutritional management for healthy aging'. A booklet and four leaflets were developed based on lesson plans. Topics of the lesson plans included eating habit assessment, Korean food guide pyramid, meal planning, eating sensibly and weight management. The titles of the leaflets were 'Eating right for healthy aging', 'Eat calcium-rich foods', 'Enjoy fruits & vegetables' and 'Weight management'. Illustrations and icons appropriate to the texts were designed using Illustrator 9.0 and Photoshop 6.0. Booklet (letter size, 5 chapters, 44 pages) and leaflets (B4 size, 6 sections) focused on modifying undesirable eating habits, providing practical tips for desirable behaviors, and behavioral modification such as recording in a food diary, goal setting and increasing self-efficacy. The drafts were pilot-tested by interviews with older adults(n=10), and minor changes were made. The characteristics of revised materials are as follows; i) materials focused on providing desirable eating behaviors for healthy aging, ii) messages were simple and specific, iii) large fonts(13 pt) were used and materials included interesting pictures and illustrations, iv) materials provided tips for balanced diets and recipes for older adults, v) materials included sections for participation of learners including assessment of nutritional risk factors and obesity, meal planning and games. The revised materials are self-explanatory and can be used by older adults and in nutrition education for older adults.
- 207 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Comparison of Nutrient Intake and Meal Service Satisfaction of Elderly at the Local Community Centers:Free and Reduced Meal Service Charge
- Bong Soon Choi, Sun Young Kwon, Ju Young Seo, In Sook Lee, Hee Ja Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2005;10(3):303-310. Published online June 30, 2005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to compare the nutrient intake and foodservice satisfaction of homebound elderly had lunch at the local community centers by the difference of meal service charge. Two local community center with congregate meal service program located in Daegu and Gyongsan were selected; one with free of meal service charge (F), and the other with 500-1,000 won for meal service charge (K). According to the dietary assessment, energy and nutrient intakes of the 156 elderly subjects were as a whole under the Korean Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA). Elderly of F service center showed higher % RDA for the selected nutrients and MAR (mean adequacy ratio) than those of K service center (p<0.001). Participants were satisfied with most of the congregation meal service from community center with different reasons such as 'tasty (K service center)' and 'free of charge (F service center)'. In conclusion, elderly had the lunch at the community center with free of meal service charge was poor nutrition status and lower socioeconomic level than the other type of community center in this area. Therefore, healthy menu for elderly should be developed and managed by professional dietitian, as well as its impact on health status of this group, and congregate meal service system might be extended to the homebound elderly of whole community with free of charge.
- 212 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Plasma Carotenoid Levels in Healthy men and Acute Cardiovascular Disease Patients in Taegu
- Sung Hee Cho, Nan Hee Lee, Suna Im, Jung Gyo Im, bok Seon Bae, Young Sun Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 1997;2(5):728-734. Published online December 31, 1997
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Plasma carotenoid levels were compared among 64 healthy male subjects (control) and 38 patients of ischemic heart disease(IHD) and 20 ones of cerebral infarction(CI) all of whom were over 50years of age. Another 98 healthy male subjects aged 23 to 58 were selected to compare their plasma carotenoid levels by age groups, Levels of lutein, zeaxanthin and crpytoxanthin were lower in IHD(34+/-2, 13+/-1 and 62+/-7 microgram/dl)and CI(36+/-3, 12+/-2 and 41+/-6 microgram/dl)patient groups than in control group (84+/-5, 16+/-2 and 69+/-3 microgram/dl) while those of lycopene, alpha-and beta-carotene varied little among the three groups. The sum of the six carotenoid levels were levels were, therefore,highest(205+/-14 microgram/dl) in the control group followed by IHD(155+/-15 microgram/dl) and CI(128+/-17 microgram/dl) patient groups, Among the 98 healthy male subject for the age group study, levels of the three major carotenoids increased with age from the twenties to the fifities ; lutein, from 64+/-6 to 89+/-8 microgram/dl, cryptoxanthin, 57+/-8 to 73+/-4 microgram/dl and beta-carotene were more significantly correlated(r=0.30 to 0.61, p<0.01), whereas levels of lycopene and alpha-caroteme were significantly(r=0.21 - 0.23, p<0.05) correlated.
- 190 View
- 0 Download


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



