Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review
- [Korean]
- Current status of nutrition education media and its utilization in providing customized nutrition information for older adults in Korea: a scoping review based on the transtheoretical model and food literacy
- Seojin Yun, Jiwon An, Kirang Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(3):175-182. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00094

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
This study analyzes the status of nutrition education media among Korean older adults based on the transtheoretical model (TTM) and their food literacy to propose effective strategies for the development and utilization of educational media.
Methods
A literature review was conducted using The Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) protocol. The literature search was performed using government and local government agency websites, as well as those of affiliated institutions, health and nutrition-related academic societies, and academic search engines. A total of 144 studies were identified, and after a cross-evaluation by two reviewers based on the literature selection criteria, 73 studies were included in the final analysis.
Results
Among the types of nutrition education media, card news had the highest proportion, followed by video media. The development and distribution of nutrition education media for older adults were primarily carried out by government and local government agencies, as well as related affiliated institutions, accounting for 80.8% (n = 59) of the total. When nutrition education topics in the media were categorized according to the stages of behavior change in the TTM, the largest proportion, 64.6% (n = 61), was applicable to the precontemplation and contemplation stages. When categorized by food literacy domains, all topics fell under the categories of nutrition and safety.
Conclusion
Nutrition education media for older adults were found to be primarily focused on knowledge acquisition and information delivery, making them mostly applicable to the precontemplation and contemplation stages of behavior change. The concept of food literacy addressed in the different types of media was limited to the domains of nutrition and safety, with no content covering the cultural and relational domains or the social and ecological domains. For tailored nutrition education, it is necessary to develop diverse educational materials that comprehensively reflect each stage of the TTM and all aspects of food literacy.
- 1,450 View
- 75 Download

Research Article
- [English]
- Nutrition quotient for preschoolers and key impacting factors in Korea: a cross-sectional study on food literacy, social support, and the food environment of primary caregivers
- Danbi Gwon, Ji-Yun Hwang, Jieun Oh
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):16-26. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00311
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
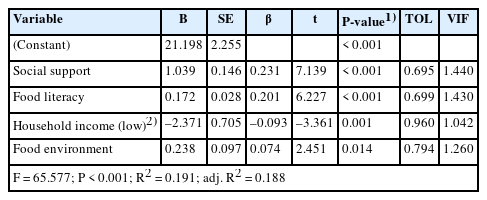
This study evaluated the nutrition quotient for preschoolers (NQ-P) and analyzed the impact of key factors, such as caregivers’ food literacy, social support, and food environment, on the eating habits of preschool children in Korea. This study also sought to provide foundational data for developing tailored nutrition education programs by identifying the nutrition education needs of caregivers.
Methods
This study was conducted among caregivers of preschool children (aged 0–6 years) using an online self-administered survey conducted from August 22 to August 28, 2023. A total of 1,116 survey responses were analyzed. This study assessed children’s NQ-P score, caregivers’ food literacy, social support, food environment, and nutritional education needs. Data were analyzed using SPSS 29.0 (IBM Co.).
Results
The average NQ-P score for preschool children was 52, showing a tendency for the balance score to decrease and the moderation score to increase with age. Children from rural and low-income areas exhibited significantly lower NQ-P scores. Caregivers’ food literacy was higher in urban and higher-income groups. Multiple regression analysis revealed that social support, food literacy, income, and food environment significantly affected children's NQ-P scores. The effectiveness of nutrition education varied based on the income level, with nutrition education on healthy eating being the most preferred topic for preschool children.
Conclusion
This study confirmed that caregivers’ food literacy and social support significantly affected preschool children’s nutritional status. This suggests a need for tailored nutritional education and dietary support policies, particularly for low-income and rural populations.
- 1,973 View
- 55 Download

Educational Materials
- [English]
- Development of a campus-based intervention program to strengthen food literacy among university students: A qualitative formative study
- Eunji Ko, Eunjin Jang, Jiwon Sim, Minjeong Jeong, Sohyun Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(6):495-508. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.6.495
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to develop a campus-based intervention program to enhance food literacy (FL) among university students.
Methods
In the initial phase, we conducted a literature review of FL intervention studies and held in-depth interviews with university students to identify facilitators and barriers to improving and practicing FL. Expert counseling sessions were conducted with nutrition education, marketing, and service design professionals. The results of this phase led to the creation of an initial curriculum draft. In the second phase, a follow-up survey was conducted with young adults to assess the acceptability of the developed curriculum. After the follow-up survey, additional meetings were conducted with the aforementioned experts, and the curriculum was further refined based on their input.
Results
An 11-week FL intervention program was devised using constructs from the Social Cognitive Theory. The weekly curriculum consisted of 90-min theory-based and 90-min hands-on experience sessions. Three primary aspects of FL were covered: nutrition and food safety, cultural and relational dimensions, and socio-ecological aspects. Program highlights included cooking sessions for crafting traditional Korean desserts, lectures on animal welfare, insights into zero-waste practices, and communal eating experiences. Based on the study team’s previous research, the program also addressed mindful eating, helping participants understand the relationship with their eating habits, and providing strategies to manage negative emotions without resorting to food. Yoga sessions and local farm visits were incorporated into the curriculum to promote holistic well-being.
Conclusions
This study elucidated the comprehensive process of creating a campus-based curriculum to enhance FL among university students, a group particularly susceptible to problematic eating behaviors and low FL levels. The developed program can serve as a blueprint for adaptation to other campuses seeking to bolster students’ FL. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of nutrition class with cooking lab on college students’ eating behaviors and well-being in the United States: a mixed-methods study
Borham Yoon, Kyungyul Jun
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(2): 305. CrossRef - Evaluating the effectiveness of a food literacy pilot program for university students: using a mixed-methods research approach
Eunji Ko, Eunjin Jang, Jiwon Sim, Minjeong Jeong, Sohyun Park
Nutrition Research and Practice.2024; 18(6): 885. CrossRef - A pilot investigation of a combined food literacy and exercise program for college students: a one-group pre-post intervention study
Minjeong Jeong, Jinhyun Kim, Dahye Han, Eunjin Jang, Kyoungho Choi, Sohyun Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 455. CrossRef
- Effects of nutrition class with cooking lab on college students’ eating behaviors and well-being in the United States: a mixed-methods study
- 1,944 View
- 58 Download
- 3 Crossref

Review
- [English]
- Defining Food Literacy and Its Application to Nutrition Interventions: A scoping Review
- Hye lim Yoo, Eun bin Jo, Kirang Kim, Sohyun Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(2):77-92. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.2.77
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Food literacy (FL) can be an important concept that embodies the nutritional capabilities of individuals. The purpose of this study was to introduce the definition and core elements of FL from previous literature, to summarize measurement tools and intervention programs with FL, and to suggest the direction of future research and programs to integrate the concept of FL. Methods: The literature review was conducted through PubMed and Google Scholar databases by combining the search term ‘food literacy’ with ‘definition’, ‘measurement’, ‘questionnaire’, ‘intervention’, and ‘program’. Among the 94 papers primarily reviewed 31 manuscripts that suited the purpose of the study were used for analyses. Results: There is no consensus on the definition of FL that encompasses the multidimensional aspects of the concept. The definitions of FL were slightly different depending on the authors, and the interpretation of the core elements also varied. Based on the review, we propose a framework of FL that is in line with the current discussion among international researchers. This focuses on the core elements adapted from health literacy, namely functional, interactive, and critical FL. Specifically, we suggest some detailed elements for interactive and critical FL, which were often the subject of divergent views among researchers in previous literature. We found that most of the tools in the reviewed literature provided information on validity and reliability and were developed for a specific target population. Also, most of the tools were focused on functional FL. Similarly, most of the interventions targeted functional FL. Conclusions: This study reviewed the definition and core elements of FL, available measurement tools, and intervention programs using validated tools. We propose the development of tools with sound reliability and validity that encompass the three core elements of FL for different age groups. This will help to understand whether improving food literacy can translate into better nutritional intake and health status among individuals and communities. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A qualitative study of facilitators and barriers to healthy eating among older adults in China based on nutritional literacy and the capability opportunity motivation behaviour model
Qian Li, Qian Wang
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Current status of nutrition education media and its utilization in providing customized nutrition information for older adults in Korea: a scoping review based on the transtheoretical model and food literacy
Seojin Yun, Jiwon An, Kirang Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(3): 175. CrossRef - How food literacy levels shape healthy eating intentions: a cross-sectional study of adults in Shandong Province, China, using the theory of planned behavior
Baicai Xu, Ji-Yun Hwang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(4): 566. CrossRef - The Concept and Application of the Healing Industry: A Scoping Review
Ji Seong Yi, Sung Yee Yoon, Jae Soo Kim
Journal of People, Plants, and Environment.2025; 28(4): 537. CrossRef - Development of an evaluation tool for dietary guideline adherence in the elderly
Young-Suk Lim, Ji Soo Oh, Hye-Young Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(1): 1. CrossRef - The development, psychometric properties and refinement of a food literacy scale for specific and general application
Hennie Fisher, Marietjie Potgieter
International Journal of Gastronomy and Food Science.2024; 35: 100862. CrossRef - Status of Food Literacy and Association with the Nutrition Quotient among Korean Adults
Geum-Bi Ryu, Young-Ran Heo
Human Ecology Research.2024; 62(3): 399. CrossRef - Evaluating the effectiveness of a food literacy pilot program for university students: using a mixed-methods research approach
Eunji Ko, Eunjin Jang, Jiwon Sim, Minjeong Jeong, Sohyun Park
Nutrition Research and Practice.2024; 18(6): 885. CrossRef - A pilot investigation of a combined food literacy and exercise program for college students: a one-group pre-post intervention study
Minjeong Jeong, Jinhyun Kim, Dahye Han, Eunjin Jang, Kyoungho Choi, Sohyun Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 455. CrossRef - Who has a high level of food literacy, and who does not?: a qualitative study of college students in South Korea
Hyelim Yoo, Eunbin Jo, Hyeongyeong Lee, Eunji Ko, Eunjin Jang, Jiwon Sim, Sohyun Park
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(6): 1155. CrossRef - Development of a campus-based intervention program to strengthen food literacy among university students: A qualitative formative study
Eunji Ko, Eunjin Jang, Jiwon Sim, Minjeong Jeong, Sohyun Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(6): 495. CrossRef - Food literacy and its relationship with food intake: a comparison between adults and older adults using 2021 Seoul Food Survey data
Seulgi Lee, Sohyun Park, Kirang Kim
Epidemiology and Health.2023; 45: e2023062. CrossRef - Nutrition and Food Literacy in the MENA Region: A Review to Inform Nutrition Research and Policy Makers
Hala Mohsen, Yonna Sacre, Lara Hanna-Wakim, Maha Hoteit
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(16): 10190. CrossRef - Development of a Food Literacy Assessment Tool for Healthy, Joyful, and Sustainable Diet in South Korea
Hyelim Yoo, Eunbin Jo, Hyeongyeong Lee, Sohyun Park
Nutrients.2022; 14(7): 1507. CrossRef - Effects of University Students’ Perceived Food Literacy on Ecological Eating Behavior towards Sustainability
Yoojin Lee, Taehee Kim, Hyosun Jung
Sustainability.2022; 14(9): 5242. CrossRef - The Relationships between Food Literacy, Health Promotion Literacy and Healthy Eating Habits among Young Adults in South Korea
Yoojin Lee, Taehee Kim, Hyosun Jung
Foods.2022; 11(16): 2467. CrossRef
- A qualitative study of facilitators and barriers to healthy eating among older adults in China based on nutritional literacy and the capability opportunity motivation behaviour model
- 2,289 View
- 82 Download
- 16 Crossref


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



